一.应用启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
开发SpirngBoot应用时,入口类就这简单的几行。但是却完成了N多服务的初始化、加载和发布。那么这几行代码究竟干了什么呢,SpringBoot应用到底是怎么启动的。
本文中相关源码来自Springboot2.3.3, spring不同版本之间的代码可能有些许差别,但整体的过程是大同小异的
二.@SpringBootApplication注解
2.1.SpringBootApplication注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
@SpringBootApplication=@SpringBootConfiguration+@EnableAutoConfiguration+@ComponentScan,是这三个注解的复合注解
2.2.@SpringBootConfiguration
/**
* Indicates that a class Spring Boot application
* {@link Configuration @Configuration}. Can be used as an alternative to the Spring's
* standard {@code @Configuration} annotation so that configuration can be found
* automatically (for example in tests).
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {}
SpringBootConfiguration注解和Spring的@Configuration注解作用一样。标注当前类是配置类,并会将当前类内声明的一个或多个以@Bean注解标记的方法的实例纳入到spring容器中.
2.3.@ComponentScan
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
/**
* Configures component scanning directives for use with @{@link Configuration} classes.
* Provides support parallel with Spring XML's {@code } element.
*
* Either {@link #basePackageClasses} or {@link #basePackages} (or its alias
* {@link #value}) may be specified to define specific packages to scan. If specific
* packages are not defined, scanning will occur from the package of the
* class that declares this annotation.
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Repeatable(ComponentScans.class)
public @interface ComponentScan{}
@ComponentScan扫描指定的包路径,若未指定包路径,则以声明这个注解的类作为基本包路径。比如@SpringBootApplication就没有指定包路径,则DemoApplication的包路径将作为扫描的基本包路径,因此强烈建议将主类放在顶层目录下。
excludeFilters属性指定哪些类型不符合组件扫描的条件,会在扫描的时候过滤掉。
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class)
比如上面这段代码。@Filter声明了过滤器类型类为自定义类型(需要实现TypeFilter接口),过滤器为AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter。当match方法为true,返回扫描类对象,否则过滤掉。但是要注意@ComponentScan的key为excludeFilters,因此ComponentScan在扫描时满足过滤器条件(match返回true)的这些类型将在包扫描的时候过滤掉,是不会将该类加载到容器的。
@Override
public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory)
throws IOException {
//如果是Springboot自动配置类,则不将其加载到Bean容器
return isConfiguration(metadataReader) && isAutoConfiguration(metadataReader);
}
//判断是否是配置类
private boolean isConfiguration(MetadataReader metadataReader) {
return metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata().isAnnotated(Configuration.class.getName());
}
//判断是否为EnableAutoConfiguration类
private boolean isAutoConfiguration(MetadataReader metadataReader) {
return getAutoConfigurations().contains(metadataReader.getClassMetadata().getClassName());
}
2.3.@EnableAutoConfiguration
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {}
这个注解是SpringBoot能进行自动配置的关键
selectImports方法:根据导入Configuration类的AnnotationMetadata选择并返回应导入的类的名称
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);
//返回自动配置类名数组
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
//根据导入Configuration类的AnnotationMetadata返回AutoConfigurationEntry
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
//返回@EnableAutoConfiguration 注解上的排除属性
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
//通过SPI加载候选的自动配置类名
List configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
//移除重复的类名
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
//获取注解上和 spring.autoconfigure.exclude 配置的排除类名
Set exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
//检查加载到的类名的合法性
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
//排除需要移除的类
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
//通过元数据再次过滤
configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);
//监听器发布自动配置导入事件并进行相应的处理
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
@Import注解用于导入配置类,导入类AutoConfigurationImportSelector。
在 AbstractApplicationContext--->refresh()--->invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()中,会调用AutoConfigurationImportSelector类的selectImports方法,最终通过调SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames方法,
扫描META-INF/spring.factories文件自动配置类(key为EnableAutoConfiguration),通过对其全类名的反射获取到自动导入类的类元信息,并注册到Bean工厂
三.从SpringApplication.run开始解析
3.1 Springboot的启动流程主要分为三个部分:
- SpringApplication的创建和初始化以及启动之前的一些配置(启动前)
- SpringApplication的具体启动过程(启动过程)
- SpringBoot的核心即自动配置模块
3.2.SpringApplication的创建和初始化
3.2.1.构造器
/**
* Create a new {@link SpringApplication} instance. The application context will load
* beans from the specified primary sources (see {@link SpringApplication class-level}
* documentation for details. The instance can be customized before calling
* {@link #run(String...)}.
