在上一篇《Zygote启动流程》中已经了解到,ZygoteInit.java的main函数中会去创建ServerSocket,创建应用进程时,AMS会连接ServerSocket发起创建进程的请求。因此AMS是Socket Client端,Zygote是Socket Server端,创建进程时,Client连接Server端发起创建进程的请求。
一、Client端(AMS)
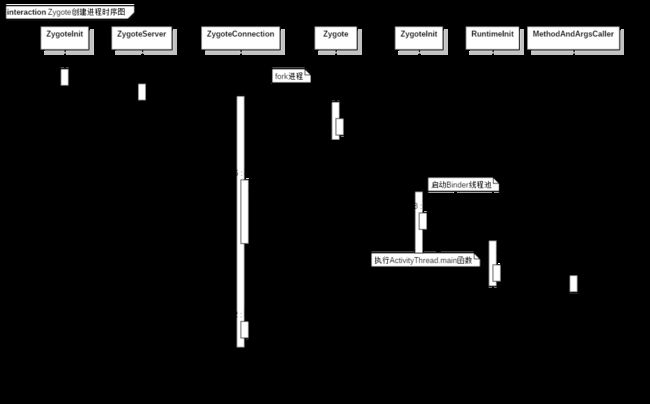
首先来了解下AMS发起创建进程请求的流程,以下是流程时序图。
在调用AMS的
startProcessLocked函数来向Zygote发起fork进程的求情,在AMS中
startProcessLocked函数最终会调用
startProcess函数,首先看下
startProcess函数。
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
private ProcessStartResult startProcess(String hostingType, String entryPoint,
ProcessRecord app, int uid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags, int mountExternal,
String seInfo, String requiredAbi, String instructionSet, String invokeWith,
long startTime) {
try {
......
final ProcessStartResult startResult;
if (hostingType.equals("webview_service")) {
......
} else {
startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, runtimeFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, invokeWith,
new String[] {PROC_START_SEQ_IDENT + app.startSeq});
}
......
} finally {
......
}
}
startProcess函数接着会调用Process的start函数来发起fork进程请求,接下来研究下Process的start函数。
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Process.java
public static final ProcessStartResult start(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
int uid, int gid, int[] gids,
int runtimeFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String abi,
String instructionSet,
String appDataDir,
String invokeWith,
String[] zygoteArgs) {
return zygoteProcess.start(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
runtimeFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,
abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, invokeWith, zygoteArgs);
}
Process的start函数又跳转到ZygoteProcess.start函数。
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ZygoteProcess.java
public final Process.ProcessStartResult start(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
int uid, int gid, int[] gids,
int runtimeFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String abi,
String instructionSet,
String appDataDir,
String invokeWith,
String[] zygoteArgs) {
try {
return startViaZygote(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
runtimeFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,
abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, invokeWith, false /* startChildZygote */,
zygoteArgs);
} catch (ZygoteStartFailedEx ex) {
......
}
}
继续跳转到startViaZygote函数
private Process.ProcessStartResult startViaZygote(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
final int uid, final int gid,
final int[] gids,
int runtimeFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String abi,
String instructionSet,
String appDataDir,
String invokeWith,
boolean startChildZygote,
String[] extraArgs)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
ArrayList argsForZygote = new ArrayList();
.....
//初始化进程的启动参数列表argsForZygote逻辑
synchronized(mLock) {
return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi), argsForZygote);
}
}
接下来先看下openZygoteSocketIfNeeded函数,该函数主要是调用ZygoteState.connect函数连接ZygoteInit.main函数中创建的ServerSocket,这个在《Zygote启动流程》中已经说过,ZygoteState就是ZygoteProcess的一个静态内部类,主要是维持Zygote进程socket服务的连接逻辑,ZygoteState.connet函数也是连接socket。
private ZygoteState openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(String abi) throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
Preconditions.checkState(Thread.holdsLock(mLock), "ZygoteProcess lock not held");
if (primaryZygoteState == null || primaryZygoteState.isClosed()) {
try {
primaryZygoteState = ZygoteState.connect(mSocket);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Error connecting to primary zygote", ioe);
}
maybeSetApiBlacklistExemptions(primaryZygoteState, false);
maybeSetHiddenApiAccessLogSampleRate(primaryZygoteState);
}
if (primaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) {
return primaryZygoteState;
}
// The primary zygote didn't match. Try the secondary.
