共1083字,阅读需要2分钟
泛型实参的继承关系对泛型类型的影响
协变:泛型类型与实参的继承关系相同
逆变:泛型类型与实参的继承关系相反
不变:泛型类型没有关系
协变点:返回值类型是泛型参数类型
逆变点:入参类型是泛型参数类型
@UnsafeVariance:协变点违例,告诉编译器,没事,你就按照我的意思执行
1、泛型
什么是泛型?泛化的类型或者是类型的抽象,鸭子类型(看起来像鸭子,走起来也像鸭子,就是鸭子类型)在静态语言中的一种静态实现
1、抽象类,是这个类的本质,它是什么
2、接口,关心类能够做什么,行为能力
举两个例子
两个数的比较大小
// 需要有对比的功能,没有的话就会报错a> maxOf(a:T,b:T):T{
return if (a方法调用
val a=2
val b=3
val maxOf = maxOf(2, 3)
println("shiming "+maxOf)
输出结果
shiming 3
让一个类具备对比的能
data class Complex(val a:Double,val b:Double):Comparable{
override fun compareTo(other: Complex): Int {
return (value()-other.value()).toInt()
}
fun value():Double{
return a*a+b*b
}
override fun toString(): String {
return "$a*$a+$b*$b="+(a*a+b*b)
}
}
方法调用
val Complex1=Complex(4.0,5.0)
val Complex2=Complex(5.0,6.0)
println("shiming Complex1="+Complex1)
println("shiming Complex2="+Complex2)
println("shiming"+Complex1.compareTo(Complex2))
输出结果
04-16 11:22:10.824 26429-26429/com.kotlin.demo I/System.out: shiming Complex1=4.0*a+5.0*b=41.0
04-16 11:22:10.824 26429-26429/com.kotlin.demo I/System.out: shiming Complex2=5.0*a+6.0*b=61.0
04-16 11:22:10.824 26429-26429/com.kotlin.demo I/System.out: shiming-20
通过Demo的测试的结果的发现:泛型不管你到底是什么,它只管你能够做什么事情
定义多个泛型参数
kotlin中的例子
(1..2).map { println("shiming $it=="+it) }
/**
* Returns a list containing the results of applying the given [transform] function
* to each element in the original collection.
(1..2).map调用的底层的方法
*/
public inline fun Iterable.map(transform: (T) -> R): List {
return mapTo(ArrayList(collectionSizeOrDefault(10)), transform)
}
/** A function that takes 22 arguments. function中最多的参数22.一共有23个方法 */
public interface Function22 : Function {
/** Invokes the function with the specified arguments. */
public operator fun invoke(p1: P1, p2: P2, p3: P3, p4: P4, p5: P5, p6: P6, p7: P7, p8: P8, p9: P9, p10: P10, p11: P11, p12: P12, p13: P13, p14: P14, p15: P15, p16: P16, p17: P17, p18: P18, p19: P19, p20: P20, p21: P21, p22: P22): R
}
kotlin中的类传入泛型
data class ComplexNumber< T : Number>(val a:T,val b:T){
override fun toString(): String {
return "$a*$a+$b*$b"
}
}
泛型的实现的机制
何为伪泛型(Java 、Kotlin)?编译完了,泛型就没有了(真正的原因就是最开始写Java编译器的几个人偷懒取巧,留下了历史问题,Martin Odersky爆料。Martin Odersky是Typesafe的联合创始人,也是Scala编程语言的发明者。)
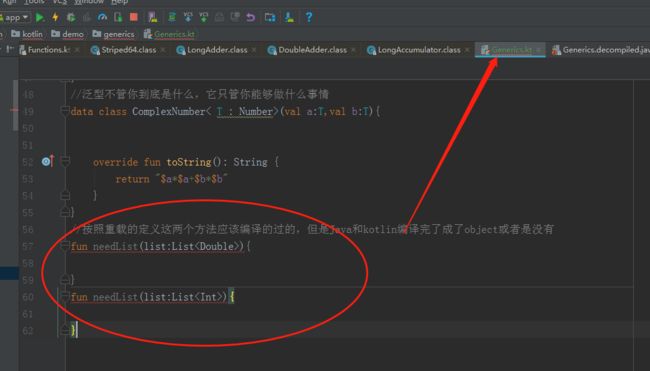
//按照重载的定义这两个方法应该编译的过的,但是Java和kotlin编译完了成了object或者是没有
fun needList(list:List){
}
fun needList(list:List){
}
通过反编译可以看到,卧槽我的泛型没有了
public static final void needList(@NotNull List list) {
Intrinsics.checkParameterIsNotNull(list, "list");
}
public static final void needList(@NotNull List list) {
Intrinsics.checkParameterIsNotNull(list, "list");
}
何为真泛型(C#)?编译完了,还在
如果把以上的代码放在C#中,就不会报错,原因是C#的泛型不仅存在于编译器,也存在运行期
java1.5才有的泛型特性,迫于现实的需求!用的人太多,但是C#第一个版本也没有泛型,但是用的人少,所以C#使用的是真泛型
但是有一种方式可以在编译器得到泛型类型:
reified让泛型参数具体化,定义在inline中 ,kotlin实现为伪泛型,需要这个关键字植入到调用出才可以
//inline inline可用内联函数(inline function)消除这些额外内存开销,
//说白了就是在调用处插入函数体代码,以此减少新建函数栈和对象的内存开销!
