原文链接:https://blog.lujun.co/2017/05/09/ignored-parameter-defStyleAttr-in-view-construct/
前言
一个好的 APP 总是不断演进,版本迭代的同时跟随着产品形态的变化,自定义 View 算是 Android 开发中常用满足产品需求的技巧之一。
- 定义
declare-styleable中的自定义属性; - 构造函数,初始化自定义属性;
- 实现
onMeasure、onLayout和onDraw等方法。
使用上面这几个步骤,根据自己的具体逻辑,一个自定义 View 就可以简单使用了。现在要关注的是一个不起眼的家伙,构造函数中的 defStyleAttr 参数。
探寻
首先看看 Button 源码中的几个构造方法:
public Button(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public Button(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, com.android.internal.R.attr.buttonStyle);
}
public Button(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
this(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, 0);
}
public Button(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
可以观察到第一个构造方法调用的是第二个构造方法,第二个调用的是第三个构造方法,最终前三个构造方法调用都是第四个构造方法。这里有几种情况:
- 使用
new Button(context)直接实例化一个 Button 会调用第一个方法; - 在 .xml 文件中使用 Button 调用第二个构造方法。
这里重点关注第二个构造方法。方法的第一参数是 Context,第二个参数是我们自定义属性的集合,那么第三个参数是什么?进入源码继续看,最后来到 View 的代码,看到对于该参数的解释:
An attribute in the current theme that contains a reference to a style resource that supplies default values for the view. Can be 0 to not look for defaults.
大意是:当前主题中一个包含 style 资源引用(Style 中有该 View 默认属性值集合)的值,这个引用对应的资源属性/值会填充 attrs 中没有声明的属性。如果是 0 则不会寻找默认属性值填充。
对上面的解释进行验证,分别使用第二个和第三个构造方法:
Button button1 = new Button(this, null);
Button button2 = new Button(this, null, 0);
button1.setText("button1");
button2.setText("button2");
效果:
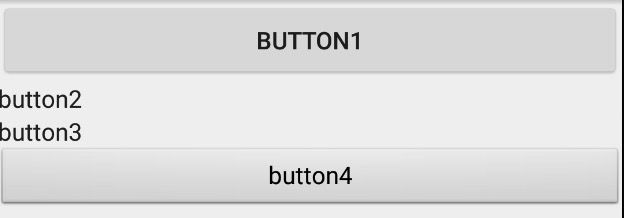
运行可以发现 button1 有 Button 预置的一些基础属性(如背景、点击效果等),而 button2 没有。其中 button1 的预置属性从 com.android.internal.R.attr.buttonStyle 中获得。
更近一步,我们知道了这个参数是为一个 View 提供基础的属性,下面尝试实现这样的功能:
- 定义一个 attribute
- 在我们当前的 Theme 中,为上面定义的 attribute 添加一个 style
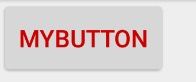
其中 style 继承自 Button style,但修改了 Button 文字颜色为红色。
- 在自定义 View 中使用自定义 attribute
public class MyButton extends Button {
public MyButton(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public MyButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, R.attr.myButtonStyle);
}
public MyButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
this(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, 0);
}
public MyButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
}
最后在 .xml 中使用 MyButton,由于默认填充使用了 Button style(文字颜色被修改为红色),所以样式如下:
看完 defStyleAttr,第四个构造方法中的 defStyleRes 参数又引起了我们的注意,进入 View 的源码,同样可以看到对于该参数的解释:
A resource identifier of a style resource that supplies default values for the view, used only if defStyleAttr is 0 or can not be found in the theme. Can be 0 to not look for defaults.
大意是:为 View 提供默认值的一个样式资源标识符(不局限于当前 Theme 中),仅在 defStyleAttr 为 0 或 defStyleAttr 指定的 style 中无法找到默认值。如果设置为 0 无效。
继续看:
Button button3 = new Button(this, null, 0, 0);
Button button4 = new Button(this, null, 0, android.R.style.Widget_Button_Small);
button3.setText("button3");
button4.setText("button4");
效果(连同第一、二种情况对比):
这里设置 defStyleRes 为 android.R.style.Widget_Button_Small style,相比默认的 Button style 有区别。
分析
attribute 值的确定过程分析
利用 Context 的 obtainStyledAttributes 方法,可以将属性值取回到一个 TypedArray 中(为什么使用 TypedArray)。
一个 attribute 值的确定过程大致如下:
- xml 中查找,若未找到进入第 2 步;
- xml 中的 style 查找,若未找到进入第 3 步;
- 若 defStyleAttr 不为 0,由 defStyleAttr 指定的 style 中寻找,若未找到进入第 4 步;
- 若 defStyleAttr 为 0 或 defStyleAttr 指定的 style 中寻找失败,进入 defStyleRes 指定的 style 中寻找,若寻找失败,进入第 5 步查找;
- 查找在当前 Theme 中指定的属性值。
进入 TextView 的源码,一路找寻 obtainStyledAttributes 的调用链,如下(tl;dr):
TextView
public TextView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
// ...
