前言
关于计算机视觉的学习教程暂时告于段落,预计八月中旬以后我将会更新关于CV项目开发的学习笔记以及相关教程。现在的粉丝数已经过百了,感谢家人朋友给我的支持,以及机器学习爱好者们对我的肯定,我将会继续坚持我学习路线,分享给大家。接下来这节内容,选材来自昨天学习交流群中一位朋友,提出了有关激活函数的问题。我在收集了一下相关内容,在此整理集合对比激活函数的缺点和不足。
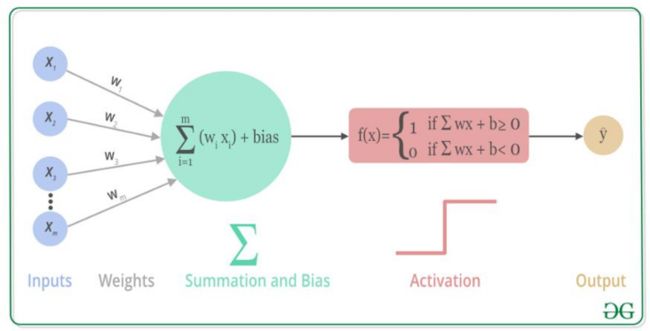
什么是激活函数
文章主要从激活函数概念,数学形式分析,Python代码形式展现,优缺点对比等方面进行学习。关于激活函数的定义 维基百科解释是:节点的激活函数定义了给定一个输入或一组输入的节点的输出。标准集成电路可以被视为激活函数的数字网络,根据输入可以是“ON”(1)或“OFF”(0)。此定义与逻辑回归的定义相似。
换句话说,激活函数是一种添加到神经网络中的函数,旨在帮助网络学习数据中的复杂模式。类似于人类大脑中基于神经元的模型,激活函数最终决定了要传送给下一个神经元的内容。在人工神经网络中,一个节点的激活函数定义了该节点在给定的输入或输入集合下的输出。激活函数就是确定神经网络输出的数学方程。

当神经元接收到了其他神经元或外界传来的数字信号,神经元通过权重和偏置对输入信息进行线性变换,由于线性方程很简单解决复杂问题的能力有限,因此加入激活函数对输入进行非线性变换使其能够学习和执行更复杂的任务。此时激活函数的意义尤为重要,合适的激活函数也十分重要。
激活函数种类
常见的激活函数可以分为三类:岭函数,径向函数,以及应用在卷积神经网络中的折叠激活函数。
岭函数:作用与输入变量的线性组合多元函数
线性函数:
$$ {\displaystyle \phi (\mathbf {v} )=a+\mathbf {v} '\mathbf {b} } $$
ReLU函数:
$$ {\displaystyle \phi (\mathbf {v} )=\max(0,a+\mathbf {v} '\mathbf {b} )}{\displaystyle \phi (\mathbf {v} )=\max(0,a+\mathbf {v} '\mathbf {b} )} $$
Heaviside函数:
$$ {\displaystyle \phi (\mathbf {v} )=1_{a+\mathbf {v} '\mathbf {b} >0}}{\displaystyle \phi (\mathbf {v} )=1_{a+\mathbf {v} '\mathbf {b} >0}} $$
- Logistic函数:
$$ {\displaystyle \phi (\mathbf {v} )=(1+\exp(-a-\mathbf {v} '\mathbf {b} ))^{-1}}{\displaystyle \phi (\mathbf {v} )=(1+\exp(-a-\mathbf {v} '\mathbf {b} ))^{-1}} $$
径向激活函数:在欧几里得空间中求得点与点之间距离,作为通用的函数逼近器具有很好的效果。
高斯函数:
$$ {\displaystyle f(x)=a\cdot \exp \left(-{\frac {(v-c)^{2}}{2c^{2}}}\right)} $$
多项式函数:
$$ {\displaystyle \,\phi (\mathbf {v} )={\sqrt {\|\mathbf {v} -\mathbf {c} \|^{2}+a^{2}}}} $$
注意:c为函数中心的向量和,a为影响半径传播的参数
- 折叠激活函数:广泛使用池层在卷积神经网络中和多分类网络的输出层中。激活函数使用取均值,最小值或最大值。在多分类中,经常使用software激活
激活函数数学特性
每个激活函数都有着其特性,根据特性它可能适用在某一种模型中能够展现更好的效果。除了数学结构,激活函数还具有不同的数学特性:
- 非线性:当激活函数为非线性,那么可以证明两层神经网络是一个通用函数逼近器。换句话说神经网络是由很多层神经元组成的,使用非线性激活函数可以把整个网络看作一个单层模型。使得神经网络可以任意逼近任何非线性函数,这个特性使神经网络应用到众多非线性模型中。
- 范围:激活函数的输出值的范围可以是有限的也可以是无限的。当输出值是有限的时候,基于梯度的优化方法会更加稳定,因为特征的表示受有限权值的影响更加显著;当输出值无限时,模型的训练会更加高效。注意在这种情况,一般需要更小的学习率。
- 连续可微:这个特性并不是必须的(ReLu部分点不可微影响不大)这个特性保证了优化中梯度的可计算性。
- 非饱和性:饱和指的是某些区间梯度接近0(梯度消失),使得参数无法继续更新。Sigmoid它的导数在接近正无穷和负无穷时都会接近0。跃阶函数几乎所有位置梯度都为0,无法作为激活函数。因此有一些学者提出了一些改进激活函数解决这类问题
- 单调性:即导数符号不变,大部分激活函数都具有该特点。换句话说就是单调性使得激活函数的梯度方向不会经常改变,使训练更容易收敛,效果更佳。
- 接近恒等变换:这个特性使得网络更加稳定,存在于少量激活函数中在Tanh中只有原点附近导数为1,ReLu只在x>0时为线性。这一结构设计与CNN中的ReNet和RNN中的LSTM
- 参数少:参数少可以减少网络的大小
- 归一化:主要思想是使样本分布自动归一化到零均值,单位方差的分布,从而稳定训练。
这些数学特性不会决定性的影响模型效果,也不存在唯一有用属性,通过这些属性可以方便我们在构建模型时选出合适的激活函数。
激活函数比较
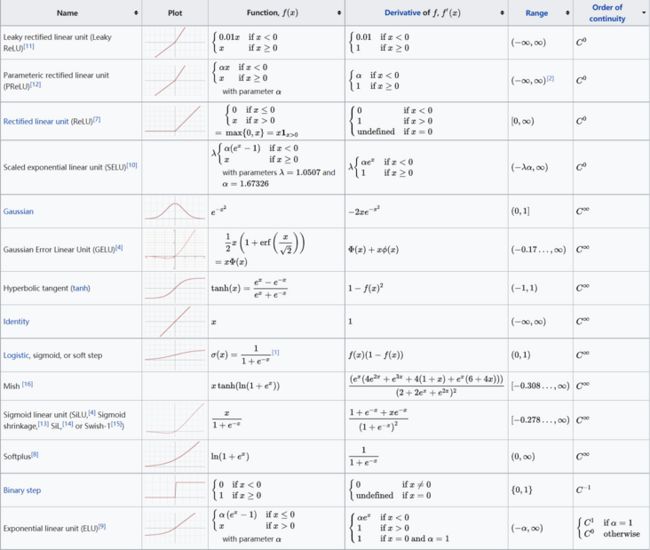
接下来到了最关键的部分,激活函数的对比,我们以及掌握了激活函数的种类以及特性,那么都有哪些常用的激活函数,以及他们的特性都有哪些呢。如下所示为多种常见激活函数的收集整理,里面包含内容有函数曲线,数学结构,范围,可导区间,以及连续性。
