前言:开发时,总是需要写大量的Getter,Setter,hasCode等方法,浪费我们的时间,影响代码的整洁,干扰我们理解代码的核心逻辑,对于这些烦不胜烦却不得不写的代码,是时候交给自动生成代码工具去完成了!当前java语言最流行的自动代码生成工具当属Lombok、AutoValue和Immutables了,然三者各有千秋,因此,了解并会使用这三款工具对于开发者很有必要。本文将详细对比介绍这三款工具的使用方式,工具特点,适用场景,以及内部原理。
背景
实际开发中,一般我们都会定义一些dto(网络协议交互)和bean(数据库交互协议)等数据结构。这些类一般都需要有构造函数,字段的Getter,Setter方法,以及equals,hasCode方法和toString等方法。举个例子,假如我们需要一个包含姓名和年龄两个字段的Person类,那么他的代码可能如下面所示:
public final class Person{
private final String name;
private final int age;
public Person(String name,int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String name(){
return name;
}
public int age(){
return age;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(@Nullable Object o){
if(o instanceof Person){
Person person = (Person) o;
return name.equals(person.name) && age == person.age;
}
return false;
}
@Overrride
public int hashCode(){
return Objects.hashCode(name,age);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return Objects.toStringHelper(this)
.add("name",name)
.add("age",age)
.tostring();
}
}
可以发现:
1)简简单单的一个类代码却很长,或许你觉的可以不写equals、hashCode和toString来减少代码长度,但是就会有如下问题:
- 类对象不能放入HashSet中;
- 类对象不能作为一个key放入HashMap, Cache等等;
- 类对象不能放入任何collection,也不能进行contains判断;
- 类对象之间无法完成比较(比如测试时需要比较);
- 如果不写toString,打日志和debug时不方便。
2) 写这些代码劳神费时,还容易出错;
3) 非核心代码太多,影响用户理解核心逻辑;
然而,仔细观察上面的类的方法,可以发现,其实对于所有的dto,bean都是一样的,都需要这些方法。那么其实可以抽一个模版出来,自动生成这些代码,因此,自动生成代码工具诞生了!当前用的比较多的三种工具就是Lombok、AutoValue和Immutables,本文将详细对比分析这三款工具。
Lombok介绍
Lombok官方原版介绍如下:
Project Lombok is a java library that automatically plugs into your editor and build tools, spicing up your java. Never write another getter or equals method again, with one annotation your class has a fully featured builder, Automate your logging variables, and much more.
Lombok使用
使用Lombok,首先是给IDEA安装插件,然后在使用时添加Lombok maven依赖,在相应的类上加上Lombok注解即可。
Lombok环境安装
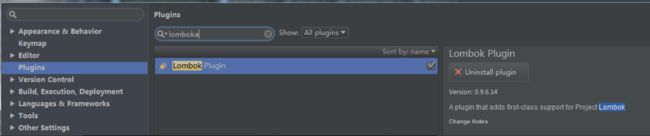
1、通过IDEA的插件中心安装
2、Install Plugin
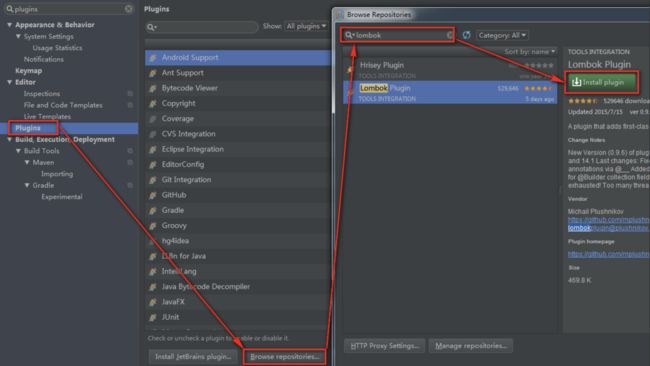
有可能因为网络原因,插件安装不上,那么可以选择本地安装:
1)首先下载Lombok插件包:从官方插件仓库 或者 Github Release 下载均可(注意Lombok版本与IDEA版本要对应);
2)进入IDEA-->Settings/Preferences-->Plugins,在Plugins面板中有'install from disk'按钮,点击选择刚下载的Lombok插件即可;
3)安装成功。
为什么要安装Lombok插件?
