Method Swizzling参考资料
1.用到的运行时基础知识介绍
- SEL : 方法选择器,SEL是函数objc_msgSend第二个参数的数据类型,表示方法选择器 ;其实它就是映射到方法的C字符串,你可以通过Objc编译器命令@selector()/NSSelectorFromString()或者Runtime系统的sel_registerName函数来获取一个SEL类型的方法选择器
- Method : 就是一个指向objc_method结构体指针,它存储了方法名(method_name)、方法类型(method_types)和一个指向方法实现的函数指针(method_imp)等信息
- IMP : IMP本质上就是一个函数指针,指向方法的实现,当你向某个对象发送一条信息,可以由这个函数指针来指定方法的实现,它最终就会执行那段代码,这样可以绕开消息传递阶段而去执行另一个方法实现
- class_getInstanceMethod(Class cls, SEL name),获取指定类中,方法选择器对应的方法,需要注意
在搜索方法的时候,会先从指定类的方法列表中搜索,如果搜索不到(当前类没有实现此方法),就会去superclasses 中搜索
/**
* @note This function searches superclasses for implementations, whereas \c class_copyMethodList does not.
*/
OBJC_EXPORT Method class_getInstanceMethod(Class cls, SEL name)
OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.0, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0);
- OBJC_EXPORT IMP method_getImplementation(Method m)
获取某个方法对应的方法实现 - OBJC_EXPORT BOOL class_addMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types) 为该类添加一个方法,但不会去重写已有实现的方法,如果已经有相同方法名称则会返回NO;
注意:父类中有对应的方法而当前类没有,会添加成功
/**
* Adds a new method to a class with a given name and implementation.
*
* @param cls The class to which to add a method.
* @param name A selector that specifies the name of the method being added.
* @param imp A function which is the implementation of the new method. The function must take at least two arguments—self and _cmd.
* @param types An array of characters that describe the types of the arguments to the method.
*
* @return YES if the method was added successfully, otherwise NO
* (for example, the class already contains a method implementation with that name).
*
* @note class_addMethod will add an override of a superclass's implementation,
* but will not replace an existing implementation in this class.
* To change an existing implementation, use method_setImplementation.
*/
OBJC_EXPORT BOOL class_addMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp,
const char *types)
OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.5, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0);
- OBJC_EXPORT IMP class_replaceMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types) ,替换某个类中方法选择器对应方法的方法实现
/**
* Replaces the implementation of a method for a given class.
*
* @param cls The class you want to modify.
* @param name A selector that identifies the method whose implementation you want to replace.
* @param imp The new implementation for the method identified by name for the class identified by cls.
* @param types An array of characters that describe the types of the arguments to the method.
* Since the function must take at least two arguments—self and _cmd, the second and third characters
* must be “@:” (the first character is the return type).
*
* @return The previous implementation of the method identified by \e name for the class identified by \e cls.
*
* @note This function behaves in two different ways:
* - If the method identified by \e name does not yet exist, it is added as if \c class_addMethod were called.
* The type encoding specified by \e types is used as given.
* - If the method identified by \e name does exist, its \c IMP is replaced as if \c method_setImplementation were called.
* The type encoding specified by \e types is ignored.
*/
OBJC_EXPORT IMP class_replaceMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp,
const char *types)
OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.5, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0);
- method_exchangeImplementations(Method m1, Method m2) 交换两个方法的方法实现
/**
* Exchanges the implementations of two methods.
*
* @param m1 Method to exchange with second method.
* @param m2 Method to exchange with first method.
*
* @note This is an atomic version of the following:
* \code
* IMP imp1 = method_getImplementation(m1);
* IMP imp2 = method_getImplementation(m2);
* method_setImplementation(m1, imp2);
* method_setImplementation(m2, imp1);
* \endcode
*/
OBJC_EXPORT void method_exchangeImplementations(Method m1, Method m2)
OBJC_AVAILABLE(10.5, 2.0, 9.0, 1.0);
2. 方法交换
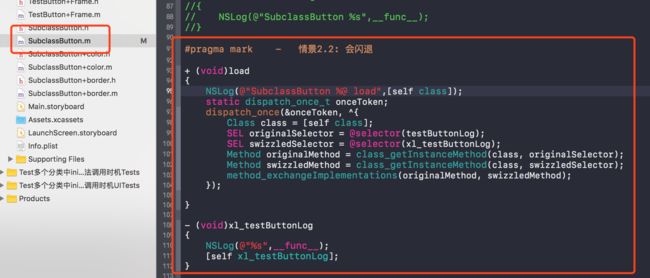
2.1 写法一:有缺陷版本,不建议使用
+ (void)load
{
Class class = [self class];
SEL originalSelector = @selector(testButtonLog);
SEL swizzledSelector = @selector(xl_testButtonLog);
Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, originalSelector);
Method swizzledMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, swizzledSelector);