常见激活函数全收集!
以及折叠函数的:
如何选取恰当的激活函数
通过了解这些函数的,以及特性分析,我们可以总结一下如何选择正确的激活函数;根据问题的性质,我们可以为构建模型作出更佳选择。结合一些文章提供的经验之说选取规则如下所示(仅供参考)
- 首先考虑常见的激活函数:Sigmoid,TanH,ReLU,Leaky ReLU,ELU,SoftPlus,Binary step,Maxout,以及Mish
- 用于分类器时,Sigmoid函数及其组合通常效果更好
- 关于避免梯度消失问题,需要避免使用Sigmoid,TanH
- 首先考虑ReLU,速度最快,观察模型的表现,如果效果不好可以尝试Leaky ReLU,Maxout
- ReLU只能在隐藏层中使用
- 当层数不多时的CNN中,激活函数影响不大。
代码实现
搞定了理论基础,接下来就该实战准备造轮子环节了,建议收藏这些代码部分以备不时之需。
Sigmoid代码实现:适用于二分类,多分类,效果一般,注意梯度消失问题
import numpy as np
def sigmoid(x):
s = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
return s
# Tensorflow2.0版
sigmoid_fc = tf.keras.activations.sigmoid(x)
# pytorch版
sigmoid_fc = torch.nn.Sigmoid()
output = sigmoid_fc(x)TanH代码实现:注意梯度消失问题
import numpy as np
def tanh(x):
s1 = np.exp(x) - np.exp(-x)
s2 = np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x)
s = s1 / s2
return s
# Tensorflow2.0版
tanh_fc = tf.keras.activations.tanh(x)
# pytorch版
tanh_fc = torch.nn.Tanh()
output = tanh_fc(x)ReLU代码实现:最常用,只用于隐藏层
import numpy as np
def relu(x):
s = np.where(x < 0, 0, x)
return s
# Tensorflow2.0版
relu_fc = tf.keras.activations.relu(x)
# pytorch版
relu_fc = torch.nn.Relu()
output = relu_fc(x)Leaky ReLU代码实现:应用于 当构建网络中存在大量未激活神经元时
import numpy as np
def lrelu(x):
s = np.where(x >= 0, x, αx)
return s
# Tensorflow2.0版
lrelu_fc = tf.keras.activations.relu(x,alpha=0.01) # 需要指定alpha的大小
# pytorch版
lrelu_fc = torch.nn.LeakyReLU(0.01)
output = lrelu_fc(x)ELU代码实现
import numpy as np
def elu(x):
s = np.where(x >= 0, x, α(np.exp(x)-1)
return s
# Tensorflow2.0版
elu_fc = tf.keras.activations.elu(x,alpha=0.1) # 需要指定alpha的大小
# pytorch版
elu_fc = torch.nn.ELU(0.1)
output = elu_fc(x)Softmax代码实现
def softmax(x):
x_exp = np.exp(x)
x_sum = np.sum(x_exp, axis=1, keepdims=True)
s = x_exp / x_sum
return s
# Tensorflow2.0版
softmax_fc = tf.keras.activations.softmax(x)
# pytorch版
softmax_fc = torch.nn.Softmax()
output = softmax_fc(x)Binary step代码实现
def binaryStep(x):
''' It returns '0' is the input is less then zero otherwise it returns one '''
return np.heaviside(x,1)
x = np.linspace(-10, 10)
plt.plot(x, binaryStep(x))
plt.axis('tight')
plt.title('Activation Function :binaryStep')
plt.show()Maxout代码实现:比赛中使用
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.random_normal([5,3])
m = 4
k = 3
d = 3
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[d, m, k])) # 3*4*3
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape = [m, k])) # 4*3
dot_z = tf.tensordot(x, W, axes=1) + b # 5 * 4 * 3
print(dot_z)
z = tf.reduce_max(dot_z, axis=2) # 5 * 4