答:举个例子,现在有一个A类,其中有一些字段,没有创建它们的setter和getter方法,使用了lombok的注解生成,另外有一个B类,它调用了A类实例的相应字段的setter和getter方法。编译A类,并不会报错,因为最终生成的A类字节码文件中存在相应字段的setter和getter方法。但是,编译B却不行,IDE发现B类源代码中所使用的A类实例的setter和getter方法在A类源代码中找不到定义,IDE会认为这是错误要解决。此时就需要下载安装Intellij Idea中的"Lombok plugin",可以帮助B类找到A类自动生成的代码(Class文件中)。Lombok详细原理后面会介绍。
3、Maven添加依赖
插件安装成功后,项目使用Lombok时,还需要添加Lombok macen依赖:
org.projectlombok
lombok
1.16.8
经过以上三步,就可以开始使用Lombok了!
Lombok使用Demo
我们仍然想要上面的代码效果,使用Lombok的方式如下:
@Data
AllArgsConstructor
public final class Person{
private final String name;
private final int age;
}
生成的代码(Class文件)如下:
public class Person {
private String naem;
private int age;
public Person() {
}
public String getNaem() {
return this.naem;
}
public int getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public void setNaem(String naem) {
this.naem = naem;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
} else if (!(o instanceof Person)) {
return false;
} else {
Person other = (Person)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
} else {
Object this$naem = this.getNaem();
Object other$naem = other.getNaem();
if (this$naem == null) {
if (other$naem == null) {
return this.getAge() == other.getAge();
}
} else if (this$naem.equals(other$naem)) {
return this.getAge() == other.getAge();
}
return false;
}
}
}
protected boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return other instanceof Person;
}
public int hashCode() {
int PRIME = true;
int result = 1;
Object $naem = this.getNaem();
int result = result * 59 + ($naem == null ? 43 : $naem.hashCode());
result = result * 59 + this.getAge();
return result;
}
public String toString() {
return "Person(naem=" + this.getNaem() + ", age=" + this.getAge() + ")";
}
}
可以发现是在原class文件上进行了增强,添加了其他生成的代码。Data注解会生成无参构造函数,以及Getter,Setter,equals、hasCode和toString方法(Class文件中)。Lombok还包含很多其他注解可以使用,详细说明如下表格所示。
Lombok更多使用说明
Lombok使用比较方便简单,只需要添加相应的注解即可,lombok提供的注解有:
| 注解 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| @Data | 注解在类上,将类提供的所有属性都添加,包括get、set、equals、hashCode、toString方法 |
| @NoArgsConstructor | 注解在类上,为类创建一个无参构造函数 |
| @AllArgsConstructor | 注解在类上,为类创建一个全参构造函数 |
| @Setter | 注解在类上,为类所有属性添加set方法;注解在属性上,为该属性提供set方法 |
| @Getter | 注解在类上,为所有的属性添加get方法;注解在属性上,为该属性提供get方法 |
| @ToString | 注解在类上,为类提供一个toString方法 |
| @NotNull | 在参数中使用时,如果调用时传了null值,就会抛出空指针异常 |
| @Synchronized | 用于方法,可以锁定指定的对象,如果不指定,则默认创建一个对象锁定 |
| @Log | 作用于类,创建一个log属性 |
| @Builder | 使用builder模式创建对象 |
| @Accessors(chain = true) | 使用链式设置属性,set方法返回的是this对象 |
| @RequiredArgsConstructor | 创建对象, 例: 在class上添加 |
| @RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName = "of") | 会创建生成一个静态方法 |
| @UtilityClass | 工具类 |
| @ExtensionMethod | 设置父类 |
| @FieldDefaults | 设置属性的使用范围,如private、public等,也可以设置属性是否被final修饰 |
| @Cleanup | 关闭流、连接点 |
| @EqualsAndHashCode | 重写equals和hashcode方法 |
| @toString | 创建toString方法 |
| @Cleanup | 用于流等可以不需要关闭使用流对象 |
AutoValue介绍
AutoValue是Google开源的一个Java源代码生成器,用于为值对象或值类型对象生成源代码。官方原版介绍如下:
AutoValue provides an easier way to create immutable value classes, with a lot less code and less room for error, while not restricting your freedom to code almost any aspect of your class exactly the way you want it.