* @param resourceLoader the resource loader to use
* @param primarySources the primary bean sources
* @see #run(Class, String[])
* @see #setSources(Set)
*/
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
//1.根据应用是否存在某些类推断应用类型,分为响应式web应用,servlet类型web应用和非web应用,在后面用于确定实例化applicationContext的类型
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
//2.设置初始化器,读取spring.factories文件key ApplicationContextInitializer对应的value并实例化.ApplicationContextInitializer接口用于在Spring上下文被刷新之前进行初始化的操作
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//3.设置监听器,读取spring.factories文件key ApplicationListener对应的value并实例化
//interface ApplicationListener extends EventListener
//ApplicationListener继承EventListener,实现了观察者模式。对于Spring框架的观察者模式实现,它限定感兴趣的事件类型需要是ApplicationEvent类型事件
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
//4.配置应用入口类class对象
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
如上源码,在构造器里主要干了2件事,一是设置初始化器,二是设置监听器
3.2.2.设置初始化器ApplicationContextInitializer
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
private Collection getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class type) {
return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class[] {});
}
private Collection getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class type,Class[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
//从类路径的META-INF处读取相应配置文件spring.factories,然后进行遍历,读取配置文件中Key(type)对应的value
Set names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
//通过反射将names的对象实例化
List instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes,classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
根据入参type类型ApplicationContextInitializer.class从类路径的META-INF处读取相应配置文件spring.factories并实例化对应Initializer。
SpringApplication启动中获取指定自动配置类型的实例时反复用到了上面这2个函数。
- ApplicationContextInitializer是Spring框架原有的东西,这个类的主要作用就是在ConfigurableApplicationContext类型(或者子类型)的ApplicationContext做refresh之前,允许我们对ConfiurableApplicationContext的实例做进一步的设置和处理。关于Spring中具体的ApplicationContextInitializer介绍请移步这里:Spring中的ApplicationContextInitializer
SpringBoot默认META-INF/spring.factories中的ApplicationContextInitializer配置如下:
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.rsocket.context.RSocketPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.web.context.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer
3.2.3.设置监听器ApplicationListener
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
和设置初始化器是相同的过程,通过getSpringFactoriesInstances函数实例化监听器。
- ApplicationListener使用了观察者设计模式,主要作用是在springboot启动过程的不同阶段,通过监听到发布的不同的事件从而去执行一些相应的操作。关于Spring中具体的ApplicationListener介绍请移步这里:Spring中的监听器详解与观察者模式
SpringBoot默认META-INF/spring.factories中的ApplicationListener配置如下:
# Application Listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
org.springframework.boot.ClearCachesApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.logging.ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener
3.3.SpringApplication具体的启动过程分析
3.3.1.启动过程的核心 run方法
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
//计时器,记录程序的运行时间
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
//设置java.awt.headless系统属性为true,Headless模式是系统的一种配置模式。
// 在该模式下,系统缺少了显示设备、键盘或鼠标。但是服务器生成的数据需要提供给显示设备等使用。
// 因此使用headless模式,一般是在程序开始激活headless模式,告诉程序,现在你要工作在Headless mode下,依靠系统的计算能力模拟出这些特性来
configureHeadlessProperty();
//获取监听器集合对象
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
//1.发出开始执行的事件。
listeners.starting();
try {
//根据main函数传入的参数,创建DefaultApplicationArguments对象
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
//2.根据扫描到的监听器对象和函数传入参数,进行环境准备。
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,applicationArguments);
//读取spring.beaninfo.ignore,并加入到Spring内部的Bean信息缓存中
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
//通过Banner.Model和相关的配置打印Banner信息
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//创建ApplicationContext,类型为ConfigurableApplicationContext
context = createApplicationContext();
//和上面套路一样,读取spring.factories文件key SpringBootExceptionReporter对应的Class,用于支持SpringbootApplication启动过程中异常的回调
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
//准备和加载运行环境
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,printedBanner);
//和上面的一样,context准备完成之后,将触发SpringApplicationRunListener的contextPrepared执行
refreshContext(context);
//其实啥也没干。但是老版本的callRunners好像是在这里执行的。
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
//发布ApplicationStartedEvent事件,发出结束执行的事件
listeners.started(context);
//在某些情况下,我们希望在容器bean加载完成后执行一些操作,会实现ApplicationRunner或者CommandLineRunner接口
