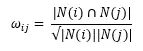基于物品(Item)的协同过滤算法
一、数据准备
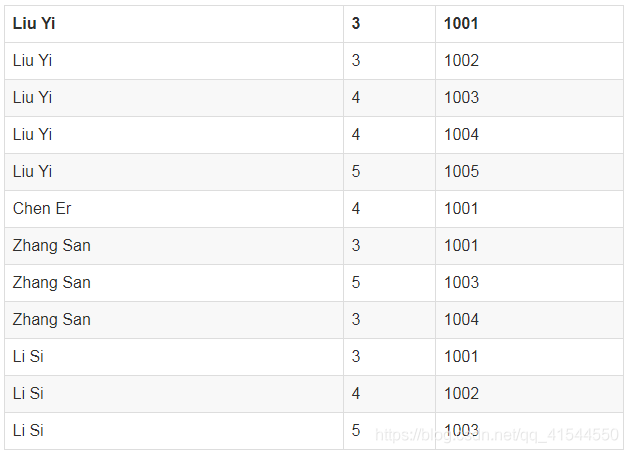
Liu Yi,3,1001
Chen Er,4,1001
Zhang San,3,1001
Li Si,3,1001
Liu Yi,3,1002
Li Si,4,1002
Liu Yi,4,1003
Zhang San,5,1003
Li Si,5,1003
Liu Yi,4,1004
Zhang San,3,1004
Liu Yi,5,1005二、计算物品和物品之间的共现矩阵
对上面的数据作一下调整,按用户排列
用户 评分 物品(BookId)
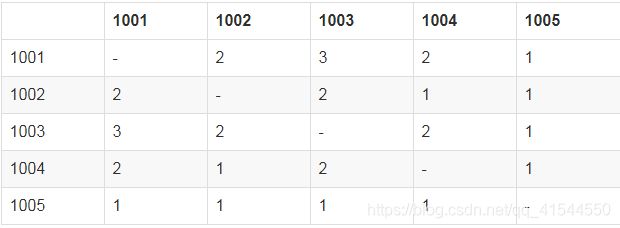
再计算物品和物品的共现矩阵中的每一个元素
1001和1002,同时被Liu Yi和Li Si两个用户购买,所以其共现值为2
1001和1003,同时被Liu Yi, Zhang San和Li Si三个用户购买,所以其共现值为3
1001和1004,同时被Liu Yi和Zhang San两个用户购买,所以其共现值为2
1001和1005,只同时被Liu Yi购买, 所以其共现值为1
1002和1003,同时被Liu Yi和Li Si两个用户购买,所以其共现值为2
1002和1004,只同时被Liui Yi购买, 所以其共现值为1
1002和1005,只同时被Liui Yi购买, 所以其共现值为1
1003和1004,同时被Liu Yi和Zhang San两个用户购买,所以其共现值为2
1003和1005,只同时被Liui Yi购买, 所以其共现值为1
1004和1005,只同时被Liui Yi购买, 所以其共现值为1
最终,得到的共现矩阵为
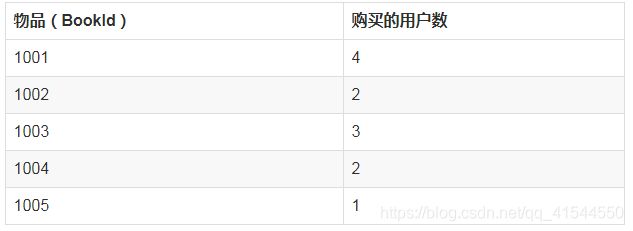
三、计算物品被多少个不同的用户购买
购买1001的有Liu Yi, Chen Er, Zhang San和Li Si
购买1002的有Liu Yi和Li Si
购买1003的有Liu Yi, Zhang San和Li Si
购买1004的有Liu Yi和Zhang San
购买1005的有Liu Yi
四、计算相似度矩阵
两个物品余弦相似度的计算公式为:
根据此公式,
1001与1002的相似度为2 / sqrt(4 * 2) = 0.707
1001与1003的相似度为3 / sqrt(4 * 3) = 0.866
1001与1004的相似度为2 / sqrt(4 * 2) = 0.707
1001与1005的相似度为1 / sqrt(4 * 1) = 0.5
1002与1003的相似度为2 / sqrt(2 * 3) = 0.816
1002与1004的相似度为1 / sqrt(2 * 2) = 0.5
1002与1005的相似度为1 / sqrt(2 * 1) = 0.707
1003与1004的相似度为2 / sqrt(3 * 2) = 0.816
1003与1005的相似度为1 / sqrt(3 * 1) = 0.577
1004与1005的相似度为1 / sqrt(2 * 1) = 0.707
所以,相似度矩阵为
假设取K=3
(1) 对于Li Si买过的1001来说,相似度排在前3名的物品和评分为:
1003,0.866
1002,0.707
1004,0.707
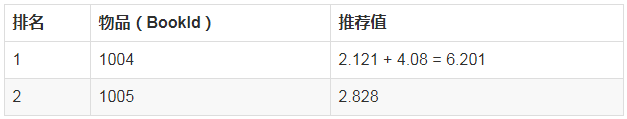
这三个物品中,只有1004是Li Si不曾买过的,其推荐值为
1004与1001的相似度 * Li Si对1001的评分 = 0.707 * 3 = 2.121
(2) 对于Li Si买过的1002来说,相似度排在前3名的物品和评分为:
1003,0.816
1001,0.707
1005,0.707
这三个物品中,只有1005是Li Si不曾买过的,其推荐值为
1005与1002的相似度 * Li Si对1002的评分 = 0.707 * 4 = 2.828