AutoValue使用
使用AutoValue,在项目中添加相应的Maven依赖即可,详细使用方法如下:
- 写一个抽象类;
- 抽象类添加AutoValue注解;
- 不定义字段,而是定义抽象的获得字段的方法;
- 定义一个获取类实例的方法,方法返回子类(Auto_开头)实例;
- Javac编译一下当前类就会生成一个Auto_开头的子类(子类包含父类的字段,构造函数,Getter,toString,equals,hasCode);
AutoValue环境依赖
AutoValue不需要安装插件,只需要在使用时添加jar包即可,maven依赖如下:
com.google.auto.value
auto-value-annotations
1.6.6
com.google.auto.value
auto-value
1.6.6
provided
AutoValue使用Demo
我们仍然以Person类作为示例,那么此时Person就如下面所示:
import com.google.auto.value.AutoValue;
@AutoValue
public abstract class Person {
public static Person create(String name, int age) {
return new AutoValue_Person(name, age);
}
public abstract String name();
public abstract int age();
}
编译一下上面的代码,就会生成Person的子类Auto_Person,类代码(.java)如下:
import javax.annotation.Generated;
@Generated("com.google.auto.value.processor.AutoValueProcessor")
final class AutoValue_Person extends Person {
private final String name;
private final int age;
AutoValue_Person(String name,int age) {
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("Null name");
}
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String name() {
return name;
}
@Override
public int age() {
return age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{"
+ "name=" + name + ", "
+ "age=" + age
+ "}";
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) {
return true;
}
if (o instanceof Person) {
Person that = (Person) o;
return this.name.equals(that.name())
&& this.age == that.age();
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int h$ = 1;
h$ *= 1000003;
h$ ^= name.hashCode();
h$ *= 1000003;
h$ ^= age;
return h$;
}
}
AutoValue与Lombok不同,它生成的是Java源文件,因此也不需要添加其他插件了,其他类想要用此类的Getter法,直接用即可。
Immutables介绍
Immutables官方介绍:
Java annotation processors to generate simple, safe and consistent value objects. Do not repeat yourself, try Immutables, the most comprehensive tool in this field!
Immutables使用
使用Immutables,首先需要简单的设置一下IDE环境,然后项目中添加相应的Maven依赖,接下来就可以使用Immutables了,使用方法与AutoValue类似,如下:
- 写一个抽象类或接口;
- 抽象类添加Immutables的注解;
- 不定义字段,而是定义抽象的获得字段的方法;
- Javac编译一下当前类就会生成一个子类(一般均是Immutable开头,子类提供构父类的方法,以及getter,toString,equals,hasCode等模版方法);
Immutables环境依赖
1、设置IDE
IDEA的设置比较简单,如下所示:
更多关于Eclipse以及IDEA配置,请看官方文档:Using annotation processor in IDE
2、Maven添加依赖
org.immutables
value
2.7.4
provided
Immutables使用Demo
@Value.Immutable
public interface TypicalUseDemo {
String name();
int age();
}
然后就会生成如下代码(.java):
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
import org.immutables.value.Generated;
@Generated(
from = "TypicalUseDemo",
generator = "Immutables"
)
public final class ImmutableTypicalUseDemo implements TypicalUseDemo {
private final String name;
private final int age;
private ImmutableTypicalUseDemo(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String name() {
return this.name;
}
public int age() {
return this.age;
}