inline fun getT(){
println("shiming"+T::class.java)
}
调用
getT()
getT()
//通过反编译得到的结果,说白了,其实就是打印了,这样永远都不会丢失
String var21 = "shiming" + String.class;
System.out.println(var21);
var21 = "shiming" + Double.class;
System.out.println(var21);
得到
04-16 15:28:59.775 31782-31782/com.kotlin.demo I/System.out: shimingclass java.lang.String
04-16 15:28:59.775 31782-31782/com.kotlin.demo I/System.out: shimingclass java.lang.Double
在实际工作中可以这样用
data class Person(val name:String,val age:Int){
//重写,得到json字符串
override fun toString(): String {
return "{name="+"\""+name+"\","+"age="+age+"}"
}
}
//例子 通过inline把这个前面的代码植入到后面
// reified让泛型参数具体化,定义在inline中 ,kotlin实现为伪泛型,需要这个关键字植入到调用出才可以
inline fun Gson.fromJson(json:String):T=fromJson(json,T::class.java)
//模拟网络请求返回的json数据,得到bean类
val person=Person("shiming",20)
println("shiming "+person)
val toString = person.toString()
val person1= Gson().fromJson(toString)
println("shiming person1"+person1)
//上面一段代码的反编译的结果,和java是一样的,执行的流程
Person person = new Person("shiming", 20);
String toString = "shiming " + person;
System.out.println(toString);
toString = person.toString();
Gson $receiver$iv = new Gson();
Person person1 = (Person)$receiver$iv.fromJson(toString, Person.class);
String var25 = "shiming person1" + person1;
System.out.println(var25);
具体的关系
f(⋅)是逆变(contravariant)的,当A≤B时有f(B)≤f(A)成立;
f(⋅)是协变(covariant)的,当A≤B时有成立f(A)≤f(B)成立;
f(⋅)是不变(invariant)的,当A≤B时上述两个式子均不成立,即f(A)与f(B)相互之间没有继承关系。
协变
在kotlin中List不是Java中的List,它只是只读的,查看源码如下List
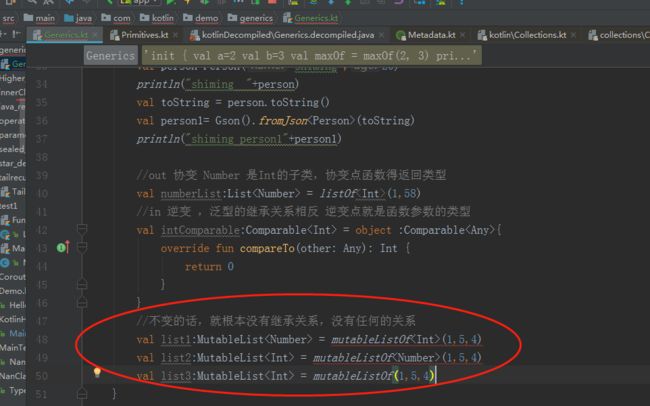
//out 协变 Number 是Int的父类,协变点函数得返回类型
val numberList:List
public interface List : Collection {
// Query Operations
override val size: Int
override fun isEmpty(): Boolean
//告诉编译器 我知道,你不要管我知道怎么搞
override fun contains(element: @UnsafeVariance E): Boolean
override fun iterator(): Iterator
// Bulk Operations
override fun containsAll(elements: Collection<@UnsafeVariance E>): Boolean
// Positional Access Operations
/**
* Returns the element at the specified index in the list.、
返回值的类型是E
*/
public operator fun get(index: Int): E
// Search Operations
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in the list, or -1 if the specified
* element is not contained in the list.
*/
public fun indexOf(element: @UnsafeVariance E): Int
/**
* Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in the list, or -1 if the specified
* element is not contained in the list.
*/
public fun lastIndexOf(element: @UnsafeVariance E): Int
// List Iterators
/**
* Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper sequence).
*/
public fun listIterator(): ListIterator
/**
* Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper sequence), starting at the specified [index].
*/
public fun listIterator(index: Int): ListIterator
// View
/**
* Returns a view of the portion of this list between the specified [fromIndex] (inclusive) and [toIndex] (exclusive).
* The returned list is backed by this list, so non-structural changes in the returned list are reflected in this list, and vice-versa.
*
* Structural changes in the base list make the behavior of the view undefined.
