TensorFlow2.0基本操作(四)
1 FashionMnist实战
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
# datasets数据集的管理, layers, optimizers优化器,sequential容器, metrics测试的度量器
from tensorflow.keras import datasets, layers, optimizers, Sequential, metrics
import os
(x, y), (x_test, y_test) = datasets.fashion_mnist.load_data()
print(x.shape, y.shape)
# 对数据集做一些预处理
# def preprocess(x, y):
# 首先把x,y转化到一个tensorflow上边去
# x = tf.convert_to_tensor(x, dtype=tf.float32)/255.
# y = tf.convert_to_tensor(y, dtype=tf.int32)
# return x, y
def preprocess(x, y):
x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32)/255.
y = tf.cast(y, dtype=tf.int32)
return x, y
# 构造一个数据集
batchz = 128
db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x, y)) # 要构建Dataset内存中的数据
db = db.map(preprocess).shuffle(10000).batch(batchz) # map()表示在这里映射一下函数就可以了,代表对每一个x,y进行一个这样的处理
# shuffle() 将数据打乱的混乱程度 # batch()从数据集中取出数据集的个数
db_test = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test, y_test)) # 要构建Dataset内存中的数据
db_test = db_test.map(preprocess).batch(batchz)
db_iter = iter(db)
sample = next(db_iter)
print('batch:', sample[0].shape, sample[1].shape)
model = Sequential([ # Sequential是一个容器,里面的每一项要用‘,’相连,表示一个列表
layers.Dense(256, activation = tf.nn.relu), #[b,784] => [b,256]
layers.Dense(128, activation = tf.nn.relu), #[b,256] => [b,128]
layers.Dense(64, activation = tf.nn.relu), #[b,128] => [b,64]
layers.Dense(32, activation = tf.nn.relu), #[b,64] => [b,32]
layers.Dense(10) #[b,32] => [b,10] 330 = 33*10 + 10
])
model.build(input_shape=[None, 28*28]) # 输入一个数,构建一个权值。因为这个model()需要一个输入的维度的
model.summary() # summary()是一个调试的过程,可以把网络结构打印出来
# 此处运行以后可知有24万个连接,每一个连接是4个字节的float,因此是大概100万的节数,再除以1000,大概是100k的一个单元,因此仅参数量已经占用100k了。
# grident占的的数据比参数两是更大的。
# 一个字节是8位,float32是4个字节,一个汉字 = 两个字母 = 2个字节。1kb = 1024byte
# w = w - lr*grad
optimizer = optimizers.Adam(lr=1e-3)
def main():
# 完成一个前向传播
for epoch in range(3):
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(db):
# x: [b,28 , 28] => [b, 784]
# y: [b]
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28*28])
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# [b, 784] => [b,10]
logits = model(x)
y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=10)
# b
loss_mse = tf.reduce_mean(tf.losses.MSE(y_onehot, logits))
loss_ce = tf.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_onehot, logits, from_logits=True)
loss_ce = tf.reduce_mean(loss_ce) # 此处如果缺少这一步会报错,说这loss不是一个标量
grads = tape.gradient(loss_ce, model.trainable_variables)
# zip()是将每一个grads和trainable_variables进行一一对应,进行一个原地更新
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.trainable_variables))
if step % 100 ==0:
print(epoch, step, 'loss:', float(loss_ce), float(loss_mse))
# test
total_correct = 0
total_num = 0
for x, y in db_test:
# x: [b,28 , 28] => [b, 784]
# y: [b]
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28 * 28])
# [b, 10]
logits = model(x)
# logits => prob, [b, 10]
prob = tf.nn.softmax(logits, axis=1)
# [b, 10] => [b]
pred = tf.argmax(prob, axis=1) # 求出最大元素所在的位置
pred = tf.cast(pred, dtype=tf.int32)
# pred:[b]
# y:[b]
# correct :[b] ,True :equal, False:not equal
correct = tf.equal(pred, y)
correct = tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(correct, dtype=tf.float32))
total_correct += int(correct) # tensor转化为numpy
total_num += x.shape[0]
acc = total_correct / total_num
print(epoch, 'test_acc: ', acc)
pass
# 所有的函数都写在main函数里,避免全局变量的一个污染
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
(60000, 28, 28) (60000,)
batch: (128, 28, 28) (128,)
Model: "sequential"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
dense (Dense) multiple 200960
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) multiple 32896