}
View
public View(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
// ...
final TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.View, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
// ...
}
Context
public final TypedArray obtainStyledAttributes(AttributeSet set, @StyleableRes int[] attrs, @AttrRes int defStyleAttr, @StyleRes int defStyleRes) {
return getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(set, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
Resource.Theme
public TypedArray obtainStyledAttributes(AttributeSet set, @StyleableRes int[] attrs, @AttrRes int defStyleAttr, @StyleRes int defStyleRes) {
return mThemeImpl.obtainStyledAttributes(this, set, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
来到 Resource 类,该类的作用就是帮助我们获取 Application 的资源,其中内部类 Theme 持有当前主题中所有定义的属性值(也就是上面说到的确定 attribute 值的第 5 步)。方法中调用了 mThemeImpl 的 obtainStyledAttributes 方法,ThemeImpl 类就是 Theme 类的"实现",进入到 ThemeImpl 类 obtainStyledAttributes 方法:
TypedArray obtainStyledAttributes(@NonNull Resources.Theme wrapper, AttributeSet set, @StyleableRes int[] attrs, @AttrRes int defStyleAttr, @StyleRes int defStyleRes) {
synchronized (mKey) {
final int len = attrs.length;
final TypedArray array = TypedArray.obtain(wrapper.getResources(), len);
// XXX note that for now we only work with compiled XML files.
// To support generic XML files we will need to manually parse
// out the attributes from the XML file (applying type information
// contained in the resources and such).
final XmlBlock.Parser parser = (XmlBlock.Parser) set;
AssetManager.applyStyle(mTheme, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes, parser != null ? parser.mParseState : 0, attrs, array.mData, array.mIndices);
array.mTheme = wrapper;
array.mXml = parser;
return array;
}
}
这里 obtain 了我们需要的 TypedArray,根据之前说过的规则通过调用 AssetManager 的 applyStyle 方法(本地方法),确定了最后各个 attribute 的值。
下面看看 android_util_AssetManager.cpp 中 android_content_AssetManager_applyStyle 函数的源码,里面有我们需要的 native applyStyle 方法(代码很长,只保留了注释):
static jboolean android_content_AssetManager_applyStyle(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz, jint themeToken, jint defStyleAttr, jint defStyleRes, jint xmlParserToken, jintArray attrs, jintArray outValues, jintArray outIndices)
{
// ...
// Retrieve the style class associated with the current XML tag.
// 检索与当前 XML 标签关联的样式类
// ...
// Now lock down the resource object and start pulling stuff from it.
// 锁定资源对象并开始从其中抽取所需要的内容
// ...
// Retrieve the default style bag, if requested.
// 如有需要取出默认样式
//...
// Retrieve the XML attributes, if requested.
// 如有需要检索 XML 属性
// ...
// Now iterate through all of the attributes that the client has requested,
// filling in each with whatever data we can find.
// 遍历客户端请求的所有属性,填充每个可以找到的数据
// ...
for (// ...) {
// ...
// Try to find a value for this attribute... we prioritize values
// coming from, first XML attributes, then XML style, then default
// style, and finally the theme.
// 尝试找到这个属性的值... 优先级:
// 首先是 XML 中定义的,其次是 XML 中的 style 定义的,然后是默认样式,最后是主题
// ...
}
return JNI_TRUE;
}
到此,attribute 值的查找过程结束。attribute 值的确定是按照一系列规则来最终确定的。
看看 TypedArray 这个类
使用 TypedArray 类可以帮助我们简化获取 attribute 值的流程。类介绍也表明了其作用:
ontainer for an array of values that were retrieved with
Resources.Theme#obtainStyledAttributesorResources#obtainAttributes. [Be sure to callrecyclewhen done with them.]The indices used to retrieve values from this structure correspond to the positions of the attributes given to obtainStyledAttributes.
注意上面用 [] 括起来的一句话:用完之后必须调用 recycle 方法。对,我们通常都会这么做,但是为什么要这么做? 查看这个方法源码:
public void recycle() {
if (mRecycled) {
throw new RuntimeException(toString() + " recycled twice!");
}
mRecycled = true;
// These may have been set by the client.