public final ImmutableTypicalUseDemo withName(String value) {
String newValue = (String)Objects.requireNonNull(value, "name");
return this.name.equals(newValue) ? this : new ImmutableTypicalUseDemo(newValue, this.age);
}
public final ImmutableTypicalUseDemo withAge(int value) {
return this.age == value ? this : new ImmutableTypicalUseDemo(this.name, value);
}
public boolean equals(Object another) {
if (this == another) {
return true;
} else {
return another instanceof ImmutableTypicalUseDemo && this.equalTo((ImmutableTypicalUseDemo)another);
}
}
private boolean equalTo(ImmutableTypicalUseDemo another) {
return this.name.equals(another.name) && this.age == another.age;
}
public int hashCode() {
int h = 5381;
int h = h + (h << 5) + this.name.hashCode();
h += (h << 5) + this.age;
return h;
}
public String toString() {
return "TypicalUseDemo{name=" + this.name + ", age=" + this.age + "}";
}
public static ImmutableTypicalUseDemo copyOf(TypicalUseDemo instance) {
return instance instanceof ImmutableTypicalUseDemo ? (ImmutableTypicalUseDemo)instance : builder().from(instance).build();
}
public static ImmutableTypicalUseDemo.Builder builder() {
return new ImmutableTypicalUseDemo.Builder();
}
@Generated(
from = "TypicalUseDemo",
generator = "Immutables"
)
public static final class Builder {
private static final long INIT_BIT_NAME = 1L;
private static final long INIT_BIT_AGE = 2L;
private long initBits;
private String name;
private int age;
private Builder() {
this.initBits = 3L;
}
public final ImmutableTypicalUseDemo.Builder from(TypicalUseDemo instance) {
Objects.requireNonNull(instance, "instance");
this.name(instance.name());
this.age(instance.age());
return this;
}
public final ImmutableTypicalUseDemo.Builder name(String name) {
this.name = (String)Objects.requireNonNull(name, "name");
this.initBits &= -2L;
return this;
}
public final ImmutableTypicalUseDemo.Builder age(int age) {
this.age = age;
this.initBits &= -3L;
return this;
}
public ImmutableTypicalUseDemo build() {
if (this.initBits != 0L) {
throw new IllegalStateException(this.formatRequiredAttributesMessage());
} else {
return new ImmutableTypicalUseDemo(this.name, this.age);
}
}
private String formatRequiredAttributesMessage() {
List attributes = new ArrayList();
if ((this.initBits & 1L) != 0L) {
attributes.add("name");
}
if ((this.initBits & 2L) != 0L) {
attributes.add("age");
}
return "Cannot build TypicalUseDemo, some of required attributes are not set " + attributes;
}
}
}
Immutables更多使用说明
Immutables支持的特性较多,很灵活,包括:
设置可见范围
设置可见范围注解如下:
@Value.Style(visibility = Value.Style.ImplementationVisibility.PRIVATE)
可见范围可以设置为:PUBLIC,SAME,SAME_NON_RETURNED,PACKAGE,PRIVATE,不同的可见范围,ImmutableVisibilityDemo的位置以及可见范围不同,如下代码为可见范围为PRIVATE的Demo:
@Value.Immutable
@Value.Style(visibility = Value.Style.ImplementationVisibility.PRIVATE)