(3) 对于Li Si买过的1003来说,相似度排在前3名的物品和评分为:
1001,0.866
1002,0.816
1004,0.816
这三个物品中,只有1004是Li Si不曾买过的,其推荐值为
1004与1003的相似度 * Li Si对1003的评分 = 0.816 * 5 = 4.08
综上,可以给Li Si推荐的书为
代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*-coding:utf-8-*-
import math
import pdb
class ItemBasedCF:
def __init__(self,train_file):
self.train_file = train_file
self.readData()
def readData(self):
#读取文件,并生成用户-物品的评分表和测试集
self.train = dict()
#用户-物品的评分表
for line in open(self.train_file):
user,score,item = line.strip().split(",")
self.train.setdefault(user,{})
self.train[user][item] = int(float(score))
def ItemSimilarity(self):
#建立物品-物品的共现矩阵
cooccur = dict() #物品-物品的共现矩阵
buy = dict() #物品被多少个不同用户购买N
for user,items in self.train.items():
for i in items.keys():
buy.setdefault(i,0)
buy[i] += 1
cooccur.setdefault(i,{})
for j in items.keys():
if i == j : continue
cooccur[i].setdefault(j,0)
cooccur[i][j] += 1
#计算相似度矩阵
self.similar = dict()
for i,related_items in cooccur.items():
self.similar.setdefault(i,{})
for j,cij in related_items.items():
self.similar[i][j] = cij / (math.sqrt(buy[i] * buy[j]))
return self.similar
#给用户user推荐,前K个相关用户,前N个物品
def Recommend(self,user,K=3,N=10):
rank = dict()
action_item = self.train[user]
#用户user产生过行为的item和评分
for item,score in action_item.items():
sortedItems = sorted(self.similar[item].items(),key=lambda x:x[1],reverse=True)[0:K]
for j,wj in sortedItems:
if j in action_item.keys():
continue
rank.setdefault(j,0)
rank[j] += score * wj
return dict(sorted(rank.items(),key=lambda x:x[1],reverse=True)[0:N])
#声明一个ItemBasedCF的对象
item = ItemBasedCF("item_book.txt")
item.ItemSimilarity()
recommedDict = item.Recommend("Li Si")
for k,v in recommedDict.items():
print(k,"\t",v)运行结果:
1004 6.203803248198273
1005 2.82842712474619