_________________________________________________________________
dense_2 (Dense) multiple 8256
_________________________________________________________________
dense_3 (Dense) multiple 2080
_________________________________________________________________
dense_4 (Dense) multiple 330
=================================================================
Total params: 244,522
Trainable params: 244,522
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
0 0 loss: 2.3851113319396973 0.17211219668388367
0 100 loss: 0.5261880159378052 21.759647369384766
0 200 loss: 0.5219479203224182 22.946624755859375
0 300 loss: 0.43728747963905334 22.286693572998047
0 400 loss: 0.38215288519859314 23.043254852294922
0 test_acc: 0.8436
1 0 loss: 0.3006373345851898 25.290546417236328
1 100 loss: 0.32774943113327026 25.244503021240234
1 200 loss: 0.4082777500152588 26.816308975219727
1 300 loss: 0.3400842547416687 21.91988754272461
1 400 loss: 0.32032591104507446 26.119770050048828
1 test_acc: 0.8537
2 0 loss: 0.2736729383468628 24.64272689819336
2 100 loss: 0.3129444420337677 30.01264762878418
2 200 loss: 0.32730722427368164 33.122718811035156
2 300 loss: 0.29275721311569214 29.02569580078125
2 400 loss: 0.30236032605171204 33.527427673339844
2 test_acc: 0.851
2 TensorBoard的使用
''''
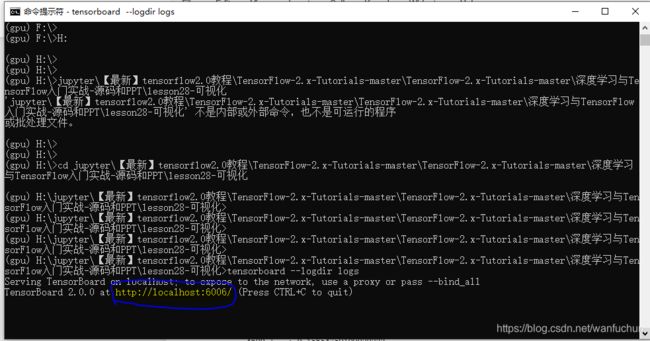
可视化监听步骤:
step1: run listener 打开一个监听器,使用cmd操作,注意不同版本之间的tensorflow会导致报错
step2: build summary 在代码中进行,如下方85行所示
step3: fed scalar 喂数据, 如下方117行
'''
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import datasets, layers, optimizers, Sequential, metrics
import datetime
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import io
# 数据做一个预处理
def preprocess(x, y):
x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
y = tf.cast(y, dtype=tf.int32)
return x, y
# 下方的两个plot_to_image()和image_grid()是合并显示图片的api,无需明白,直接调用就可
def plot_to_image(figure):
"""Converts the matplotlib plot specified by 'figure' to a PNG image and
returns it. The supplied figure is closed and inaccessible after this call."""
# Save the plot to a PNG in memory.
buf = io.BytesIO()
plt.savefig(buf, format='png')
# Closing the figure prevents it from being displayed directly inside
# the notebook.
plt.close(figure)
buf.seek(0)
# Convert PNG buffer to TF image
image = tf.image.decode_png(buf.getvalue(), channels=4)
# Add the batch dimension
image = tf.expand_dims(image, 0)
return image
# 可以把多张图片组合成一张图片
def image_grid(images):
"""Return a 5x5 grid of the MNIST images as a matplotlib figure."""
# Create a figure to contain the plot.
figure = plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
for i in range(25):
# Start next subplot.
plt.subplot(5, 5, i + 1, title='name')
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.grid(False)
plt.imshow(images[i], cmap=plt.cm.binary)
return figure
# 首先,把数据集加载进来
batchsz = 128
(x, y), (x_val, y_val) = datasets.mnist.load_data()
print('datasets:', x.shape, y.shape, x.min(), x.max())
# 然后,转化成两个dataset
db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x,y))
db = db.map(preprocess).shuffle(60000).batch(batchsz).repeat(10)
ds_val = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_val, y_val))
ds_val = ds_val.map(preprocess).batch(batchsz, drop_remainder=True)
# 接下来,通过这样一个五层神经网路结构
network = Sequential([layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(32, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(10)])
network.build(input_shape=(None, 28*28))
network.summary()
optimizer = optimizers.Adam(lr=0.01)
# 再然后,创建一个这样的writer
# build summary
current_time = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S")
log_dir = 'logs/' + current_time
summary_writer = tf.summary.create_file_writer(log_dir) # 这个路径就是我们要监听的路径
