thinkphp5 两个控制器传参数_ThinkPhp5.0.x 远程RCE简单分析
ThinkPhp5.0.x 远程RCE简单分析
0x1 前言
周五考完试,正在准备复习的时候,无聊的时候跑去水群,然后看到有师傅丢了个payload和文档,说是thinkphp5.0.x的远程rce,于是来分析了一波。
0x2 漏洞分析
本文以thinkphp5.0.11为分析:
0x2.1 执行流程
thinkphp如何接收参数,如何获取数据这些,你可以从入口开始读
/Users/xq17/www/test2/thinkphp/thinkphp/start.php
namespace think;// ThinkPHP 引导文件// 加载基础文件require __DIR__ . '/base.php';// 执行应用App::run()->send();//跟进APP类下run方法/Users/xq17/www/test2/thinkphp/thinkphp/library/think/App.php
107line 跟进
public static function run(Request $request = null) {
is_null($request) && $request = Request::instance(); ......................//加载配置,初始化代码省略 if (empty($dispatch)) {
// 进行URL路由检测 $dispatch = self::routeCheck($request, $config);//跟进当前类的routeCheck }is_null($request) && $request = Request::instance();
(1)包含了request文件,然后Request::instance()->$request (Request类实例)
继续向下分析:
public static function routeCheck($request, array $config) {
$path = $request->path(); $depr = $config['pathinfo_depr']; $result = false;..................................................... // 路由检测(根据路由定义返回不同的URL调度) $result = Route::check($request, $path, $depr, $config['url_domain_deploy']); $must = !is_null(self::$routeMust) ? self::$routeMust : $config['url_route_must']; if ($must && false === $result) {
// 路由无效 throw new RouteNotFoundException(); } }跟进$result = Route::check($request , $path, $depr, $config['url_domain_deploy']);
这里传入的参数$request 对应上面说的Request实例
public static function check($request, $url, $depr = '/', $checkDomain = false) {
// 分隔符替换 确保路由定义使用统一的分隔符 $url = str_replace($depr, '|', $url);............................................... $method = strtolower($request->method());//跟进这里 // 获取当前请求类型的路由规则 $rules = isset(self::$rules[$method]) ? self::$rules[$method] : [];$request->method() 调用了Request类的method方法,跟进
0x2.2 进入漏洞点
/Users/xq17/www/test2/thinkphp/thinkphp/library/think/Request.php
lines 503
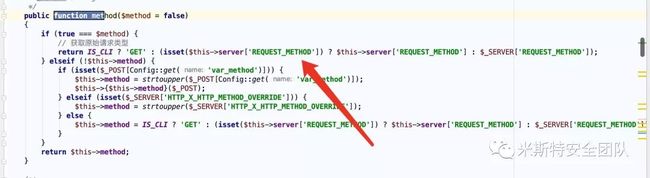
public function method($method = false) {
if (true === $method) {
// 获取原始请求类型 return IS_CLI ? 'GET' : (isset($this->server['REQUEST_METHOD']) ? $this->server['REQUEST_METHOD'] : $_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD']); } elseif (!$this->method) {
if (isset($_POST[Config::get('var_method')])) {
$this->method = strtoupper($_POST[Config::get('var_method')]); $this->{
$this->method}($_POST); } elseif (isset($_SERVER['HTTP_X_HTTP_METHOD_OVERRIDE'])) {
$this->method = strtoupper($_SERVER['HTTP_X_HTTP_METHOD_OVERRIDE']); } else {
$this->method = IS_CLI ? 'GET' : (isset($this->server['REQUEST_METHOD']) ? $this->server['REQUEST_METHOD'] : $_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD']); } } return $this->method; }参数为空,进入elseif流程
elseif (!$this->method) {
if (isset($_POST[Config::get('var_method')])) {
$this->method = strtoupper($_POST[Config::get('var_method')]); $this->{
$this->method}($_POST); } elseif (isset($_SERVER['HTTP_X_HTTP_METHOD_OVERRIDE'])) {
$this->method = strtoupper($_SERVER['HTTP_X_HTTP_METHOD_OVERRIDE']); } else {
$this->method = IS_CLI ? 'GET' : (isset($this->server['REQUEST_METHOD']) ? $this->server['REQUEST_METHOD'] : $_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD']);isset($_POST[Config::get('var_method')])
Config::get('var_method') 获取请求中的参数的值(跟进get函数就行了) //从简分析大概理解流程就行了
得到Config::get('var_method') => _method的值
所以说我们$_POST _method=__construct的值就可以继续执行下去
$this->method = strtoupper($_POST[Config::get('var_method')]); //大写赋值给$this->method
此时$this->method = __construct
继续跟进下一条语句:
$this->{
$this->method}($_POST);这个时候就等价:
$this->__construct($_POST);把$_POST数组作为参数传回了构造函数,跟进分析下
Lines 130
protected function __construct($options = []) {
foreach ($options as $name => $item) {
if (property_exists($this, $name)) { //遍历判断$_POST的键值是否存在类的属性中 $this->$name = $item; } } if (is_null($this->filter)) {