mXml = null;
mTheme = null;
mAssets = null;
mResources.mTypedArrayPool.release(this);
}
其中主要就是释放了相应的资源,注意看到 mResources.mTypedArrayPool.release(this); 这一行代码,mTypedArrayPool 是 Resource 类中的一个同步对象(存储 TypedArray 对象)池,这里使用了 Pool 来进行优化。
既然是用了 Pool,那就肯定有获取对象的方法,焦点来到 obtain 方法:
static TypedArray obtain(Resources res, int len) {
final TypedArray attrs = res.mTypedArrayPool.acquire();
if (attrs != null) {
// 重置从 Pool 中获取到的对象
return attrs;
}
// 如果对象池是空,返回一个新对象
return new TypedArray(res, new int[len*AssetManager.STYLE_NUM_ENTRIES], new int[1+len], len);
}
简单总结这两个方法如下:
-
recycle方法就相当于 Pool 中的 release,用于归还对象到 Pool 中; -
obtain方法就相当于 Pool 中的 acquire,用于从 Pool 中请求对象。
对于 mTypedArrayPool 的大小 Android 默认是 5。对象池不能太大也不能太小,太大可能造成内存占用,太小可能造成无效对象或有无对象池无明显效果等问题。具体大小的设置,是需要根据具体的场景结合数据分析得到。
Android 应用程序就是由大量 View 构成,因此 View 成了最经常使用的对象。一个 View 创建过程中有大量的 attributes 需要设置,Android 使用了 TypedArray 来简化流程,当频繁的创建和销毁对象(对象的创建成本还比较大)时,会有一定的成本及比较差的体验(如内存抖动导致掉帧)。通过使用 Pool 来实现对 TypedArray 的缓存和复用,达到优化的目的。
TypedArray 中还有很多类似 getDrawable 的方法用于从 TypedArray 中根据索引获取值,下面就看看 getDrawable 方法,源码如下:
public Drawable getDrawable(@StyleableRes int index) {
if (mRecycled) {
throw new RuntimeException("Cannot make calls to a recycled instance!");
}
final TypedValue value = mValue;
if (getValueAt(index*AssetManager.STYLE_NUM_ENTRIES, value)) {
if (value.type == TypedValue.TYPE_ATTRIBUTE) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Failed to resolve attribute at index " + index + ": " + value);
}
return mResources.loadDrawable(value, value.resourceId, mTheme);
}
return null;
}
首先是进行一系列判断,最后调用 mResources.loadDrawable 方法获取 drawable,这里调用的是 Resource 类的方法,Resource.loadDrawable 又调用 ResourceImpl.loadDrawable 方法,所以看到 ResourceImpl.loadDrawable:
Drawable loadDrawable(Resources wrapper, TypedValue value, int id, Resources.Theme theme, boolean useCache) throws NotFoundException {
try {
// ...
// First, check whether we have a cached version of this drawable
// that was inflated against the specified theme. Skip the cache if
// we're currently preloading or we're not using the cache.
// 检查是否缓存有指定主题下这个版本的 drawable,
// 如果正在预加载或者不使用缓存,跳过此步
if (!mPreloading && useCache) {
final Drawable cachedDrawable = caches.getInstance(key, wrapper, theme);
if (cachedDrawable != null) {
return cachedDrawable;
}
}
// Next, check preloaded drawables. Preloaded drawables may contain
// unresolved theme attributes.
// 检查预加载过的 drawables。预加载的 drawables 可能包含没有解析的主题属性。
final Drawable.ConstantState cs;
if (isColorDrawable) {
cs = sPreloadedColorDrawables.get(key);
} else {
cs = sPreloadedDrawables[mConfiguration.getLayoutDirection()].get(key);
}
Drawable dr;
if (cs != null) {
dr = cs.newDrawable(wrapper);
} else if (isColorDrawable) {
dr = new ColorDrawable(value.data);
} else {
dr = loadDrawableForCookie(wrapper, value, id, null);
}
// Determine if the drawable has unresolved theme attributes. If it
// does, we'll need to apply a theme and store it in a theme-specific
// cache.
// 确定是否 drawable 有未解析的主题属性。
// 如果有则应用该主题到 drawable 并存储到特定的主题缓存中。
final boolean canApplyTheme = dr != null && dr.canApplyTheme();
if (canApplyTheme && theme != null) {
dr = dr.mutate();
dr.applyTheme(theme);
dr.clearMutated();
}
// If we were able to obtain a drawable, store it in the appropriate
// cache: preload, not themed, null theme, or theme-specific. Don't
// pollute the cache with drawables loaded from a foreign density.
// 如果拿到 drawable,将它存储到适当的缓存中:
// 比如 reload, not themed, null theme, or theme-specific
if (dr != null && useCache) {
dr.setChangingConfigurations(value.changingConfigurations);
cacheDrawable(value, isColorDrawable, caches, theme, canApplyTheme, key, dr);
}
return dr;
} catch (Exception e) {
// ...
final NotFoundException nfe = new NotFoundException("Drawable " + name
+ " with resource ID #0x" + Integer.toHexString(id), e);
nfe.setStackTrace(new StackTraceElement[0]);
throw nfe;
}
}
总结下来就是以下几步:
- 检查指定主题下是否缓存有这个版本的 drawable,如果正在预加载或者不使用缓存,进入下一步,否则返回这个 缓存的drawable;
- 检查预加载过的 drawables,预加载的 drawables 可能包含没有解析的主题属性;
- 确定是否 drawable 有未解析的主题属性。如果有则应用该主题到 drawable 并存储到特定的主题缓存中;
- 如果拿到 drawable,将它存储到适当的缓存中:比如 reload, not themed, null theme, or theme-specific,最后返回。
以上就是通过 attribute 值代表的引用取得 drawable 的过程,获取其它资源也大同小异。
示例源码
https://github.com/whilu/IgnoredDefStyleAttr
参考
- http://blog.danlew.net/2016/07/19/a-deep-dive-into-android-view-constructors/