定义
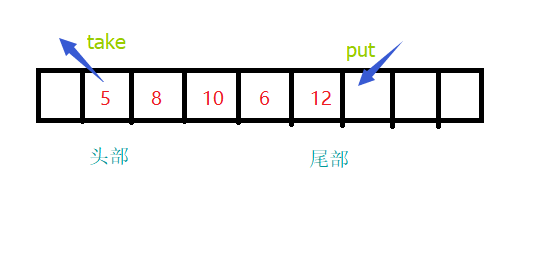
一个由数组支持的有界阻塞队列。此队列按FIFO(先进先出)原则对元素进行排序。队列的头部是在队列中存在时间最长的元素。队列的尾部是在队列中存在时间最短的元素。新元素插入到队列的尾部,队列获取操作则是从队列头部开始获得元素。
模型
这是一个典型的 “有界缓存区”,固定大小的数组在其中保持生产者插入的元素和使用者提取的元素。一旦创建了这样的缓存区,就不能再增加其容量。试图向已满队列中放入元素会导致操作受阻塞;试图向空队列中提取元素将导致类似阻塞。
策略
此类支持对等待的生产者线程和使用者线程进行排序的可选公平策略。默认情况下,不保证是这种排序。然而,通过将公平性 (fairness) 设置为 true 而构造的队列允许按照 FIFO 顺序访问线程。公平性通常会降低吞吐量,但也减少了可变性和避免了“不平衡性”。
具体实现
如上,我们知道ArrayBlockingQueue继承于AbstractQueue,并实现了BlockingQueue和Serializable接口:
public class MyArrayBlockingQueue extends AbstractQueue
implements BlockingQueue,Serializable
- 变量和常量的定义:
//用于存储数据的数组
final Object[] items;
//移除的位置
int takeIndex;
//添加的位置
int putIndex;
//队列的大小
int count;
//互斥锁
final ReentrantLock lock;
//保证不为空的情况下进行消费
private final Condition notEmpty;
//保证队列未满的情况下生产
private final Condition notFull;
- 构造函数的实现:
//构造函数,提供设置队列的大小以及锁的公平性设置
public MyArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair){
if (capacity <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.items = new Object[capacity];
lock = new ReentrantLock(fair);
notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
notFull = lock.newCondition();
}
public MyArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity){
this(capacity,false);
}
- 添加操作的实现:
//设置添加操作
public boolean add(E e){
return super.add(e);
}
/**
* 实现插入元素到队列的尾部,若队列未满,则插入成功,否则插入失败,属于非阻塞式插入
* @param e
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean offer(E e) {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (count == items.length)
return false;
else{
enqueue(e);
return true;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//检查插入的元素是否为空,若为空,则抛出异常
private static void checkNotNull(Object v){
if (v == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
}
//在持有锁的情况下,进行插入元素
private void enqueue(E e){
final Object[] items = this.items;
items[putIndex] = e;
//若达到数组尾部,则回到首部,因为这里使用的是循环数组
if (++putIndex == items.length)
putIndex = 0;
count ++;
//生产了一个元素,可唤醒一个消费者进行消费
notEmpty.signal();
}
//在限定时间内插入元素操作,若插入成功,则返回true,否则返回false
public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e);
//进行单位转换
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
//可中断加锁
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == items.length){
//等待超时的结果
if (nanos <= 0)
return false;
//造成当前线程在接到信号,被中断或到达指定等待时间之间一直处于等待状态
//该方法会返回一个估计值,以等待锁提供的等待时间,若超时,则会返回一个负数,否则继续下一次等待
nanos = notFull.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
enqueue(e);
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//实现阻塞式插入,若队列未满,则直接插入,否则等待队列未满,再插入。
@Override
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
//等待队列未被填满
while (count == items.length)
notFull.await();
enqueue(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
- 查找操作的实现:
//实现在队列中查找元素是否存在
public boolean contains(Object o){
if (o == null) return false;
final Object[] items = this.items;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (count > 0){
//获取到移除位置和插入位置
final int putIndex = this.putIndex;
int i = takeIndex;
//从头部开始遍历直到到达尾部
do {
//找到则返回true
if (o.equals(items[takeIndex]))
return true;
//到达数组尾部,则从头部继续开始
if (++ i == items.length)
i = 0;
} while (i != putIndex);
}
return false;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//阻塞式获取移除并获取头部元素
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
//阻塞直到队列不为空
while (count == 0)
notEmpty.await();
return dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//移除队列中的头部元素,并返回移除的元素
@Override
public E poll() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
//若队列为空,则返回null
return (count == 0) ? null : dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//实现在限定时间内移除头部元素,若超时,则返回null,否则返回头部元素
@Override
public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == 0){