if (secondaryZygoteState == null || secondaryZygoteState.isClosed()) {
try {
secondaryZygoteState = ZygoteState.connect(mSecondarySocket);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Error connecting to secondary zygote", ioe);
}
maybeSetApiBlacklistExemptions(secondaryZygoteState, false);
maybeSetHiddenApiAccessLogSampleRate(secondaryZygoteState);
}
if (secondaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) {
return secondaryZygoteState;
}
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Unsupported zygote ABI: " + abi);
}
再看下zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult函数。
private static Process.ProcessStartResult zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(
ZygoteState zygoteState, ArrayList args)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
try {
......
//将要创建的应用进程启动参数传给ZygoteState对象中
final BufferedWriter writer = zygoteState.writer;
final DataInputStream inputStream = zygoteState.inputStream;
writer.write(Integer.toString(args.size()));
writer.newLine();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
String arg = args.get(i);
writer.write(arg);
writer.newLine();
}
writer.flush();
Process.ProcessStartResult result = new Process.ProcessStartResult();
//通过Socket读取Zygote建成功的进程PID
// Socket 对端的请求在 ZygoteInit.runSelectLoop中进行处理
result.pid = inputStream.readInt();
result.usingWrapper = inputStream.readBoolean();
if (result.pid < 0) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("fork() failed");
}
return result;
} catch (IOException ex) {
zygoteState.close();
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx(ex);
}
}
二、Server端(Zygote)
AMS发起创建进程请求,Zygote端接受请求的流程。《Zygote启动流程》中已经分析了ZygoteInit.main函数会创建ServerSocket,且在ZygoteServer.java.runSelectLoop等待AMS连接和发起请求。
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
public static void main(String argv[]) {
......
try {
......
//创建Server Socket
zygoteServer.registerServerSocketFromEnv(socketName);
......
//等待AMS socket连接,请求fork新进程
caller = zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
}
......
}
ZygoteInit.main函数中会调用zygoteServer.registerServerSocketFromEnv创建一个LocalServerSocket对象,该对象封装了ServerSocket逻辑。 zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList)函数会调用LocalServerSocket.accept函数和ZygoteConnection.processOneCommand函数,accept函数等待客户端的连接,processOneCommand函数处理fork进程逻辑,这个在《Zygote启动流程》已经了解过。
ZygoteConnection.processOneCommand函数主要执行这三个操作:
- 1.调用 Zygote.forkAndSpecialize 进行进程复制操作
- 2.调用 handleChildProc 处理新建进程资源初始化,如创建 Binder 线程池,启动一个主线程消息队列
- 3.调用 handleParentProc 将新建进程的 PID 返回给 system_server,表示创建结果。
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteConnection.java
Runnable processOneCommand(ZygoteServer zygoteServer) {
......
//fork 进程,
//pid == 0:新进程,调用handleChildProc
//pid != 0:当前进程,调用handleParentProc
pid = Zygote.forkAndSpecialize(parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid, parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.runtimeFlags, rlimits, parsedArgs.mountExternal, parsedArgs.seInfo,
parsedArgs.niceName, fdsToClose, fdsToIgnore, parsedArgs.startChildZygote,
parsedArgs.instructionSet, parsedArgs.appDataDir);
try {
if (pid == 0) {
// in child
// 创建出的新进程
zygoteServer.setForkChild();
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();//关闭socket
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
serverPipeFd = null;
return handleChildProc(parsedArgs, descriptors, childPipeFd,
parsedArgs.startChildZygote);
} else {
// In the parent. A pid < 0 indicates a failure and will be handled in
// handleParentProc.