#下方几行代码是展示向tensorboard喂一张图片的数据
# get x from (x,y)
sample_img = next(iter(db))[0]
# get first image instance
sample_img = sample_img[0]
sample_img = tf.reshape(sample_img, [1, 28, 28, 1])
with summary_writer.as_default():
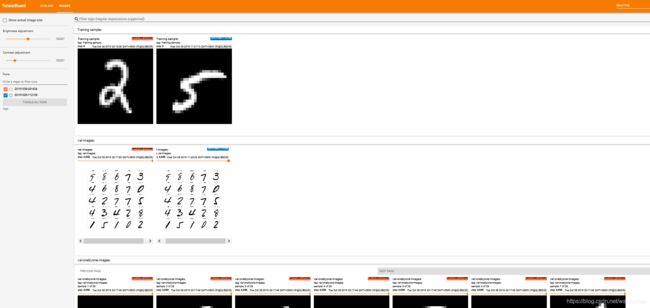
tf.summary.image("Training sample:", sample_img, step=0)
for step, (x,y) in enumerate(db):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# [b, 28, 28] => [b, 784]
x = tf.reshape(x, (-1, 28*28))
# [b, 784] => [b, 10]
out = network(x)
# [b] => [b, 10]
y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=10)
# [b]
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_onehot, out, from_logits=True))
grads = tape.gradient(loss, network.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, network.trainable_variables))
if step % 100 == 0:
# 下方几行代码是展示向tensorboard喂一个标量的数据
print(step, 'loss:', float(loss))
with summary_writer.as_default():
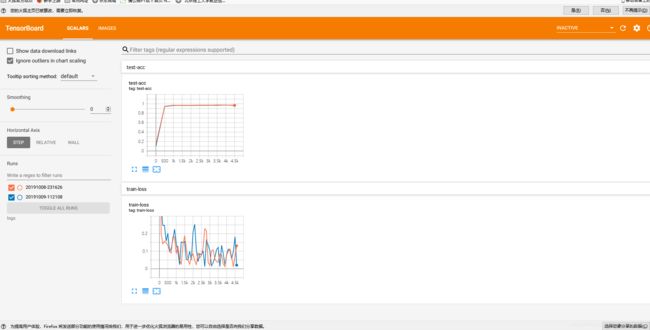
tf.summary.scalar('train-loss', float(loss), step=step) # ''是图的名字,以string为ip;float()将loss这一个张量转化为一个数值;这里step默认为x轴
# evaluate
if step % 500 == 0:
total, total_correct = 0., 0
for _, (x, y) in enumerate(ds_val):
# [b, 28, 28] => [b, 784]
x = tf.reshape(x, (-1, 28*28))
# [b, 784] => [b, 10]
out = network(x)
# [b, 10] => [b]
pred = tf.argmax(out, axis=1)
pred = tf.cast(pred, dtype=tf.int32)
# bool type
correct = tf.equal(pred, y)
# bool tensor => int tensor => numpy
total_correct += tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(correct, dtype=tf.int32)).numpy()
total += x.shape[0]
print(step, 'Evaluate Acc:', total_correct/total)
# 多张图片的tensorboard显示
# print(x.shape)
val_images = x[:25]
val_images = tf.reshape(val_images, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
with summary_writer.as_default():
tf.summary.scalar('test-acc', float(total_correct/total), step=step)
tf.summary.image("val-onebyone-images:", val_images, max_outputs=25, step=step)
# 自己设计一个函数来把要显示的多张图片组合起来,teensorflow自己是是没有做这样的一个函数的
val_images = tf.reshape(val_images, [-1, 28, 28])
figure = image_grid(val_images) # 自己编写的image_grid(),可转到定义
tf.summary.image('val-images:', plot_to_image(figure), step=step)
datasets: (60000, 28, 28) (60000,) 0 255
Model: "sequential"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
dense (Dense) multiple 200960
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) multiple 32896
_________________________________________________________________
dense_2 (Dense) multiple 8256
_________________________________________________________________
dense_3 (Dense) multiple 2080
_________________________________________________________________
dense_4 (Dense) multiple 330
=================================================================
Total params: 244,522
Trainable params: 244,522
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
0 loss: 2.3159594535827637
0 Evaluate Acc: 0.14332932692307693
100 loss: 0.42323487997055054
200 loss: 0.23160609602928162
300 loss: 0.2491304874420166
400 loss: 0.23897933959960938
500 loss: 0.1115313172340393
500 Evaluate Acc: 0.9577323717948718
600 loss: 0.14311788976192474
700 loss: 0.09293900430202484
800 loss: 0.10313019156455994
900 loss: 0.16938796639442444
1000 loss: 0.02754649519920349
1000 Evaluate Acc: 0.9637419871794872
1100 loss: 0.09247124195098877
1200 loss: 0.1360766440629959
1300 loss: 0.05838527902960777
1400 loss: 0.1162179559469223
1500 loss: 0.07719220966100693
1500 Evaluate Acc: 0.9663461538461539
1600 loss: 0.06336888670921326
1700 loss: 0.10078078508377075
1800 loss: 0.1662529706954956
1900 loss: 0.12264891713857651
2000 loss: 0.16240128874778748
2000 Evaluate Acc: 0.9646434294871795
2100 loss: 0.058490827679634094