$this->filter = Config::get('default_filter'); } // 保存 php://input $this->input = file_get_contents('php://input'); }这里我们假设重新post _method=__construct&filter=assert到这里的流程
foreach ($options as $name => $item) {
if (property_exists($this, $name)) { //遍历判断$_POST的键值是否存在类的属性中 $this->$name = $item; }首先_method 属性当前类不存在 pass
但是filter属性当前类存在进入$this->$name = $item; //被覆盖为我们传入assert
我们可以回到Request类定义看看filter属性是干嘛用的
全局过滤规则,熟悉tp框架应该就知道会调用这个全局规律规则去过滤pathinfo的参数值,这里我从简分析下流程
回到上面那个APP文件
if (empty($dispatch)) {
// 进行URL路由检测 $dispatch = self::routeCheck($request, $config);//上文分析到这里 } // 记录当前调度信息............................ $data = self::exec($dispatch, $config);//跟进这里 protected static function exec($dispatch, $config) {
switch ($dispatch['type']) {
case 'redirect': // 执行重定向跳转 $data = Response::create($dispatch['url'], 'redirect')->code($dispatch['status']); break; case 'module': // 模块/控制器/操作 $data = self::module($dispatch['module'], $config, isset($dispatch['convert']) ? $dispatch['convert'] : null); //跟进module模块 public static function module($result, $config, $convert = null) {
....................... return self::invokeMethod($call, $vars);//跟进这里 } public static function invokeMethod($method, $vars = []) {
........................ $args = self::bindParams($reflect, $vars);//跟进这里 self::$debug && Log::record('[ RUN ] ' . $reflect->class . '->' . $reflect->name . '[ ' . $reflect->getFileName() . ' ]', 'info'); return $reflect->invokeArgs(isset($class) ? $class : null, $args); } private static function bindParams($reflect, $vars = []) {
if (empty($vars)) {
// 自动获取请求变量 if (Config::get('url_param_type')) {
$vars = Request::instance()->route(); } else {
$vars = Request::instance()->param();//跟进这里 } } ............... }前面一连串调用其实就是工作流程而已,大概理解就行了
Request::instance()->param(); //这里就是payload执行地方了,跟进仔细分析
调用了Request类方法生成Request实例->param() //ps这里就回到了我们之前设置全局$filter规则地方
public function param($name = '', $default = null, $filter = '') {
.................. return $this->input($this->param, $name, $default, $filter); //$filter=assert }跟进input函数
public function input($data = [], $name = '', $default = null, $filter = '') {
................... // 解析过滤器 $filter = $this->getFilter($filter, $default); if (is_array($data)) {
array_walk_recursive($data, [$this, 'filterValue'], $filter);//跟进这里 reset($data); } else {
$this->filterValue($data, $name, $filter); } if (isset($type) && $data !== $default) {
// 强制类型转换 $this->typeCast($data, $type); } return $data; }array_walk_recursive($data, [$this, 'filterValue'], $filter);调用了当前类下的filterValue
跟进这个函数:
private function filterValue(&$value, $key, $filters) {
$default = array_pop($filters); foreach ($filters as $filter) {
if (is_callable($filter)) {
// 调用函数或者方法过滤 $value = call_user_func($filter, $value);//这里执行payload } elseif (is_scalar($value)) {
if (false !== strpos($filter, '/')) {
$value = call_user_func($filter, $value);//这里调用了assert执行了payload
到了这里,一个payload的完整利用流程已经出来轮廓了。
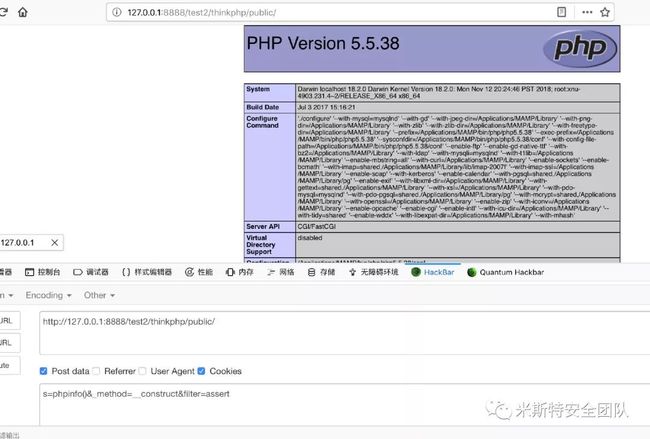
0x2.3 漏洞演示
0x2.4 谈谈漏洞版本影响
这个分析和payload我测试过了5.0.10,5.0,11都是可以的,理论来说是5.0.1x通杀,只要代码是这样走的,而且这个也不要求开启debug模式,5.0.23其中一个利用payload是要求开启debug的。
这里讲下为啥5.0.23的payload没办法用到5.0.1x上,其实主要的代码区别是在于: 5.0.23版的method有server函数处理,才会有了那篇满天飞的文档接下来nb的分析(tql)
而5.0.1版本是:
很明显就没有进入$this->server()函数的过程,对比清楚哈,别看花了。
那问题又来了,那为啥5.0.1x不能用在5.0.23上呢,其实文档作者也说了
就是在$filter进入执行payload之前,中间流程就被重复赋值覆盖掉了
这样到了那个调用$filter就为空了。(因为作者文档写的很清楚这个利用我就不再进行仔细分析了)
对比差异,多了句设置$filter的语句
说到这里,我只想说这个漏洞作者Tql。
0x3 感想
两个小时的分析,总算完成分析任务,这篇文章实在粗糙,诸多纰漏,但还是尽量从简出发,让大家对漏洞的流程有这种执行过程的观念,才能知其payload,在利用其payload,时间匆忙,明天还要考试,其实我还想找下通杀全版本的payload,从那个任意调用函数出发吧,如果有幸,坐等我的第二篇文章,最后打波广告,跟我一样的萌新想学习代码审计,可以关注我在安全客写的ECTOUCH2.0分析代码审计流程 ,这个系列是从我这个小白自身出发,让你上手php代码审计。