文章来自我的博客
正文之前
之前介绍过了ArrayList的源码了,在刚学Java的时候,书籍中就经常拿ArrayList和LinkedList来举例子,学完了ArrayList最常用部分的源码后,就打算把LinkedList也学完,源码中有两种操作,一种是列表操作,一种是队列操作,分两篇文章来讲,今天先讲列表操作
今天的内容有这些:
- LinkedList 概念介绍
- 结点
- 类的基本信息
- 构造
- 增删改查
正文
1. 概念介绍
* Doubly-linked list implementation of the {@code List} and {@code Deque}
* interfaces. Implements all optional list operations, and permits all
* elements (including {@code null}).
*
* All of the operations perform as could be expected for a doubly-linked
* list. Operations that index into the list will traverse the list from
* the beginning or the end, whichever is closer to the specified index.
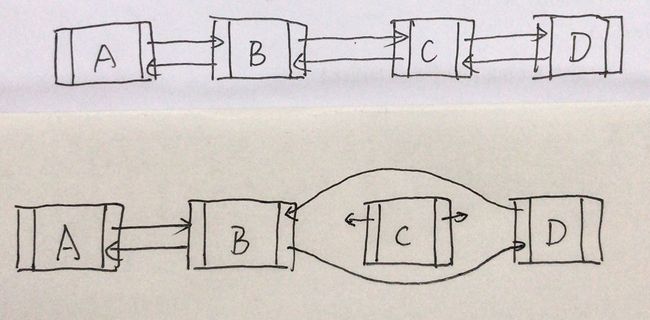
按照注释给出的,LinkedList叫做“双向链表”,实现了List(列表)接口和Deque(双向队列)接口,支持队列的操作
对特定的元素的操作,可以从列表的首或者尾开始,哪边离得近就从哪边开始
* Note that this implementation is not synchronized.
* If multiple threads access a linked list concurrently, and at least
* one of the threads modifies the list structurally, it must be
* synchronized externally. (A structural modification is any operation
* that adds or deletes one or more elements; merely setting the value of
* an element is not a structural modification.) This is typically
* accomplished by synchronizing on some object that naturally
* encapsulates the list.
*
* If no such object exists, the list should be "wrapped" using the
* {@link Collections#synchronizedList Collections.synchronizedList}
* method. This is best done at creation time, to prevent accidental
* unsynchronized access to the list:
* List list = Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList(...));
和ArrayList一样,这个容器也是非线程安全的,如果要在多线程环境下使用,也要使用synchronizedList包装起来
在源码中还有一些注释是关于迭代器的,等到以后的文章中再说明
2. 节点
- 节点的表示
需要先统一以下说法,Node叫做节点,Node.item叫做元素
//当前节点的类型是泛型
private static class Node {
E item;
//前后节点都是Node类型,其中又包括了其当前节点和前后节点
Node next;
Node prev;
Node(Node prev, E element, Node next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
- 根据索引寻找节点
在查找的过程要一个一个节点的迭代,所以LinkedList随机读取的开销要比ArrayList大
/**
* Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.
*/
Node node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
//if-else来判断从头部还是尾部开始查找
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node x = first;
//一直迭代然后得到特定节点
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
3. 类的基本信息
先来看看这个类继承了什么类,实现了什么接口
public class LinkedList
extends AbstractSequentialList
implements List, Deque, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{
}
继承了AbstractSequentialList
变量:
//大小
transient int size = 0;
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
//第一个节点,满足上面这两个条件之一
transient Node first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
//最后一个节点,满足上面这两个条件之一
transient Node last;
4. 构造
- 空链表
/**
* Constructs an empty list.
*/
public LinkedList() {
}
- 带有其他容器元素的链表
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public LinkedList(Collection c) {
//先构造一个空链表
this();
//添加指定容器的元素的方法,下文讲述
addAll(c);
}
5. 增删改查
增
因为链表是双向的,所以在增加元素的时候,要设置节点两边的指向,接下来说明指向的时候,会说明是向前指向还是向后指向,下文说的删除指向,就是把指向设为null
主要内容
- addFirst()
- linkFirst()
- addLast()
- linkLast()
- add()
- linkLast()
- linkBefore()
- addAll()
从内往外,先将内部方法,再讲公用方法:
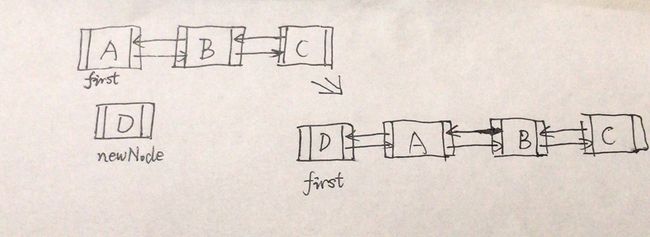
增加至表头
/**
* Links e as first element.
