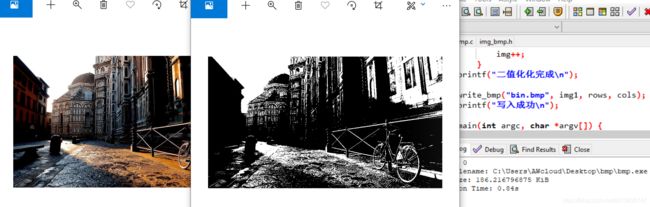
C语言实现bmp图片二值化
一、介绍
二值化公式有很多
这里用的手动阈值
tmp1 = tmp1 > 127 ? 255 : 0;
二、实现
img_bmp.c
#include img_bmp.h
#ifndef __IMG_BMP_H
#define __IMG_BMP_H
void read_bmp (const char* filename, unsigned int** img_data, int *height, int *width);
void write_bmp (const char* filename, unsigned int* img_data, int height, int width);
#endif
#include