public interface VisibilityDemo {
String name();
int age();
}
//test
VisibilityDemo demo = new VisibilityDemoBuilder().name("pioneeryi").age(26).build();
根据构造函数构造
作为构造对象一种方式,Immutable实现类将提供一个静态的方法of用来构造对象。此时类的每个属性需要加上如下注解:
@Value.Parameter
类的属性都加上Value.Parameter的注解后,我们在构造对象即可不采用Builder模式,而采用构造函数模式,同时我们还可以关闭Builder模式,此时生成的代码中就不会Builder模式代码了,仅有构造函数一种构造对象方法,使用Demo如下:
@Value.Immutable(builder = false, copy = false)
public interface ConstructorDemo {
@Value.Parameter String name();
@Value.Parameter
int age();
}
//test
ConstructorDemo demo = ImmutableConstructorDemo.of("pioneeryi", 26);
设置默认值
我们希望给类对象属性,提供默认值,此时可以使用如下注解,注解相应属性:
@Value.Default
使用此注解后,那么如果构造时没有设置属性值即使用默认值,使用Demo如下:
@Value.Immutable
public abstract class DefaultAttributesDemo {
public abstract String name();
@Value.Default
public int age() {
return 26;
}
}
//test
DefaultAttributesDemo demo = ImmutableDefaultAttributesDemo.builder().name("pioneeryi").build();
String expect = "DefaultAttributesDemo{name=pioneeryi, age=26}";
Assert.assertTrue(demo.toString().equals(expect));
DefaultAttributesDemo demo = ImmutableDefaultAttributesDemo.builder().name("pioneeryi").age(18).build();
String expect = "DefaultAttributesDemo{name=pioneeryi, age=18}";
Assert.assertTrue(demo.toString().equals(expect));
参数校验
如果需要校验属性的值是否合法,可以使用如下注解:
@Value.Check
详细使用Demo如下:
@Value.Immutable
public abstract class PreconditionDemo {
public abstract String name();
public abstract int age();
@Value.Check
protected void check() {
Preconditions.checkArgument(name() != null && !name().equals(""), "name can not be empty");
Preconditions.checkArgument(age() > 0, "age is not valid");
}
}
变成可变类
如果希望将类由不可变类变成可变类,可以使用如下注解:
@Value.Modifiable
使用此注解后,会生成两个子实现类,一个时不可变的,另一个是可变的,Demo如下:
@Value.Immutable
@Value.Modifiable
public interface ModifiableDemo {
String getName();
int getAge();
}
//test immutable
ModifiableDemo demo = ImmutableModifiableDemo.builder().name("pioneeryi").age(26).build();
String expect = "ModifiableDemo{name=pioneeryi, age=26}";
Assert.assertTrue(demo.toString().equals(expect));
//test modifiable
ModifiableDemo demo = ModifiableModifiableDemo.create();
((ModifiableModifiableDemo) demo).setName("pioneeryi");
((ModifiableModifiableDemo) demo).setAge(26);
String expect = "ModifiableModifiableDemo{name=pioneeryi, age=26}";
Assert.assertTrue(demo.toString().equals(expect));
更多Immutables的特性和使用技巧,请看官方介绍文档:Immutable objects
对比分析
值对象
Lombok、AutoValue和immutable都支持“值对象”的生成。
AutoValue专注于生成值对象,并支持基于模板类中的抽象方法生成字段、构造函数/构建器、具体的访问器方法,以及公共方法equals(Object)、hashCode()和toString()的实现;
Immutables提供了与AutoValue类似的功能,并添加了使用@value.modiizable生成可修改类的功能,同时还提供了其他功能,见Immutable更多使用说明;
Lombok提供了与使用@Value注释的AutoValue类似的值类生成功能,并提供了使用@Data注释生成可修改类的功能,同时还提供了其他功能,见Lombok更多使用说明。
原理
三者原理都是基于“Annotation Processing“,每个工具都在他们的JAR文件的“META-INF/services”中定义了一个javax.annotation.processing.Processor,最终完成了“从一个简洁的模板类生成包含更多方法(Getter,toString,hasCode,equals等)的生成类”的目的。