//后置操作,就是在容器完成刷新后,依次调用注册的Runners,多个Runner时可以通过@Order注解设置各runner的执行顺序。
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}try {
//发布ApplicationReadyEvent事件。上下文已刷新并且所有的CommandLineRunners和ApplicationRunner都已被调用,应用上下文创建完成
listeners.running(context);
}catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
SpringApplication核心的启动运行方法如上所示,过程分析:
- listeners.starting(): 发布ApplicationStartingEvent,运行过程开始
- 创建并配置运行环境:
- 程序运行的环境,主要包含了两种信息,一种是profiles,用来描述哪些bean definitions是可用的;一种是properties,用来描述系统的配置,其来源可能是配置文件、JVM属性文件、操作系统环境变量等等。
- 发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent环境准备就绪事件
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) { if (this.addConversionService) { ConversionService conversionService = ApplicationConversionService.getSharedInstance(); environment.setConversionService((ConfigurableConversionService) conversionService); } configurePropertySources(environment, args); configureProfiles(environment, args); } - context = createApplicationContext():创建ApplicationContext
这里通过this.webApplicationType判断具体要创建哪种类型的ApplicationContext.protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() { Class contextClass = this.applicationContextClass; if (contextClass == null) { try { switch (this.webApplicationType) { case SERVLET: contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS); break; case REACTIVE: contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS); break; default: contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex); } } return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); }
比如web类型为servlet类型,就会实例化org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext类型的context。
在这里BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass)是通过instantiateClass(clazz.getDeclaredConstructor())进行初始化,也就是说这里是用来空参构造函数来进行实例化的。下面是其构造函数:
构造方法中初始化了两个成员变量,类型分别为AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader和ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner用以加载使用注解的bean定义:/** * Create a new {@link AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext} that needs * to be populated through {@link #register} calls and then manually * {@linkplain #refresh refreshed}. */ public AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext() { this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this); this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this); }
在实例化上下文的时候,会向ApplicationContext.beanFacroty内部注册几个核心的后处理器:// 调用父类AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的构造函数 public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() { // 实例化一个注解bena定义读取器 this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this); this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this); } public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Environment environment) { Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null"); Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null"); // 维护一个ApplicationContext上下文索引 this.registry = registry; // 声明一个条件评估器,用来评估一个@Condition注解的类是否符合注入条件 this.conditionEvaluator = new ConditionEvaluator(registry, environment, null); // 这里会事先向beanFacroty注入几个核心后处理器 AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry); }- internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor:ConfigurationClassPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor: 用于@Configuration配置类的处理,包括postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry,postProcessBeanFactory,processConfigBeanDefinitions三个主要方法
- internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor:AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:处理@Autowired,@Injected注解字段,向其注入实际依赖的bean
- internalCommonAnnotationProcessor:CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor: 处理@PostConstruct,@PreDestroy,@Resource等注解
- internalPersistenceAnnotationProcessor:PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:如果引入了JPA,这个类时处理JPA注解
- internalEventListenerProcessor:EventListenerMethodProcessor:将EventListenner方法注册为ApplicationListener
- internalEventListenerFactory:DefaultEventListenerFactory:默认的EventListenerFactory实现,支持@EventListener注解
- prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,printedBanner):context前置处理阶段
