Java写一个链表实现增删改遍历_【Java】——链表增删查改功能的模拟实现
1.链表:
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序来实现的。
2.链表的模拟实现:
首先,创建一个MyLinkedList类:
class Node{
public int data;//实例成员变量
public Node next;
public Node(){//无参构造
}
public Node(int data){//带有一个参数的构造方法
this.data = data;
}
}
(1)创建链表
public class MyLinkedList{
public Node head;//表示当前链表的头,其值默认为null
//1.创建链表
public void createLinked(){
this.head = new Node(10);
Node node2 = new Node(20);
Node node3 = new Node(30);
Node node4 = new Node(40);
this.head.next= node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
}
//2.打印链表
public void display(){
Node cur = this.head;
while(cur != null){
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
测试代码:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.createLinked();
myLinkedList.display();
}
}
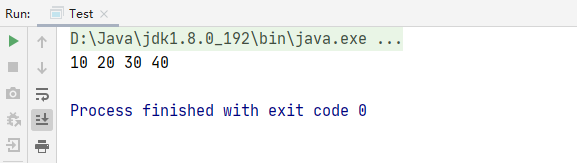
运行结果:
(2)通过遍历,打印链表的每一个元素
//3.通过遍历,打印链表的每一个元素
public void display(){
Node cur = this.head;
while(cur != null){
System.out.print(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
(3)通过遍历,找到链表的最后一个节点
//4.通过遍历,找到链表的最后一个节点
public Node findLastNode(){
if(this.head == null){
System.out.println("head == null");
return null;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while(cur.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur;
}
(4)通过遍历,找到链表的倒数第二个节点
//5.通过遍历,找到链表的倒数第二个节点
public Node findLastTwo(){
if(this.head == null){
System.out.println("一个节点也没有!");
return null;
}
if(this.head.next == null){
System.out.println("只有一个节点!");
return null;
}
Node cur = this.head;
while(cur.next.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur;
}
(5)通过遍历,找到链表的第n个节点(链表的长度 >= n)
//6.通过遍历,找到链表的第n个节点(链表的长度 >= n)
public Node findN(int n){
if(this.head == null){
System.out.println("此链表为空!");
return null;
}
if(n <= 0){
System.out.println("输入的n太小了!");
return null;
}
if(n > size()){
System.out.println("输入的n超过了链表的长度了!");
return null;
}
int count = 1;
Node cur = this.head;
while(count != n){
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur;
}
(6)通过遍历,计算链表元素的个数
//7.通过遍历,计算链表元素的个数
public int size(){
Node cur = this.head;
int count = 0;//计数
while(cur != null){
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
(7)通过遍历,找到链表中是否包含某个元素
//8.通过遍历,找到链表中是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int key){
Node cur = this.head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.data == key){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
(8)头插法
//9.头插法
public void addFirst(int data){
//0.创建节点
Node node = new Node(data);
//1.判断链表是否为空
if(this.head == null){
this.head = node;
}else{
//2.插入节点
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}
}
(9)尾插法
//10.尾插法
public void addLast(int data){
//0.创建节点
Node node = new Node(data);
if(this.head == null){
this.head = node;
}else{
//1. cur 找尾巴
Node cur = this.head;
while(cur.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
}
//2.插入
cur.next = node;
}
}
(10)任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
//11.任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data) {
if(index < 0 || index > size()){
System.out.println("index位置不合法!");
return;
}
//头插法
if(index == 0){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
//尾插法
if(index == size()){
addLast(data);
return;
}
//cur保存的是index- 1位置的节点的引用
Node cur = moveIndex(index);
Node node = new Node(data);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
/***
* 该函数的功能是找到index - 1位置的节点的引用
* @param index
* @return
*/
public Node moveIndex(int index){
Node cur = this.head;
int count = 0;
while (count != index - 1){
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
return cur;
}
(11)删除第一次出现关键字key的节点
//12.删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key) {
if(this.head == null){
System.out.println("没有节点!");
}
if(this.head.data == key){//删除头结点
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
Node prev = searchPrev(key);
if(prev == null){
System.out.println("没有这个可以的前驱!");
}
else{
Node del = prev.next;
prev.next = del.next;
}
}
/***
* 此函数的作用找到要删除节点的前驱
* @param key
* @return
*/
public Node searchPrev(int key){
Node cur = this.head;
while(cur.next != null){
if(cur.next.data == key){
return cur;//返回要删除节点的前驱
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
(12)删除所有值为key的节点
//13.删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){
if(this.head == null){
return;
}
Node curHead = this.head;
Node prev = this.head;
Node cur = this.head.next;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.data == key){
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else{
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if(this.head.data == key){
this.head = this.head.next;
}
}
3.链表的问题
链表的缺点(1)以节点为单位进行存储,不支持随机访问;
链表的优点(1)任意位置插入删除时间复杂度为O(1);
(2)没有增容问题,插入一个开辟一个空间。
本文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45991995/article/details/112014668
如您对本文有疑问或者有任何想说的,请点击进行留言回复,万千网友为您解惑!