一、前期回顾
上一篇文章JAVA NIO 编程入门(二)学习了NIO的聚集和分散,以及选择器的使用,并通过一个小demo进行实战,演示了如何进行分散和聚集,以及其主要使用场景,本文将是NIO编程入门最后一篇,进行一个RPC简单小demo框架的实现,对前面的知识进行总结性的实战,由于只是演示性质的demo,所以RPC功能并没有考虑很完善,也不涉及到性能等问题考虑。
二、什么是RPC
RPC 英文全称 Remote Procedure Calls,翻译过来就是远程过程调用,是分布式系统中不同节点间流行的通信方式。举例:假设有A服务和B服务分别位于不同的服务器,A服务想调用B服务像调用本地方法一样,这个时候就需要借助RPC方式进行调用。
三、RPC实现
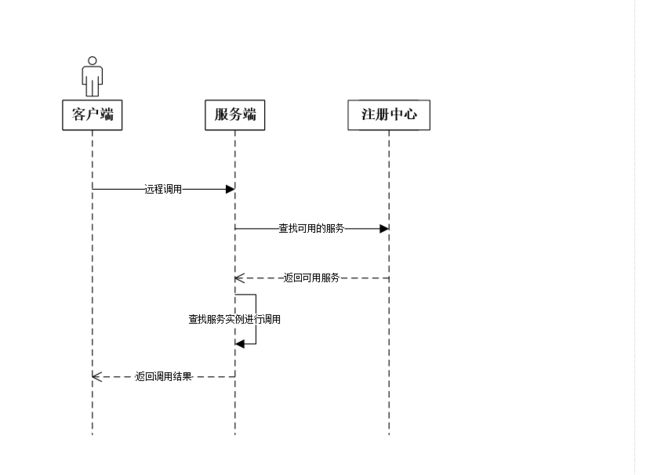
RPC由三个主要部分组成,服务提供者,服务消费者,服务注册中心,服务注册中心提供服务提供者注册服务。客户端和服务端的交互协议采用json的形式,方便演示,同时考虑到复杂性,本次RPC不利用聚集和分散进行协议设计。
- RPC调用过程解析
- 请求实体类源码
@Data
public class RpcRquest {
/**请求id*/
private String requestId;
/**请求接口名*/
private String interfaceName;
/**服务版本**/
private String serviceVersion;
/**方法名*/
private String methodName;
/**参数类型*/
private Class[] parameterTypes;
/**参数*/
private Object[] parameters;
}
- 返回实体类源码
@Data
public class RpcResponse {
/**请求流水号*/
private String requestId;
/**异常*/
private Exception exception;
/**返回结果**/
private Object result;
}
- 服务发现源码
public class RpcRegister {
/**存储注册的服务提供实现类*/
private HashMap registMap = new HashMap<>();
private static RpcRegister register=new RpcRegister();
public static RpcRegister buildRegist(){
return register;
}
public RpcRegister regist(String interfaceName,Object obj){
registMap.put(interfaceName,obj);
return this;
}
public Object findServier(String interfaceName){
return registMap.get(interfaceName);
}
}
这里利用一个map存提供服务的实例,后续再在服务端只需要通过接口就可以查找到对应的实现类。
- 服务提供者源码
public class ProviderServer implements Runnable {
/**
* 服务提供端口
*/
private int port;
public ProviderServer(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true) {
int readyChannels = selector.selectNow();
if (readyChannels == 0) continue;
Set selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator keyIterator = selectedKeys.iterator();
while (keyIterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) keyIterator.next();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel1 = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel1.accept();
ByteBuffer buf1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(2048);
socketChannel.read(buf1);
buf1.flip();
String reciveStr = new String(buf1.array());
if (buf1.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.println(">>>服务端收到数据:" + reciveStr);
//判断接受的内容是否有结束符,如果有,说明是一个请求结束。
if (reciveStr.contains(RpcConstant.PROTOCOL_END)) {
RpcRquest req = JSONObject.parseObject(reciveStr.replace(RpcConstant.PROTOCOL_END, ""), RpcRquest.class);
RpcResponse res = new RpcResponse();
res.setRequestId(req.getRequestId());
System.out.println(req.toString());
Class remoteInterface = Class.forName(req.getInterfaceName());
Method method = remoteInterface.getMethod(req.getMethodName(), req.getParameterTypes());
if (null != method) {
Object obj = method.invoke(RpcRegister.buildRegist().findServier(req.getInterfaceName()), req.getParameters());
res.setException(null);
res.setResult(obj);
}
buf1.clear();
buf1.put(JSONObject.toJSON(res).toString().getBytes());
buf1.flip();
socketChannel.write(buf1);
}
}
socketChannel.close();