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) { //关联环境 context.setEnvironment(environment); //ApplicationContext预处理,主要配置Bean生成器以及资源加载器 postProcessApplicationContext(context); //调用初始化器,执行initialize方法,前面set的初始化器终于用上了 applyInitializers(context); //发布contextPrepared事件 listeners.contextPrepared(context); if (this.logStartupInfo) { logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null); logStartupProfileInfo(context); } // Add boot specific singleton beans ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory(); //注册单例Bean ApplicationArguments到ConfigurableListableBeanFactory,用于获取启动application所需的参数 beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments); //加载打印Banner的Bean if (printedBanner != null) { beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner); } if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) { //设置是否允许重载Bean定义 ((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory) .setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding); } // Load the sources,根据primarySources加载resource。primarySources:一般为主类的class对象 Set - refreshContext: 调用父类AbstractApplicationContext刷新容器的操作.这里的refresh()方法就是Spring IOC容器加载的核心过程。Spring核心源码分析请看Spring IOC 容器源码分析
3.3.2.启动过程中的监听器的使用
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
和构造器设置初始化器一个套路,根据传入type SpringApplicationRunListener去扫描spring.factories文件,读取type对应的value并实例化。然后利用实例化对象创建SpringApplicationRunListeners对象。
查看spring.factories中的配置如下:
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\
org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener
EventPublishingRunListener的作用是在SpringApplication加载的不同阶段发布不同的SpringApplicationEvent。如下是其调用各个方法相应的阶段,也对应了run方法运行过程中的多个阶段:
@Override
//在run方法首次启动时立即调用。可用于非常早期的初始化
public void starting() {
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args));
}
@Override
//在准备好环境之后,ApplicationContext创建之前调用
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
this.initialMulticaster
.multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, environment));
}
@Override
//在ApplicationContext已经被创建和准备完毕之后,在加载资源前被调用
public void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
this.initialMulticaster
.multicastEvent(new ApplicationContextInitializedEvent(this.application, this.args, context));
}
@Override
//ApplicationContext上下文被加载后,刷新之前
public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
for (ApplicationListener listener : this.application.getListeners()) {
if (listener instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) listener).setApplicationContext(context);
}
context.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, context));
}
@Override
//上下文已刷新,应用程序已启动,但尚未调用CommandLineRunners和ApplicationRunners
public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
context.publishEvent(new ApplicationStartedEvent(this.application, this.args, context));
AvailabilityChangeEvent.publish(context, LivenessState.CORRECT);
}
@Override
//在上下文已刷新并且所有的CommandLineRunners和ApplicationRunner都已被调用,run方法完成之前
public void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
context.publishEvent(new ApplicationReadyEvent(this.application, this.args, context));
AvailabilityChangeEvent.publish(context, ReadinessState.ACCEPTING_TRAFFIC);
}
@Override
//应用程序运行过程中发生异常时被调用
public void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
ApplicationFailedEvent event = new ApplicationFailedEvent(this.application, this.args, context, exception);
if (context != null && context.isActive()) {
// Listeners have been registered to the application context so we should
// use it at this point if we can
context.publishEvent(event);
}
else {
// An inactive context may not have a multicaster so we use our multicaster to
// call all of the context's listeners instead
if (context instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
for (ApplicationListener listener : ((AbstractApplicationContext) context)
.getApplicationListeners()) {
this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
this.initialMulticaster.setErrorHandler(new LoggingErrorHandler());
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(event);
}
}
三、自动配置的奥秘---SpringBoot启动过程中自动配置Bean如何注册到BeanFactory
在 Spring-IOC容器源码分析一文中,分析到SpringBoot基于注解的运行方式是在 refresh()--->invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()方法中进行了Bean定义的解析和收集,那么自动配置类导入的Bean或直接使用或间接的去构建成其他对象,必然也需要在这一阶段进行Bean定义的注册以便在之后的过程中进行实例化
承接 Spring-IOC容器源码分析一文中 ConfigurationClassParser.java 265--->doProcessConfigurationClass方法对自动配置相关的源码继续分析:
@EnableAutoConfiguration注解中通过
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)导入了自动配置类,在这里我们直接从处理@Import注解的
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), filter, true)开始分析