*/
public fun subList(fromIndex: Int, toIndex: Int): List
}
逆变:Comparable接口
//in 逆变 ,泛型的继承关系相反 逆变点就是函数参数的类型 Any是Int的父类
val intComparable:Comparable = object :Comparable{
override fun compareTo(other: Any): Int {
return 0
}
}
public interface Comparable {
public operator fun compareTo(other: T): Int
}
不变:MutableList相当于Java中的|ArrayList,可读可写,不可变,泛型没有in 或者是out ,泛型的继承关系也没有具体的关系,前面是后面的子类或者是后面是前面的子类,都是不成立。
public interface MutableList : List, MutableCollection {
override fun add(element: E): Boolean
override fun remove(element: E): Boolean
override fun addAll(elements: Collection): Boolean
public fun addAll(index: Int, elements: Collection): Boolean
override fun removeAll(elements: Collection): Boolean
override fun retainAll(elements: Collection): Boolean
override fun clear(): Unit
public operator fun set(index: Int, element: E): E
public fun add(index: Int, element: E): Unit
public fun removeAt(index: Int): E
override fun listIterator(): MutableListIterator
override fun listIterator(index: Int): MutableListIterator
override fun subList(fromIndex: Int, toIndex: Int): MutableList
}
星投影:始终找最安全的解决方法,安全方式是定义泛型类型的这种投影,该泛型类型的每个具体实例化将是该投影的子类型
如果泛型类型具有多个类型参数,则每个类型参数都可以单独投影。
例如,如果类型被声明为 interface Function
Function<*, String> 表示 Function
Function
Function<, *> 表示 Function
可用的星投影的地方
//out 协变 Number 是Int的子类,协变点函数得返回类型
val numberList:List<*> = listOf(1,58)
val any = numberList[1] //星投影,去找父类
//in 逆变 ,泛型的继承关系相反 逆变点就是函数参数的类型
val intComparable:Comparable<*> = object :Comparable{
override fun compareTo(other: Any): Int {
return 0
}
}
//星投影,去找父类 Nothing
intComparable.compareTo()
fun hello(){
}
open class Hello{
}
//这样 就可以使用星投影
class Hello33
//这样也可以使用星投影
class Hello2:Hello>()
class Hello332:Hello>()
在kotlin中调用java的类
//这样也可以使用星投影
val raw:Raw<*> = Raw.getRaw()
public class Raw {
@Override
public String toString() {
return "老子是Raw";
}
public static Raw getRaw(){
return new Raw();
}
}
不可以使用星投影的地方
//不变的话,就根本没有继承关系,没有任何的关系 原因是这样不安全
// val list1:MutableList = mutableListOf(1,5,4)
list1.add(BigDecimal(1244444444))
// val list2:MutableList = mutableListOf(1,5,4)
//泛型的实参不要使用星号
// val numberList11d:List<*> = listOf<*>(1,58)
//
// hello<*>()
//
// val hello: Any = Hello<*>()
fun hello(){
}
open class Hello{
}
安卓中一个MvpDemo,使用到了星投影和协变!
package com.kotlin.demo.star_demo
import org.jetbrains.annotations.NotNull
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType
/**
* author: Created by shiming on 2018/4/14 15:08
* mailbox:[email protected]
*/
//Mvp 中的V层 超级接口
interface IView>>{
val presenter:P
}
//P层的超级接口
interface Ipresenter>>{
// @NotNull
// IView getView();
val view:V
}
abstract class BaseView>>:IView{
override val presenter:P
init {
presenter= findPresenterClass().newInstance()
presenter.view=this
}
/**
* 得到相对于的Class的文件
*/
private fun findPresenterClass():Class
{
//不知道,使用星投影去接收 相当于 Class thisClass = this.getClass();
var thisClass:Class<*> = this.javaClass
// while(true) {
// Type var10000 = thisClass.getGenericSuperclass();
// if(!(var10000 instanceof ParameterizedType)) {
// var10000 = null;
// }
// ParameterizedType var5 = (ParameterizedType)var10000;
// if(var5 != null) {
// Type[] var6 = var5.getActualTypeArguments();
// if(var6 != null) {
// var10000 = (Type)ArraysKt.firstOrNull((Object[])var6);
// if(var10000 != null) {
// Type var2 = var10000;
// if(var2 == null) {
// throw new TypeCastException("null cannot be cast to non-null type java.lang.Class
");
// }
//
// return (Class)var2;
// }
// }
// }
// }
//以下的代码相当于上面的代码
while (true){
(thisClass.genericSuperclass as? ParameterizedType)
?.actualTypeArguments
?.firstOrNull()
?.let {
return it as Class
}?.run{
thisClass=thisClass.superclass ?:throw IllegalAccessException()
}
}
}
}
abstract class BasePresenter>>:Ipresenter{
//lateinit 延迟初始化
//@UnsafeVariance 告诉编译器 我很安全 不要管我
override lateinit var view:@UnsafeVariance V
}
class MainView:BaseView()
class MainPresenter:BasePresenter()
class Mvp{
init {
MainView().presenter.let(::println)
//相当于下面的代码
// BasePresenter var1 = (new MainView()).getPresenter();
// System.out.println(var1);
MainView().presenter.let { println("shiming P="+it) }
//相当于下面的代码
// var1 = (new MainView()).getPresenter();
// MainPresenter it = (MainPresenter)var1;
// String var3 = "shiming P=" + it;
// System.out.println(var3);
// (new MainPresenter()).getView();
}
}
输出的结果是:shiming P=com.kotlin.demo.star_demo.MainPresenter@fc35795
以上就是大概的理解,谢谢!