24点破解的Java实现
一、基本思想
要想计算24点游戏的结果,则必须要采用基于搜索的算法(即穷举法)对每种情况进行遍历,我们怎么样才能遍历所有的情况呢?其实我们只要总结一下,还是有规律可以找的。
输入a、b、c、d,组成a Op1 bOp2 c Op3 d的表达式,其中先算哪个子表达式未知,一共有5种计算方式,如下图所示:
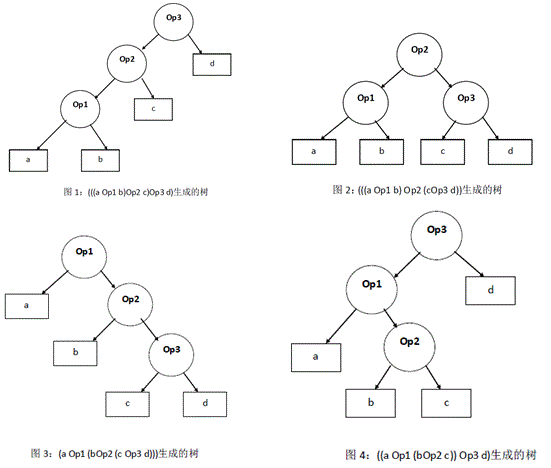
此时如果要实现该程序,需要存储5棵树,为了能够使得存储量达到最小,通过分析,其实总的来说,只需要存储2棵树即可,即:
其他树都是冗余的,因为我们可以通过a、b、c、d的交换,比如((a+(b*c))+d)可以变为(((b*c)+a)+d);
对于每棵树来说,abcd的可能性为4*3*2*1=24;op1op2 op3的可能性为4*4*4=64,因此总个数为1536,而两棵树的总个数为3072。因此只需要穷举这些方法,就可以知道结果。
TfUtils类为实现穷举24点所有可能情况的类,calculate函数用于计算,参数a、b、c、d分别为给定的4个数,而TfUtils类中的expr属性为求解的表达式。
二、代码实现
CalculatorUtils.java
package org.xiazdong;
import java.util.Stack;
public class CalculatorUtils {
/**
* 计算后缀表达式
*/
public static String calculateReversePolish(String str) {
String[] splitStr = str.split(" ");
Stack<String> s = new Stack<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < splitStr.length; i++) {
String ch = splitStr[i];
if (ch.matches("\\d+.\\d+")||ch.matches("\\d+")) {
s.push(ch);
} else {
if (s.size() >= 2) {
String c1 = s.pop();
String c2 = s.pop();
if (ch.equals("+")) {
if(c1.contains(".")||c2.contains(".")){
s.push(String.valueOf((Double.parseDouble(c2 + "") + Double
.parseDouble(c1 + ""))));
}
else{
s.push(String.valueOf((Integer.parseInt(c2 + "") + Integer
.parseInt(c1 + ""))));
}
} else if ("-".equals(ch)) {
if(c1.contains(".")||c2.contains(".")){
s.push(String.valueOf((Double.parseDouble(c2 + "") - Double
.parseDouble(c1 + ""))));
}
else{
s.push(String.valueOf((Integer.parseInt(c2 + "") - Integer
.parseInt(c1 + ""))));
}
} else if ("*".equals(ch)) {
if(c1.contains(".")||c2.contains(".")){
s.push(String.valueOf((Double.parseDouble(c2 + "") * Double
.parseDouble(c1 + ""))));
}
else{
s.push(String.valueOf((Integer.parseInt(c2 + "") * Integer
.parseInt(c1 + ""))));
}
} else if ("/".equals(ch)) {
s.push(String.valueOf((Double.parseDouble(c2 + "") / Double
.parseDouble(c1 + ""))));
}
} else {
System.out.println("式子有问题!");
return null;
}
}
}
return s.pop();
}
}
TfUtils.java
package org.xiazdong;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class TfUtils implements Serializable{
private int result;
private String expr = ""; //存放中缀表达式
public String getExpr() {
return expr;
}
public void setExpr(String expr) {
this.expr = expr;
}
/*
(操作符1)
/ \
(操作符2) (操作数4)
/ \
(操作符3) (操作数3)
/ \
(操作数1) (操作数2)
*/
private int tree1[] = new int[7];; // 存放第一棵树
//private int tree2[]; // 存放第二棵树
private final int PLUS = 1; // 加
private final int MINUS = 2; // 减
private final int MULT = 3; // 乘
private final int DIV = 4; // 除
/**
* 计算24点的主函数
*/
public void calculate(int a, int b, int c, int d) {
int data[] = { a, b, c, d };
// 1.用数组构建一棵树,其中0,1,3处填操作符;2,4,5,6填充操作数