ConfigurationClassParser.java 552
private void processImports(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass currentSourceClass,
Collection importCandidates, Predicate exclusionFilter,
boolean checkForCircularImports) {
if (importCandidates.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
if (checkForCircularImports && isChainedImportOnStack(configClass)) {
this.problemReporter.error(new CircularImportProblem(configClass, this.importStack));
}
else {
this.importStack.push(configClass);
try {
//对ImportSelector的处理
for (SourceClass candidate : importCandidates) {
if (candidate.isAssignable(ImportSelector.class)) {
// Candidate class is an ImportSelector -> delegate to it to determine imports
Class candidateClass = candidate.loadClass();
ImportSelector selector = ParserStrategyUtils.instantiateClass(candidateClass, ImportSelector.class,
this.environment, this.resourceLoader, this.registry);
Predicate selectorFilter = selector.getExclusionFilter();
if (selectorFilter != null) {
exclusionFilter = exclusionFilter.or(selectorFilter);
}
if (selector instanceof DeferredImportSelector) {
//如果是 DefferredImportSelector,则使用deferredImportSelectorHandler进行延迟处理
this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.handle(configClass, (DeferredImportSelector) selector);
}
else {
//根据ImportSelector方法的返回值来进行递归操作
String[] importClassNames = selector.selectImports(currentSourceClass.getMetadata());
Collection importSourceClasses = asSourceClasses(importClassNames, exclusionFilter);
processImports(configClass, currentSourceClass, importSourceClasses, exclusionFilter, false);
}
}
else if (candidate.isAssignable(ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class)) {
// Candidate class is an ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar ->
// delegate to it to register additional bean definitions
Class candidateClass = candidate.loadClass();
ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar registrar =
ParserStrategyUtils.instantiateClass(candidateClass, ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class,
this.environment, this.resourceLoader, this.registry);
configClass.addImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar(registrar, currentSourceClass.getMetadata());
}
else {
// Candidate class not an ImportSelector or ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar ->
// process it as an @Configuration class
//如果当前的类既不是ImportSelector也不是ImportBeanDefinitionRegistar就进行@Configuration的解析处理
this.importStack.registerImport(
currentSourceClass.getMetadata(), candidate.getMetadata().getClassName());
processConfigurationClass(candidate.asConfigClass(configClass), exclusionFilter);
}
}
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to process import candidates for configuration class [" +
configClass.getMetadata().getClassName() + "]", ex);
}
finally {
this.importStack.pop();
}
}
}
可以看到
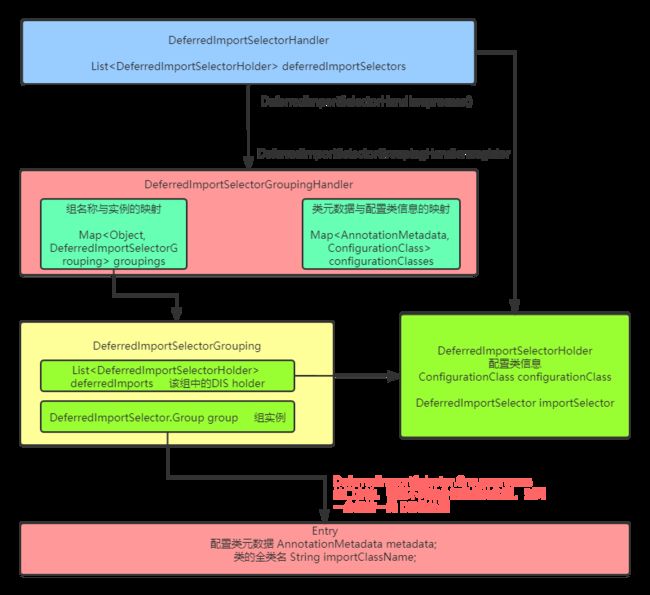
DeferredImportSelectorHandler是ConfigurationClassParser一个专门用来处理延迟导入选择器的内部类
关于SpringBoot中的其他的ImportSelctor类的使用和分析 spring中的ImportSelector接口原理与使用
真正的对于延迟ImportSelector的处理则是在下面的process()方法:
ConfigurationClassParser.java 169
public void parse(Set configCandidates) {
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : configCandidates) {
BeanDefinition bd = holder.getBeanDefinition();
try {
if (bd instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName());
}
else if (bd instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).hasBeanClass()) {
parse(((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).getBeanClass(), holder.getBeanName());
}
else {
parse(bd.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to parse configuration class [" + bd.getBeanClassName() + "]", ex);
}
}
//延迟导入选择器的处理,SpringBoot自动配置类的加载处理的关键
//因为有些自动配置类是有条件的,需要根据@Condition注解判断是否已经有指定类再进行注入
//所以在这里需要等到所有的配置类都处理完以后,最后处理这些 DeferredImportSelector类
this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.process();
}
ConfigurationClassParser.java 746
private class DeferredImportSelectorHandler {
@Nullable
private List deferredImportSelectors = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* Handle the specified {@link DeferredImportSelector}. If deferred import
* selectors are being collected, this registers this instance to the list. If
* they are being processed, the {@link DeferredImportSelector} is also processed
* immediately according to its {@link DeferredImportSelector.Group}.