//超时,返回null
if (nanos <= 0)
return null;
nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
//限定时间内,移除元素
return dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//在持有锁的情况下,移除并返回队列中的头部
private E dequeue(){
final Object[] items = this.items;
//获取到要被移除的元素
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E x = (E) items[takeIndex];
//移除元素
items[takeIndex] = null;
//判断是否到达数组末尾
if (++ takeIndex == items.length)
takeIndex = 0;
count --;
/*
if (itrs != null)
itrs.elementDequeued();
*/
//移除了一个元素,可以唤醒一个生产者工作
notFull.signal();
return x;
}
//返回队列中的头部元素
@Override
public E peek() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return itemAt(takeIndex);
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("uncheked")
private E itemAt(int i){
return (E)items[i];
}
- 删除操作的实现:
//实现清空队列的操作:从头部开始遍历直到尾部,逐个删除
public void clear(){
final Object[] items = this.items;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int k = count;
if (k > 0){
//获取到头部和尾部位置
final int putIndex = this.putIndex;
int i = takeIndex;
//遍历,删除每个元素
do {
items[i] = null;
if (++ i == items.length)
i = 0;
} while (i != putIndex);
//重置队列大小和头部位置
takeIndex = putIndex;
count = 0;
/*
if (itrs != null)
itrs.queueIsEmpty();
*/
//释放生产者信号量,所释放的个数与队列的大小一致(前提是必须有生产者在等待)
for (; k > 0 && lock.hasWaiters(notFull); k --)
notFull.signal();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//实现从队列中删除指定的某个元素
public boolean remove(Object o){
if (o == null) return false;
final Object[] items = this.items;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (count > 0){
//获取到头部和尾部
final int putIndex = this.putIndex;
int i = takeIndex;
//遍历队列直到找到指定元素
do {
//找到指定元素,进行删除该元素
if (o.equals(items[i])){
removeAt(i);
return true;
}
if (++ i == items.length)
i = 0;
} while (i != putIndex);
}
return false;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//实现删除数组中指定位置的元素,注意不在首尾时,数组的移动
void removeAt(final int removeIndex){
final Object[] items = this.items;
//删除的元素位于头部,则直接删除即可
if (removeIndex == takeIndex){
items[takeIndex] = null;
//注意删除头部后,是头部位置加一,而不是减一!!!
//结构:头部<----尾部
if (++ takeIndex == items.length)
takeIndex = 0;
count --;
/*
if (itrs != null)
itrs.elementDequeued();
*/
} else {
final int putIndex = this.putIndex;
//从要删除的元素开始遍历直到尾部
for (int i = removeIndex;;){
int next = i + 1;
if (next == items.length)
next = 0;
if (next != putIndex){
items[i] = items[next];
i = next;
} else {
//达到尾部,更新尾部位置
items[i] = null;
this.putIndex = i;
break;
}
}
count --;
/*
if (itrs != null)
itrs.removedAt(removeIndex);
*/
}
//删除后将释放一个生产者
notFull.signal();
}
//移除队列中所有可用的元素,并将它们添加到给定collection中
@Override
public int drainTo(Collection c) {
return drainTo(c,Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
//最多从此队列中移除给定的数量的可用元素,并将这些元素添加到给定collection中
@Override
public int drainTo(Collection c, int maxElements) {
checkNotNull(c);
//如果c和当前队列相同,则没有必要复制给c
if (c == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (maxElements <= 0)
return 0;
final Object[] items = this.items;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
//获取到要删除的元素个数
int n = Math.min(maxElements, count);
//从头部开始
int take = takeIndex;
int i = 0;
try {
while (i < n){
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E x = (E) items[take];
c.add(x);
items[take] = null;
if (++ take == items.length)
take = 0;
i ++;
}
return n;
} finally {
if (i > 0){
//更新队列中的大小和头部位置
count -= i;
takeIndex = take;
/*
if (itrs != null){
if (count == 0)
itrs.queueIsEmpty();
else if (i > take)
itrs.takeIndexWrapped();
*/
//释放相应的锁
for (; i > 0 && lock.hasWaiters(notFull); i --)
notFull.signal();
}
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
- 其他方法的实现:
//返回队列的大小
@Override