*/
//将元素添加至链表头
private void linkFirst(E e) {
//先定义一个节点
final Node f = first;
//newNode向后指向f
final Node newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
//新的节点作为第一个节点
first = newNode;
//如果f为null,表示链表里只有一个元素,这时候第一个和最后一个都是newNode
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
//f向前指向newNode
f.prev = newNode;
//大小加1
size++;
modCount++;
}
增加至表尾
原理是一样的,就不画图了
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
//基本套路是一样的
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node l = last;
//newNode向前指向l
final Node newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
//l向后指向newNode
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
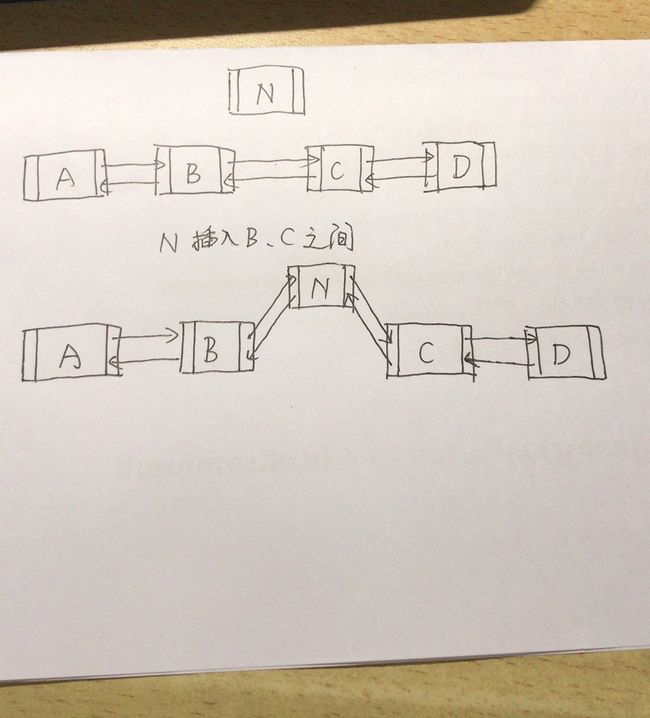
增加至指定位置
插入到指定位置,涉及三个元素,两两之间有关联,所有需要有四条指向
/**
* Inserts element e before non-null Node succ.
*/
void linkBefore(E e, Node succ) {
// assert succ != null;
//把指定位置的前一个节点拿出来
final Node pred = succ.prev;
//在创建节点的时候就有两条指向了
final Node newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
//succ向前指向newNode
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
//如果插入的位置前面没有节点,则插入的节点作为第一个
first = newNode;
else
//刚才创建的pred节点,向后指向newNode
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
刚才上面的三个方法都是为下面这些方法服务的:
//添加至头部
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
//添加至尾部
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
//和上面加至队尾是等价的,除了有返回值
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
//在指定位置添加节点
public void add(int index, E element) {
//检查元素是否越界
checkPositionIndex(index);
/**
* private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {
* if (!isPositionIndex(index))
* throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
* }
*/
//如果索引在最后,直接加至队尾
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
//调用node()方法寻找节点
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
还有直接添加另一个容器的元素至链表的方法:
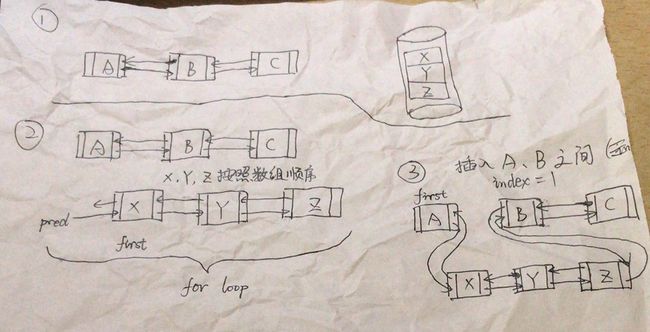
- 将指定容器的元素添加至指定位置,插入的位置在index元素之前(若index = 1,表示第2个元素,则插入第1个和第2个元素之间)
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) {
//检查是否越界
checkPositionIndex(index);
//先用数组存放
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
//前一个节点和当前节点
Node pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
//将容器内元素元素添加到表尾
pred = last;
} else {
//查找指定添加位置
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
//如果是第一个节点
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
//把前一个节点向后指向newNode
pred.next = newNode;
//这个在if-else之外,如果没有这语句,pred节点就固定是那一个节点,所以需要在每一次循环内更换节点
pred = newNode;
}
//如果是最后节点
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
//两个节点之间进行连接
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
- 将指定容器的元素添加至链表尾:
public boolean addAll(Collection c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
删
删除节点的方式,就是把节点的元素和两边的指向设为null,让GC来收集
主要内容
- removeFirst()
- unlinkFirst()
- removeLast()
- unlinkLast()
- remove()
- unlink()
- clear()
还是按照相同的顺序来:
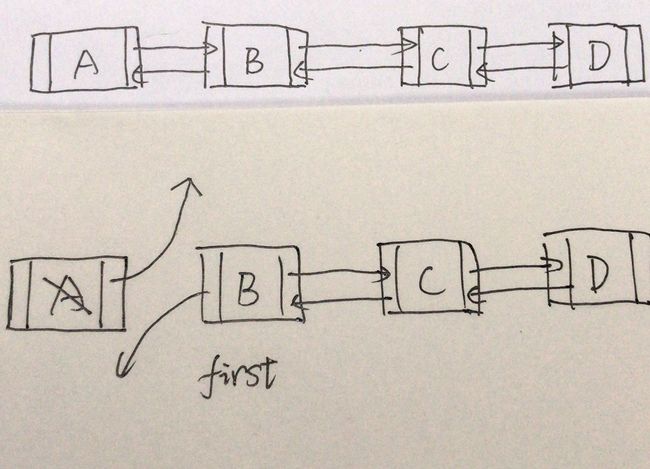
删除第一个节点
删除节点内容,删除指向
private E unlinkFirst(Node f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
//把指定节点的内容拿出来,最后返回
final E element = f.item;
final Node next = f.next;
//节点内容设为空
f.item = null;
//清空节点的向后指向