* //处理指定的 DeferredImportSelector。如果正在收集延迟导入选择器,则会将此实例注册到列表中。如果正在处理它们,将会根据DeferredImportSelector.Group组立即处理
* @param configClass the source configuration class
* @param importSelector the selector to handle
*/
public void handle(ConfigurationClass configClass, DeferredImportSelector importSelector) {
DeferredImportSelectorHolder holder = new DeferredImportSelectorHolder(configClass, importSelector);
//根据私有变量deferredImportSelectors初始化值,如果直接执行该handle方法时,this.deferredImportSelectors == null条件比不成立
if (this.deferredImportSelectors == null) {
DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler handler = new DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler();
handler.register(holder);
handler.processGroupImports();
}
else {
//将加入的importSelector封装后添加到DeferredImportSelectorHolder集合
this.deferredImportSelectors.add(holder);
}
}
public void process() {
List deferredImports = this.deferredImportSelectors;
this.deferredImportSelectors = null;
try {
if (deferredImports != null) {
//创建一个组处理器
DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler handler = new DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler();
//根据@Order注解进行排序
deferredImports.sort(DEFERRED_IMPORT_COMPARATOR);
//循环注册所有的 ImportSelector到相应的组中
deferredImports.forEach(handler::register);
//所有组分别处理相应的ImportSelector
//DeferredImportSelector会根据Group进行分组,即封装成 DeferredImportSelectorGrouping 类,并且以组为单位对同一组中的ImportSelector进行统一处理
handler.processGroupImports();
}
}
finally {
this.deferredImportSelectors = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
}
接着上面的process方法分析:
ConfigurationClassParser.java 795
public void register(DeferredImportSelectorHolder deferredImport) {
// key:组类型(在这里 AutoConfigurationGroup) value:组
private final Map groupings = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// key:配置类的注解属性 value:配置类信息(在这里是入口类即具有@SpringBootApplication类的信息)
private final Map configurationClasses = new HashMap<>();
//注册分组
public void register(DeferredImportSelectorHolder deferredImport) {
Class group = deferredImport.getImportSelector().getImportGroup(); // 这个方法有默认(default)实现,返回的是 null
/*
创建组
1. 其中 createGroup(group) 就是创建了上面的 group 对象,如果为空,则创建一个默认的组对象 DefaultDeferredImportSelectorGroup。
2. 这个方法的意思是,如果 map 中没有这个元素则用后面的方法创建,如果有则直接取出来
*/
DeferredImportSelectorGrouping grouping = this.groupings.computeIfAbsent(
(group != null ? group : deferredImport),
key -> new DeferredImportSelectorGrouping(createGroup(group)));
grouping.add(deferredImport);//创建一个组,并加入DeferredImportSelectorHolder
this.configurationClasses.put(deferredImport.getConfigurationClass().getMetadata(),
deferredImport.getConfigurationClass());//将注解属性和ConfigurationClass映射
}
ConfigurationClassParser.java 805
public void processGroupImports() {
//遍历其中的ImportSelectorGroup进行处理
for (DeferredImportSelectorGrouping grouping : this.groupings.values()) {
Predicate exclusionFilter = grouping.getCandidateFilter();
//关键点 对于默认DefaultDeferredImportSelectorGroup组下的selector直接将其类信息封装成Entry信息返回,对于AutoConfigurationGroup组下的在下面分析
grouping.getImports().forEach(entry -> {
ConfigurationClass configurationClass = this.configurationClasses.get(entry.getMetadata());
try {
//递归调用处理 @Import的方法
processImports(configurationClass, asSourceClass(configurationClass, exclusionFilter),
Collections.singleton(asSourceClass(entry.getImportClassName(), exclusionFilter)),
exclusionFilter, false);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to process import candidates for configuration class [" +
configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName() + "]", ex);