尽管Lombok、AutoValue和Immutables都使用了javac的annotation processing,但是Lombok使用注释处理的方式与AutoValue和Immutables使用注释处理的方式不同。
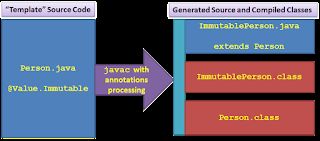
AutoValue和Immutables在更传统的意义上使用注释处理,并从源代码生成源代码。由AutoValue和Immutables生成的类源代码的名称与模板类不同,实际上扩展了模板类,它有自己的名称,包含所有生成的方法和字段,这避免了与模板类的任何名称冲突,并且使在同一个IDE项目中混合模板类源代码和生成的类源代码变得相当容易,因为它们实际上是不同的类。
AutoValue's Generation via Annotation Processing
Immutables's Generation via Annotation Processing
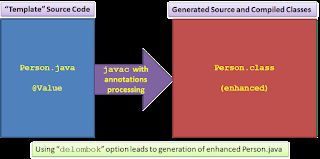
Lombok生成一个与“模板”源代码具有相同类名的编译后的.class文件,并将生成的方法添加到这个编译后的版本中。开发人员只在查看.java文件时看到简洁的模板代码,而在查看.class文件时看到编译后的.class文件,其中的方法在源代码中不存在。Lombok生成的不是另一个源文件,而是原始源文件的增强编译版本。有一个delombok选项可以与Lombok一起使用,查看增强.class文件后面生成的源代码是什么样子的,但是该项目的设计目的是直接从简洁的模板源代码转换为增强的编译类,而不需要或不使用中间增强的源文件。delombok选项可以用来看看生成的源样子或,或许更重要的是,可以使用的工具是混乱的情况下不一致的源(简洁的模板. java文件)和生成的类(增强的. class文件名称相同)在同一个空间。
Lombok's Generation via Annotation Processing
与AutoValue和Immutables使用的方法相比,Lombok的注释处理方法不那么传统,包括Lombok的创建者在内的一些人将这种方法称为“黑客”,因为它使用非标准api,因此很难与ide和其他执行自己编译的工具(如javadoc)很好地集成。但是因为AutoValue和Immutables会生成带有新类名的源代码,所以任何传统工具和ide都可以使用生成的源代码和模板源代码一起工作,而不会有任何重大问题。
三者详细差异对比
| 对比项 | Lombok | AautoValue | Immutables |
|---|---|---|---|
| License | MIT (also) | Apache 2 | Apache 2 |
| 最低java版本 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.7 |
| 生成的文件 | lombok修改了原class文件,加入生成的代码 | 生成了另外一个java子类,不侵入原有的java代码,完全遵循java的规范,可以看到两个java文件和两个class文件 | 生成了另外一个java子类,不侵入原有的java代码,完全遵循java的规范,可以看到两个java文件和两个class文件 |
| 生成类与模版类关系 | Enhanced generated class replaces template source | Generated source extends template source | Generated source extends template source |
| 查看生成类 | 使用delombok | 默认可见 | 默认可见 |
| 使用方便性 | 为类或字段添加注解即可 | 加上注解的同时,需要按照一定的规范遍写代码 | 加上注解的同时,需要按照一定的规范遍写代码 |
| 是否需要提前编译 | 不用,加上注解后,就可以用其生成的方法 | 编译一次,才能生效,编译前是找不到待生成的子类的 | 编译一次,才能生效,编译前是找不到待生成的子类的 |
| 生成的代码是否可见 | 不可见,实在要看需要反编译,不利于Debug可代码分析比如覆盖率等 | 可以看见生成的源代码,在代码调试和分析时较方便 | 可以看见生成的源代码,在代码调试和分析时较方便 |
| 不可变程度 | 可以使用set方法修改类 | 可以使用Immutability修改类 | 强支持不可变 |
如何选择这三个工具
1)AutoValue和Immutables使用标准注释处理,Lombok使用非标准注释处理方法:
- 开发者如果希望避免非标准依赖,那么应该使用AutoValue和Immutables;
- 开发者不希望添加IDE插件或者其他非javac以及非基础Java IDE支持的第三方工具,那么建议使用AutoValue和Immutables;
2)Lombok修改了原class文件,生成的类与模版类在同一个包下,并且名字相同;AutoValue和Immutables生成的类继承自基础模版类,但是在同一个包下:
- 开发者如果希望编译的class文件和源文件在同一个包下,并且同名,那么应该使用Lombok;
- 开发者如果希望可以看到生成的代码,并且不希望影响原来的代码,那么应该使用AutoValue和immutebles;
3)三个工具都不同程度上的支持自定义,因此和这个需要根据实际需要进行选择:
Lombok提供了一个configuration system ,允许根据所需的约定调整生成代码。
Immutables提供了style customization,允许对生成的代码的多个点进行调整。
AutoValue允许用户通过一些方式User Guide,自行定义一些生成代码的规则。
4)从可变性看,三者的opinionated不同,AutoValue是不支持可变的,而Lombok和Immutables支持:
- 希望类成为不可变类,使用AutoValue;
- 希望类一定程度上支持可变,那么使用Lombk或者Immutables;
参考文档
十分钟搞懂Lombok使用与原理
Immutables
AutoValue
Lombok, AutoValue, and Immutables
祝工作顺利,天天开心!