} else if (key.isConnectable()) {
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
} else if (key.isWritable()) {
}
keyIterator.remove();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这部分源码在《JAVA NIO 编程入门(二)》的基础上增加了反射的部分内容,主要根据接口调用协议,生成客户端需要调用的方法,进行调用,然后将结果返回。
- 初始化工厂类
public class RpcInitFactory {
/**
* 客户端连接远程ip地址
**/
private String ip;
/***远程端口*/
private int port;
public RpcInitFactory(String ip, int port) {
this.ip = ip;
this.port = port;
}
}
- 通用客户端
@Data
public class CommonClient {
private RpcInitFactory factory;
public CommonClient(RpcInitFactory factory) {
this.factory = factory;
}
public T invoke(RpcRquest req) {
RpcResponse response = null;
req.setRequestId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
try {
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(factory.getIp(), factory.getPort()));
ByteBuffer buf1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(2048);
buf1.put(JSONObject.toJSON(req).toString().getBytes());
buf1.put(RpcConstant.PROTOCOL_END.getBytes());
buf1.flip();
if (buf1.hasRemaining())
socketChannel.write(buf1);
buf1.clear();
ByteBuffer body = ByteBuffer.allocate(2048);
socketChannel.read(body);
body.flip();
if (body.hasRemaining()) {
response = JSONObject.parseObject(new String(body.array()), RpcResponse.class);
}
body.clear();
socketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return (T) response;
}
- 调用客户端接口
public interface Idemo {
/***加法**/
public Integer add(Integer i,Integer j);
}
- 客户端接口实现类
public class DemoRemoteImpl implements Idemo {
private CommonClient client;
public DemoRemoteImpl(CommonClient client) {
this.client = client;
}
@Override
public Integer add(Integer i, Integer j) {
//构造rpc请求实体类
RpcRquest rpcRquest=new RpcRquest();
//设置版本号
rpcRquest.setServiceVersion("123");
//设置调用的接口名称
rpcRquest.setInterfaceName(Idemo.class.getName());
//设置调用方法名称
rpcRquest.setMethodName("add");
//设置参数
rpcRquest.setParameters(new Integer[] {i,j});
//设置参数类型
rpcRquest.setParameterTypes(new Class[] {Integer.class,Integer.class});
//进行远程调用
RpcResponse response= client.invoke(rpcRquest);
if (null!=response){
return Integer.parseInt(response.getResult().toString());
}
return null;
}
}
- 服务端接口实现类
public class DemoImp implements Idemo{
@Override
public Integer add(Integer i, Integer j) {
return i+j;
}
}
测试
- 启动服务端
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProviderServer server = new ProviderServer(8090);
RpcRegister.buildRegist().regist(Idemo.class.getName(), new DemoImp());
new Thread(server).start();
}
- 启动客户端
public static void main(String[] args) {
RpcInitFactory initFactory= new RpcInitFactory("127.0.0.1",8090);
Idemo demo = new DemoRemoteImpl(new CommonClient(initFactory));
System.out.println(demo.add(2, 1));
}
- 结果:
四、总结
到这里RPC的小demo功能实现完毕,实际上的RPC框架要比这个复杂的多,真正的RPC框架要考虑性能,高可用,半包,粘包等问题,这里只是给出了一个RPC框架的实现原理,便于理解RPC框架的实现,并不能真正用于生产环境。
推荐阅读
《Java锁之ReentrantLock(一)》
《Java锁之ReentrantLock(二)》
《Java锁之ReentrantReadWriteLock》
《JAVA NIO编程入门(一)》
《JAVA NIO 编程入门(二)》