}
});
}
}
ConfigurationClassParser.java 874
public Iterable getImports() {
//遍历使用指定的DeferredImportSelector处理导入Configuration类的AnnotationMetadata
for (DeferredImportSelectorHolder deferredImport : this.deferredImports) {
this.group.process(deferredImport.getConfigurationClass().getMetadata(),
deferredImport.getImportSelector());
}
//返回该组中需要被导入的Entries
return this.group.selectImports();
}
在这里继续看AutoConfigurationGroup类中对于上述 void process(AnnotationMetadata metadata, DeferredImportSelector selector)类的实现:
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.java 428
@Override
public void process(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, DeferredImportSelector deferredImportSelector) {
Assert.state(deferredImportSelector instanceof AutoConfigurationImportSelector,
() -> String.format("Only %s implementations are supported, got %s",
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class.getSimpleName(),
deferredImportSelector.getClass().getName()));
//关键点 基于导入@Configuration类的AnnotationMetadata返回AutoConfigurationEntry,与最开始通过SPI获取自动配置类信息的分析衔接
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = ((AutoConfigurationImportSelector) deferredImportSelector)
.getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);
this.autoConfigurationEntries.add(autoConfigurationEntry);
for (String importClassName : autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations()) {
this.entries.putIfAbsent(importClassName, annotationMetadata);
}
}
与DeferredImportSelector处理相关的主要有这几个类:
- DeferredImportSelectorHandler:持有一个List
类型的list,是对 DeferredImportSelector 类型的处理类 - DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler:DeferredImportSelector的实际分组处理类,持有如下的两个属性,其 register 和 processGroupImports 方法处理 DeferredImportSelector 并填充这两个属性
private class DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler {
private final Map groupings = new LinkedHashMap<>();
private final Map configurationClasses = new HashMap<>();
...
}
- DeferredImportSelectorGrouping:持有一个DeferredImportSelector.Group组对象和DeferredImportSelectorHolder的List,存放该组中要处理的 DeferredImportSelector
private static class DeferredImportSelectorGrouping {
private final DeferredImportSelector.Group group;
private final List deferredImports = new ArrayList<>();
...
}
- DeferredImportSelectorHolder:DeferredImportSelector的封装,持有DeferredImportSelector实例及其对应的Configuration类元信息
private static class DeferredImportSelectorHolder {
private final ConfigurationClass configurationClass;
private final DeferredImportSelector importSelector;
...
}
四.开发一个自己的Starter
与Starter相关的内容其实是Springboot自动配置的部分,下面将之前的使用Netty-websocket构建一个简易的聊天室改造成一个Starter
3.1编写一个Starter主要是这么几步:
- 加入spring-boot-autoconfigure配置
- 编写自动配置类
/** * 自动装配引导类 * * @author duwenxu * @create 2021-01-21 18:29 */ @Configuration //仅当ChatServerStarter存在于类路径上时才会实例化Bean @ConditionalOnClass(ChatServerStarter.class) public class NettyWsAutoConfiguration { @Bean //仅当该BeanFactory中不存在chatServerStarter类型的Bean时注入该Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean public ChatServerStarter chatServerStarter(){ return new ChatServerStarter(); } } - 在META-INF文件夹下添加spring.factories添加自动配置类
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=com.netty.websocket.autoconf.NettyWsAutoConfiguration - maven构建jar包:
mvn clean install
3.2.需要注意:
- starter是具有一个工具包的性质,因次应该去掉主类以及pom中的mainClass配置,否则会出现不能够注入bean的问题
3.3. 引用后的效果:
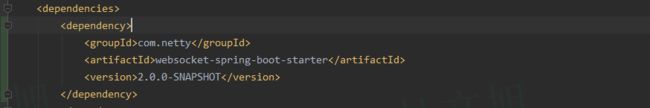
-
加入依赖
-
日志打印websocket端口的绑定信息
-
打印新Channel连入信息
 打印新的channel连接信息.png
打印新的channel连接信息.png -
可以实现websocket长连接推送功能