Mybatis核心类:
SqlSessionFactory:每个基于 MyBatis 的应用都是以一个 SqlSessionFactory 的实例为中心的。SqlSessionFactory 的实例可以通过 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 获得。而 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 则可以从 XML 配置文件或通过Java的方式构建出 SqlSessionFactory 的实例。SqlSessionFactory 一旦被创建就应该在应用的运行期间一直存在,建议使用单例模式或者静态单例模式。一个SqlSessionFactory对应配置文件中的一个环境(environment),如果你要使用多个数据库就配置多个环境分别对应一个SqlSessionFactory。
SqlSession:SqlSession是一个接口,它有2个实现类,分别是DefaultSqlSession(默认使用)以及SqlSessionManager。SqlSession通过内部存放的执行器(Executor)来对数据进行CRUD。此外SqlSession不是线程安全的,因为每一次操作完数据库后都要调用close对其进行关闭,官方建议通过try-finally来保证总是关闭SqlSession。
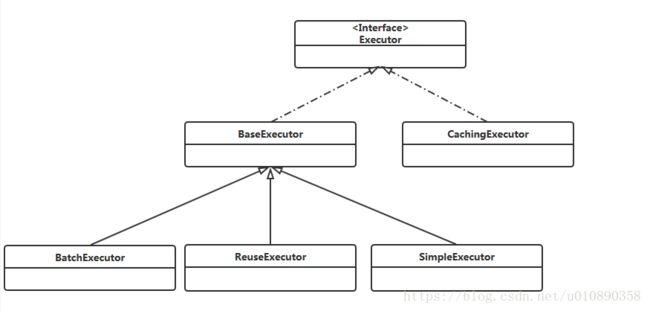
Executor:Executor(执行器)接口有两个实现类,其中BaseExecutor有三个继承类分别是BatchExecutor(重用语句并执行批量更新),ReuseExecutor(重用预处理语句prepared statements),SimpleExecutor(普通的执行器)。以上三个就是主要的Executor。通过下图可以看到Mybatis在Executor的设计上面使用了装饰者模式,我们可以用CachingExecutor来装饰前面的三个执行器目的就是用来实现缓存。
MappedStatement:MappedStatement就是用来存放我们SQL映射文件中的信息包括sql语句,输入参数,输出参数等等。一个SQL节点对应一个MappedStatement对象。
解析过程
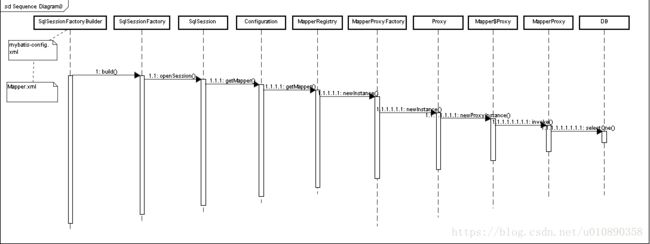
1 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build 创建DefaultSqlSessionFactory实体。
使用XMLConfigBuilder .parse()解析mybatis-config.xml, 生成Configuration对象(很重要的对象)
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
SqlSessionFactory var5;
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
var5 = this.build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception var14) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", var14);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException var13) {
}
}
return var5;
}
2 通过DefaultSqlSessionFactory.openSession创建DefaultSqlSession。
openSession->openSessionFromDataSource
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
DefaultSqlSession var8;
try {
Environment environment = this.configuration.getEnvironment();
TransactionFactory transactionFactory = this.getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
Executor executor = this.configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
var8 = new DefaultSqlSession(this.configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception var12) {
this.closeTransaction(tx);
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + var12, var12);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
return var8;
}
3 通过DefaultSqlSession拿到Mapper对象的代理MapperProxy.
mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession),生成MapperProxyFactory代理对象
public T getMapper(Class type) {
return this.configuration.getMapper(type, this);
}
public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return this.mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
MapperProxyFactory mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory)this.knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
} else {
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception var5) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + var5, var5);
}
}
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
MapperProxy mapperProxy = new MapperProxy(sqlSession, this.mapperInterface, this.methodCache);
return this.newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy mapperProxy) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{this.mapperInterface}, mapperProxy);
}
4 通过MapperProxy调用Maper中相应的方法
MapperProxy.invoke->MapperMethod.execute
先解析参数,在调sqlSession.insert执行sql.
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
}
if (this.isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return this.invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable var5) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(var5);
}
MapperMethod mapperMethod = this.cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(this.sqlSession, args);
}
// 产生MapperMethod ,这个对象很重要,是sql.xml生成的
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = (MapperMethod)this.methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(this.mapperInterface, method, this.sqlSession.getConfiguration());
this.methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
// 最终执行sql地方
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object param;
Object result;
switch(this.command.getType()) {
case INSERT:
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(this.command.getName(), param));
break;
case UPDATE:
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(this.command.getName(), param));
break;
case DELETE:
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = this.rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(this.command.getName(), param));
break;
case SELECT:
if (this.method.returnsVoid() && this.method.hasResultHandler()) {
this.executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (this.method.returnsMany()) {
result = this.executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (this.method.returnsMap()) {
result = this.executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (this.method.returnsCursor()) {
result = this.executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
param = this.method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(this.command.getName(), param);
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + this.command.getName());
}
if (result == null && this.method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !this.method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + this.command.getName() + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + this.method.getReturnType() + ").");
} else {
return result;
}
}
5 DefaultSqlSession.update执行sql
最终使用的是Executor执行sql
public int update(String statement, Object parameter) {
int var4;
try {
this.dirty = true;
MappedStatement ms = this.configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
var4 = this.executor.update(ms, this.wrapCollection(parameter));
} catch (Exception var8) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error updating database. Cause: " + var8, var8);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
return var4;
}