2200 loss: 0.03956819325685501
2300 loss: 0.11308617889881134
2400 loss: 0.06355343759059906
2500 loss: 0.2220195233821869
2500 Evaluate Acc: 0.9629407051282052
2600 loss: 0.1704622060060501
2700 loss: 0.16472263634204865
2800 loss: 0.12289105355739594
2900 loss: 0.13511228561401367
3000 loss: 0.0755765438079834
3000 Evaluate Acc: 0.9729567307692307
3100 loss: 0.056449007242918015
3200 loss: 0.19840048253536224
3300 loss: 0.10745280236005783
3400 loss: 0.044795747846364975
3500 loss: 0.11135613173246384
3500 Evaluate Acc: 0.9705528846153846
3600 loss: 0.061421073973178864
3700 loss: 0.0556926503777504
3800 loss: 0.021093009039759636
3900 loss: 0.01100428868085146
4000 loss: 0.15188974142074585
4000 Evaluate Acc: 0.9728565705128205
4100 loss: 0.12248240411281586
4200 loss: 0.11432669311761856
4300 loss: 0.018448371440172195
4400 loss: 0.006178594194352627
4500 loss: 0.02976072207093239
4500 Evaluate Acc: 0.9706530448717948
4600 loss: 0.15654759109020233
3 Keras高层API(接口)
这里的keras默认是tf的小包,不是传统意义上的。
keras是一个高层的rapper
这里主要利用它的以下五个功能:
datasets layers losses metrics optimizers
1)这里主要讲解mereics
''''步骤:
首先,新建一个meter(度量表)
其次,传入数据,update_stete
再次,输出结果,result().numpy()
最后,把数据清空,reset_states'''
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import datasets, layers, optimizers, Sequential, metrics
def preprocess(x, y):
x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
y = tf.cast(y, dtype=tf.int32)
return x,y
batchsz = 128
(x, y), (x_val, y_val) = datasets.mnist.load_data()
print('datasets:', x.shape, y.shape, x.min(), x.max())
db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x,y))
db = db.map(preprocess).shuffle(60000).batch(batchsz).repeat(10)
ds_val = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_val, y_val))
ds_val = ds_val.map(preprocess).batch(batchsz)
network = Sequential([layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(32, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(10)])
network.build(input_shape=(None, 28*28))
network.summary()
optimizer = optimizers.Adam(lr=0.01)
#新建meter
acc_meter = metrics.Accuracy() # Accuracy()是一个现成的meter
loss_meter = metrics.Mean() # 求平均值
for step, (x,y) in enumerate(db):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# [b, 28, 28] => [b, 784]
x = tf.reshape(x, (-1, 28*28))
# [b, 784] => [b, 10]
out = network(x)
# [b] => [b, 10]
y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=10)
# [b]
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_onehot, out, from_logits=True))
# 每次loss更新完以后,我们更新一次
loss_meter.update_state(loss)
grads = tape.gradient(loss, network.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, network.trainable_variables))
if step % 100 == 0:
print(step, 'loss:', loss_meter.result().numpy())
loss_meter.reset_states()
# evaluate 这一段代码是我们自己编写的,目的就是为了验证matrics是不是好使。事实证明,而这结果是一样的。简洁有效
if step % 500 == 0:
total, total_correct = 0., 0
# 清除现在已经记录的数据,这样上一次的的结果就不会被统计进来
acc_meter.reset_states()
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(ds_val):
# [b, 28, 28] => [b, 784]
x = tf.reshape(x, (-1, 28*28))
# [b, 784] => [b, 10]
out = network(x)
# [b, 10] => [b]
pred = tf.argmax(out, axis=1)
pred = tf.cast(pred, dtype=tf.int32)
# bool type
correct = tf.equal(pred, y)
# bool tensor => int tensor => numpy
total_correct += tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(correct, dtype=tf.int32)).numpy()
total += x.shape[0]
# 添加数据
acc_meter.update_state(y, pred)
# 最后把meter的数据取出来,利用acc_meter.result()这是一个tensor
# 然后把他转化成numpy的数据,这样就可以打印出来了
print(step, 'Evaluate Acc:', total_correct/total, acc_meter.result().numpy())
2) 接下来讲解complied&fit
compile 装载的功能:指定loss/优化器/指标选择
fit 来创建一系列标准的创建流程
evaluate 进行测试
predict 进行一个预测