public int size() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return count;
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//返回在无阻塞的理想情况下,此队列能接受的其他元素的数量
@Override
public int remainingCapacity() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return items.length - count;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//将队列转换为数组形式返回
@Override
public Object[] toArray() {
Object[] a;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
final int count = this.count;
a = new Object[count];
//计算数组尾部到队列头部的距离
int n = items.length - takeIndex;
//若队列尾部未满数组的长度,则直接整体复制,否则分为前后两部分分别复制
if (count <= n)
System.arraycopy(items, takeIndex, a, 0 ,count);
else{
System.arraycopy(items,takeIndex,a,0,n);
System.arraycopy(items,0,a,n,count-n);
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return a;
}
//返回一个按适当顺序包含此队列中所有元素的数组
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T[] toArray(T[] a) {
final Object[] items = this.items;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
final int count = this.count;
final int len = a.length;
//若传入的数组的大小不够装入队列,则利用反射创建一个足够大的空间
if (len < count)
a = (T[]) java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(
a.getClass().getComponentType(), count);
int n = items.length - takeIndex;
if (count <= n)
System.arraycopy(items, takeIndex, a, 0 ,count);
else{
System.arraycopy(items,takeIndex,a,0,n);
System.arraycopy(items,0,a,n,count-n);
}
//设置最后的位置为null,这里不知用意为何?
if (len > count)
a[count] = null;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return a;
}
//返回此collection的字符串表示形式
@Override
public String toString() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int k = count;
//若队列为空
if (k == 0)
return "[]";
final Object[] items = this.items;
//通过StringBuilder来构造字符串形式
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("[");
for (int i = takeIndex;;){
Object e = items[i];
sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e);
//构造结束
if (-- k == 0)
return sb.append("]").toString();
sb.append(",").append(' ');
if (++ i == items.length)
i = 0;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
- 迭代器实现:
Iterator是其创建时队列的一个快照,它所持有的关于queue的状态信息,只来自于创建的时刻,至于之后队列是否发生变化,迭代器并不关心。
这个类提供的iterator是具有弱一致性,同时它也仅仅代表iterator被创建的时刻的queue的状态:
// 构造方法
Itr() {
final ReentrantLock lock = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
lastRet = -1;
// 在iterator 被创建的时刻的状态
// remaining = count
// nextItem = itemAt(nextIndex = takeIndex)
// 有可能在这个iterator被创建之后,当前
// queue中元素又增加了,count变大了
// 而这里的 remaining 维持的还是原来的count
// 在iterator被创建之后新增加的元素,将不会被
// next方法返回。
if ((remaining = count) > 0)
nextItem = itemAt(nextIndex = takeIndex);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// next 方法
public E next() {
final ReentrantLock lock = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (remaining <= 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastRet = nextIndex;
E x = itemAt(nextIndex); // check for fresher value
if (x == null) {
// 即使当前值已经被修改
// next 方法依旧返回快照元素
// 而不是 null
x = nextItem; // we are forced to report old value
lastItem = null; // but ensure remove fails
}
else
lastItem = x;
// 跳过所有Null元素,注意 remaining 也会
// 相应减少,所以 next 能够执行的次数一定是
// <= iterator 创建时刻的queue的count的。
while (--remaining > 0 && // skip over nulls
(nextItem = itemAt(nextIndex = inc(nextIndex))) == null)
;
return x;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
由 next 方法实现可以确定,这个iterator返回的是queue的快照元素,因为在并发的情况下,nextItem 记录的元素很有可能已经被消费,而 next 方法却依旧会返回它。
这也说 iterator 是弱一致性的,iterator在循环过程中可以容忍并发地对 queue 进行修改,而不会抛出ConcurrentModificationException。
- 注意:
ArrayBlockingQueue类没有重写 addAll, containsAll, retainAll and removeAll 这四个批量操作方法,所有虽然其中的 add, contains 方法是原子操作,但是这些批量操作方法却是通过循环来完成,所以它们并不是原子操作。