f.next = null; // help GC
//指定节点的下一个节点作为第一个节点
first = next;
//如果没有下一个节点
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
//删除指向
next.prev = null;
//改变大小
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
删除最后一个节点
步骤是类似的,就画个图,代码就不解释了
/**
* Unlinks non-null last node l.
*/
private E unlinkLast(Node l) {
// assert l == last && l != null;
final E element = l.item;
final Node prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
删除指定节点
/**
* Unlinks non-null node x.
*/
E unlink(Node x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node next = x.next;
final Node prev = x.prev;
// 如果x是第一个节点,则设置下一个节点为第一节点
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
//x的前一个节点直接向后指向后一个节点
prev.next = next;
//删除x的前指向
x.prev = null;
}
//如果x是最后一个节点
if (next == null) {
//向前指向last节点
last = prev;
} else {
//把后一个节点直接向前指向前一个节点,打个比方,就是1和3节点相连,跳过节点2
next.prev = prev;
//删除指向
x.next = null;
}
//删除节点内容
x.item = null;
//改变大小
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
这三个删除的方法写来是被以下这些方法调用的:
//移除第一个节点
public E removeFirst() {
final Node f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
//移除最后节点
public E removeLast() {
final Node l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
//删除特定元素
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
//遍历链表,删去拥有和指定元素相同的内容的节点
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//删除指定位置元素
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
清空链表
没有用到上面的方法,直接将所有的设为null
public void clear() {
// Clearing all of the links between nodes is "unnecessary", but:
// - helps a generational GC if the discarded nodes inhabit
// more than one generation
// - is sure to free memory even if there is a reachable Iterator
//不断迭代,把节点的三个属性设为null
for (Node x = first; x != null; ) {
Node next = x.next;
x.item = null;
x.next = null;
x.prev = null;
x = next;
}
//把首尾设为null,改变大小
first = last = null;
size = 0;
modCount++;
}
改
链表中改变节点的方式就一个:set()方法
public E set(int index, E element) {
//检查是否越界
checkElementIndex(index);
//根据索引查找节点
Node x = node(index);
//oldVal存放需要改变的内容
E oldVal = x.item;
x.item = element;
//返回改变前的值
return oldVal;
}
查
- 查找首尾元素:
这个没什么好说的,直接上代码
public E getFirst() {
final Node f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
public E getLast() {
final Node l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
- 判断是否含有某个元素
public boolean contains(Object o) {
//indexOf()方法在下面讲述
return indexOf(o) != -1;
}
- 根据索引查找
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
//node()方法根据索引来找到节点,在用 .item 来返回节点内容
return node(index).item;
}
- 根据元素得出索引
得到特定元素第一次出现的位置:
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = 0;
//如果对象为null,则也可以查找出内容为null的节点的位置
if (o == null) {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
//迭代寻找元素
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1;
}
得到特定元素最后一次出现的位置,也就是把上面的反过来找:
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
int index = size;
if (o == null) {
for (Node x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (x.item == null)
return index;
}
} else {
for (Node x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
}
}
return -1;
}
LinkedList基于列表的操作到这里就介绍完了,下一篇会是基于队列的操作