// 2.按照参数a,b,c,d不同顺序填充树,+-*/也填充
for (int h = 0; h < 4; h++) {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if (i == h) {
continue;
}
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
if (j == i || j == h) {
continue;
}
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
if (k == h || k == i || k == j) {
continue;
}
tree1[2] = data[h];
tree1[4] = data[i];
tree1[5] = data[j];
tree1[6] = data[k];
// 填充操作符
for (int m = PLUS; m <= DIV; m++) {
for (int n = PLUS; n <= DIV; n++) {
for (int o = PLUS; o <= DIV; o++) {
tree1[0] = m;
tree1[1] = n;
tree1[3] = o;
String t[] = new String[4];
for (int z = 0; z < 4; z++) {
switch (tree1[z]) {
case PLUS:
t[z] = "+";
break;
case MINUS:
t[z] = "-";
break;
case MULT:
t[z] = "*";
break;
case DIV:
t[z] = "/";
break;
}
}
// 目前为止tree数组全部已赋值
String postexpr = tree1[5] + " " + tree1[6]
+ " " + t[3] + " " + tree1[4] + " "
+ t[1] + " " + tree1[2] + " " + t[0];
String result = CalculatorUtils
.calculateReversePolish(postexpr);
if (Double.parseDouble((result)) == 24.0) {
expr = "(((" + tree1[5] + t[3] + tree1[6]
+ ")" + t[1] + tree1[4] + ")"
+ t[0] + tree1[2] + ")";
System.out.println(expr);
return;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
//tree2 = new int[7];
for (int h = 0; h < 4; h++) {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
if (i == h) {
continue;
}
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
if (j == i || j == h) {
continue;
}
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
if (k == h || k == i || k == j) {
continue;
}
tree1[3] = data[h];
tree1[4] = data[i];
tree1[5] = data[j];
tree1[6] = data[k];
// 填充操作符
for (int m = PLUS; m <= DIV; m++) {
for (int n = PLUS; n <= DIV; n++) {
for (int o = PLUS; o <= DIV; o++) {
tree1[0] = m;
tree1[1] = n;
tree1[2] = o;
String t[] = new String[3];
for (int z = 0; z < 3; z++) {
switch (tree1[z]) {
case PLUS:
t[z] = "+";
break;
case MINUS:
t[z] = "-";
break;
case MULT:
t[z] = "*";
break;
case DIV:
t[z] = "/";
break;
}
}
// 目前为止tree数组全部已赋值
String postexpr = tree1[4] + " " + tree1[3]
+ " " + t[1] + " " + tree1[6] + " "
+ tree1[5] + " " + t[2] + " " + t[0];
String result = CalculatorUtils
.calculateReversePolish(postexpr);
if (Double.parseDouble((result)) == 24.0) {
expr = "((" + tree1[3] + t[1] + tree1[4]
+ ")" + t[0] +"("+tree1[5]
+ t[2] + tree1[6] + "))";
System.out.println(expr);
return;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
expr = "无解";
}
public int getResult() {
return result;
}
public void setResult(int result) {
this.result = result;
}
}
测试代码:
TfUtils tf = new TfUtils(); tf.calculate(d1, d2, d3, d4); System.out.println(tf.getExpr());
输入为:3,3,7,7
输出为:(((3/7)+3)*7)