print(z)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
print(sess.run([x,dot_z,z]))Mish代码实现:较新的激活函数,表现优于ReLU和Swish,TanH和Softplus组合
原理如下:有兴趣的可以看一看
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
from keras.engine.base_layer import Layer
from keras.layers import Activation, Dense
from keras import backend as K
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.optimizers import SGD
from keras.utils import np_utils
from __future__ import print_function
import keras
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers.core import Flatten
from keras.layers import Dropout
from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D
from keras.layers.normalization import BatchNormalization
import numpy as np
class Mish(Layer):
'''
Mish Activation Function.
.. math::
mish(x) = x * tanh(softplus(x)) = x * tanh(ln(1 + e^{x}))
Shape:
- Input: Arbitrary. Use the keyword argument `input_shape`
(tuple of integers, does not include the samples axis)
when using this layer as the first layer in a model.
- Output: Same shape as the input.
Examples:
>>> X_input = Input(input_shape)
>>> X = Mish()(X_input)
'''
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(Mish, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.supports_masking = True
def call(self, inputs):
return inputs * K.tanh(K.softplus(inputs))
def get_config(self):
base_config = super(Mish, self).get_config()
return dict(list(base_config.items()) + list(config.items()))
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
return input_shape
def mish(x):
return keras.layers.Lambda(lambda x: x*K.tanh(K.softplus(x)))(x)
###### Use in your model ##########
model.add(Dense(128,activation= mish))作弊代码:小样本
def tanh(x):
return (np.exp(x) - np.exp(-x))/(np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x))
def softplus(x):
return np.log(1 + np.exp(x))
def misc(x):
return x * tanh(softplus(x))结语
经过盘点总结激活函数的意义,种类,数学特性,以及使用范围等方面,我们可以很好的认识了激活函数,并且在构建模型时如何选择使用。我在学习交流群看到了有人问过这个问题,我在网上浏览很多文章,觉得这是一个值得总结,学习的问题。并且通过深入了解原理意义,理解为什么选非常重要。不能只做代码的搬运工,应该有自己的思考见解,追求境界高了,我们眼界高了,才能有更多的发展空间。不过这次文章的描写使用了很多公式展示,让我的Latex编写能力有了大大的提高,我发现使用才有价值才能更快的成长。。。。
欢迎小伙伴们交流学习!
参考文献:
1.Activation function https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki...
2.非线性激活函数 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/...
3.常见流行激活函数 https://cloud.tencent.com/dev...
4.Mish As Neural Networks Activation Function https://sefiks.com/2019/10/28...
5.Understand Maxout Activation Function in Deep Learning – Deep Learning Tutorial https://www.tutorialexample.c...
推荐阅读
![]()