method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, swizzledMethod);
}
2.2 写法二: 建议写法,交换前用class_addMethod进行一层判断处理
+ (void)load
{
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
Class class = [self class];
SEL originalSelector = @selector(testButtonLog);
SEL swizzledSelector = @selector(xl_testButtonLog);
Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, originalSelector);
Method swizzledMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, swizzledSelector);
BOOL didAddMethod = class_addMethod(class,originalSelector,method_getImplementation(swizzledMethod),method_getTypeEncoding(swizzledMethod));
if (didAddMethod) {
class_replaceMethod(class,
swizzledSelector,
method_getImplementation(originalMethod),
method_getTypeEncoding(originalMethod));
} else {
method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, swizzledMethod);
}
});
}
2.3 比较两种写法差异
- dispatch_once:保证代码块只会被执行一次并且线程安全,不过load方法中并不需要,并不会被多次调用
- 为什么需要用到class_addMethod
- 我们想要对一个类的某个方法进行扩展,应该把这种扩展限制在当前类和当前类的子类中,不应该影响到父类中的方法,因为这个父类可能还有其他派生类,修改了父类的方法可能造成一连串非预期的结果
- 异常场景 : 假设我们要扩展的方法(testButtonLog)是继承自父类(TestButton)的,
且当前类没有对此方法(testButtonLog)进行重写,按照写法一实现方法交换,最终实现的结果是把父类(TestButton)中的方法(testButtonLog)和方法(xl_testButtonLog)进行了交换,这样造成的后果如下: - 如果是当前类(或当前类的子类)的实例对象调用 testButtonLog时,运行时会去执行 xl_testButtonLog , 没有什么问题
- 如果是当前类的父类的实例对象调用testButtonLog时,会有什么后果? 会调用当前类的xl_testButtonLog方法,如果我们在xl_testButtonLog方法中这样写
```
- (void)xl_testButtonLog
{
NSLog(@"%s",func);
[self xl_testButtonLog]; // 调用此方法不会造成递归调用,因为上面做了方法交换,调用此方法,在运行时会去执行testButtonLog
}
```
会闪退,报错xl_testButtonLog方法找不到,原因:当前类的父类中并没有xl_testButtonLog方法具体可以看MethodSwizzlingDemo中情景2.2示例
- 使用class_addMethod后,如果当前类没有实现要扩展的方法(testButtonLog), class_addMethod会自动在当前类中添加一个方法(testButtonLog),这样交换后的结果就是当前类中的方法(testButtonLog)和方法(xl_testButtonLog)进行交换,不影响父类testButtonLog的正常调用
- 具体效果演示,可以参考demoMethodSwizzlingDemo中三种情景的演示
3. 扩展工具类
- 对于Method Swizzling的实现方法可以抽取出来,封装到NSObject的分类中,方便以后使用,具体看demoMethodSwizzlingDemo中的NSObject+MethodSwizzling类
- 交换两个实例方法
/**
交换两个实例方法
*/
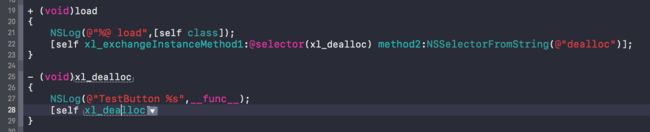
+ (void)xl_exchangeInstanceMethod1:(SEL)originalSelector method2:(SEL)swizzledSelector
{
Class class = [self class]; // 这个地方要注意
Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, originalSelector);
Method swizzledMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(class, swizzledSelector);
BOOL didAddMethod = class_addMethod(class, originalSelector, method_getImplementation(swizzledMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swizzledMethod));
if (didAddMethod) {
class_replaceMethod(class, swizzledSelector, method_getImplementation(originalMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(originalMethod));
} else {
method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, swizzledMethod);
}
}
-
使用示例:
交换两个类方法
/**
交换两个类方法
*/
+ (void)xl_exchangeClassMethod1:(SEL)originalSelector method2:(SEL)swizzledSelector
{
Class class = object_getClass((id)self); // 这个地方要注意
Method originalMethod = class_getClassMethod(class, originalSelector);
Method swizzledMethod = class_getClassMethod(class, swizzledSelector);
BOOL didAddMethod = class_addMethod(class, originalSelector, method_getImplementation(swizzledMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(swizzledMethod));
if (didAddMethod) {
class_replaceMethod(class, swizzledSelector, method_getImplementation(originalMethod), method_getTypeEncoding(originalMethod));
} else {
method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, swizzledMethod);
}
}
- 注意点:交换类方法时,获取类要用object_getClass((id)self)方法获取class, 注意和通过[self class]获取的class是不同的对象,可以通过打印hash值来看
Class class = object_getClass((id)self); // 这个地方要注意
Class class2 = [self class];
NSLog(@" class = %@ , class hash = %zd",class,[class hash]);
NSLog(@" class2 = %@ , class2 hash = %zd",class2,[class2 hash]);
//2017-05-17 18:38:00.171 EHGhostDrone3[26572:677703] class = NSObject , class hash = 4663643704
//2017-05-17 18:38:00.171 EHGhostDrone3[26572:677703] class2 = NSObject , class2 hash = 4663643784
4. Method Swizzling的弊端
Method Swizzling就像一把瑞士小刀,如果使用得当,它会有效地解决问题。但使用不当,将带来很多麻烦。在stackoverflow上有人已经提出这样一个问题:What are the Dangers of Method Swizzling in Objective C?,它的危险性主要体现以下几个方面:
Method swizzling is not atomic
Changes behavior of un-owned code
Possible naming conflicts
Swizzling changes the method's arguments
The order of swizzles matters
Difficult to understand (looks recursive)
Difficult to debug