// 父进程将在这里进行处理
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
childPipeFd = null;
handleParentProc(pid, descriptors, serverPipeFd);
return null;
}
} finally {
......
}
}
Zygote.forkAndSpecialize函数>Zygote.forkAndSpecialize>Zygote.nativeForkAndSpecialize来fork进程。
public static int forkAndSpecialize(int uid, int gid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags,
int[][] rlimits, int mountExternal, String seInfo, String niceName, int[] fdsToClose,
int[] fdsToIgnore, boolean startChildZygote, String instructionSet, String appDataDir) {
VM_HOOKS.preFork();
// Resets nice priority for zygote process.
resetNicePriority();
int pid = nativeForkAndSpecialize(
uid, gid, gids, runtimeFlags, rlimits, mountExternal, seInfo, niceName, fdsToClose,
fdsToIgnore, startChildZygote, instructionSet, appDataDir);
......
}
fork进程返回pid == 0则是新进程,会调用zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();关闭socket,还会调用handleChildProc函数执行ZygoteInit.zygoteInit()。
private Runnable handleChildProc(Arguments parsedArgs, FileDescriptor[] descriptors,
FileDescriptor pipeFd, boolean isZygote) {
closeSocket();
......
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
......
} else {
if (!isZygote) {// 新建应用进程时isZygote=false
return ZygoteInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion, parsedArgs.remainingArgs,
null /* classLoader */);
} else {
return ZygoteInit.childZygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
parsedArgs.remainingArgs, null /* classLoader */);
}
}
}
ZygoteInit.zygoteInit()主要逻辑:
- 1.nativeZygoteInit启动App进程的Binder线程池
- 2.applicationInit反射执行
ActivityThread.main函数
public static final Runnable zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) {
......
ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit();//初始化Binder线程
return RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
}
RuntimeInit.applicationInit>RuntimeInit.findStaticMain>RuntimeInit.MethodAndArgsCaller 就是利用反射调用main函数。
protected static Runnable applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv,
ClassLoader classLoader) {
......
return findStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader);
}
protected static Runnable findStaticMain(String className, String[] argv,
ClassLoader classLoader) {
Class cl;
try {
cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing class when invoking static main " + className,
ex);
}
Method m;
try {
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing static main on " + className, ex);
} catch (SecurityException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Problem getting static main on " + className, ex);
}
int modifiers = m.getModifiers();
if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Main method is not public and static on " + className);
}
/*
* This throw gets caught in ZygoteInit.main(), which responds
* by invoking the exception's run() method. This arrangement
* clears up all the stack frames that were required in setting
* up the process.
*/
return new MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
}
static class MethodAndArgsCaller implements Runnable {
......
public void run() {
try {
mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { mArgs });
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
......
}
}
}
我们来验证下,可以在Activity.onCreate函数中执行Log.d(TAG, Log.getStackTraceString(new Throwable()));函数打印堆栈。
堆栈顺序:
ZygoteInit.main>ZygoteInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run>Method.invoke>ActivityThread.main
该堆栈跟分析的流程一致。代码如下:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final String TAG = "[lynnlee]";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Log.d(TAG, Log.getStackTraceString(new Throwable()));
}
}
ActivityOncreate函数打印堆栈结果:
com.lynnlee.myapplication D/[lynnlee]: java.lang.Throwable
at com.lynnlee.myapplication.MainActivity.onCreate(MainActivity.java:19)
at android.app.Activity.performCreate(Activity.java:6309)
at android.app.Instrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(Instrumentation.java:1114)
at android.app.ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2467)
at android.app.ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2574)
at android.app.ActivityThread.access$1000(ActivityThread.java:166)
at android.app.ActivityThread$H.handleMessage(ActivityThread.java:1411)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:102)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:148)
at android.app.ActivityThread.main(ActivityThread.java:5563)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Native Method)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(ZygoteInit.java:853)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:737)
参考资料
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_34335458/article/details/87992608
《Android进阶解密》