一. 简介
俩个数据库db1,db2, db1数据库的mapper.xml和db2数据库的mapper.xml分别放到不同的目录下, 通过给不同的目录配置不同的数据源,并分别监控各自的事务。
已有新版方案: Mybatis Plus整合多数据源和读写分离,请使用新版;
二. sql脚本
db1数据库的user表:
CREATE TABLE `user` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL, `name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
db2数据库的role表:
CREATE TABLE `role` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL, `name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
三. 工程搭建
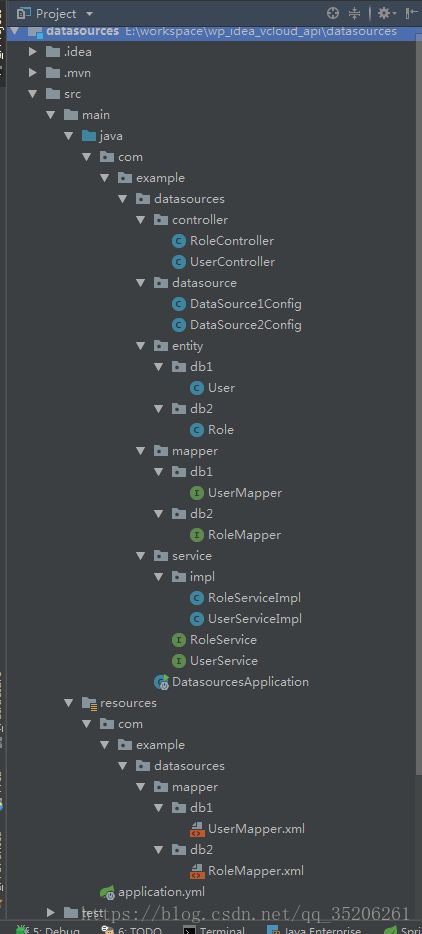
3.1 目录结构图
3.2 pom.xml文件
4.0.0 com.example datasources 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT jar datasources Demo project for Spring Boot org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-parent 2.0.4.RELEASE UTF-8 UTF-8 1.8 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-web org.mybatis.spring.boot mybatis-spring-boot-starter 1.3.2 mysql mysql-connector-java runtime org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-test test org.apache.commons commons-lang3 3.4 com.fasterxml.jackson.core jackson-core com.fasterxml.jackson.core jackson-databind com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype jackson-datatype-joda com.fasterxml.jackson.module jackson-module-parameter-names org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-aop com.github.pagehelper pagehelper-spring-boot-starter 1.2.5 com.alibaba druid-spring-boot-starter 1.1.9 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-jdbc org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-jta-atomikos io.springfox springfox-swagger2 2.6.1 io.springfox springfox-swagger-ui 2.6.1 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-maven-plugin
3.3 application.yml
server:
port: 8080
spring:
datasource:
db1:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
username: 用户名
password: 密码
# spring2.0此处为jdbc-url
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://IP:3306/db1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&allowMultiQueries=true
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
db2:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
username: 用户名
password: 密码
# spring2.0此处为jdbc-url
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://IP:3306/db2?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&allowMultiQueries=true
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
3.4 数据源配置类
3.4.1 db1数据库的数据源 (主数据源@Primary)
package com.example.datasources.datasource;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.example.datasources.mapper.db1", sqlSessionTemplateRef = "db1SqlSessionTemplate")
public class DataSource1Config {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.db1")
@Primary
public DataSource db1DataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
@Primary
public SqlSessionFactory db1SqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("db1DataSource") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
bean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath*:com/example/datasources/mapper/db1/*.xml"));
return bean.getObject();
}
@Bean
@Primary
public DataSourceTransactionManager db1TransactionManager(@Qualifier("db1DataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
@Bean
@Primary
public SqlSessionTemplate db1SqlSessionTemplate(@Qualifier("db1SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) throws Exception {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
3.4.2 db2数据库的数据源
package com.example.datasources.datasource;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.example.datasources.mapper.db2", sqlSessionTemplateRef = "db2SqlSessionTemplate")
public class DataSource2Config {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.db2")
public DataSource db2DataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactory db2SqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("db2DataSource") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
bean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath*:com/example/datasources/mapper/db2/*.xml"));
return bean.getObject();
}
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager db2TransactionManager(@Qualifier("db2DataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionTemplate db2SqlSessionTemplate(@Qualifier("db2SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) throws Exception {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
3.5 Controller
3.5.1 db1的UserController
package com.example.datasources.controller;
import com.example.datasources.entity.db1.User;
import com.example.datasources.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/select/list")
public List selectUserList() {
return this.userService.selectUserList();
}
@GetMapping("/save")
public void saveUser(User user) {
this.userService.saveUser(user);
}
}
3.5.2 db2的RoleController
package com.example.datasources.controller;
import com.example.datasources.entity.db2.Role;
import com.example.datasources.service.RoleService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/role")
public class RoleController {
@Autowired
private RoleService roleService;
@GetMapping("/select/list")
public List selectRoleList() {
return this.roleService.selectRoleList();
}
@GetMapping("/save")
public void saveRole(Role role) {
this.roleService.saveRole(role);
}
}
3.6 Service
3.6.1 db1的UserService
package com.example.datasources.service;
import com.example.datasources.entity.db1.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserService {
List selectUserList();
void saveUser(User user);
}
3.6.2 db2的RoleService
package com.example.datasources.service;
import com.example.datasources.entity.db2.Role;
import java.util.List;
public interface RoleService {
List selectRoleList();
void saveRole(Role role);
}
3.7 serviceImpl
3.7.1 db1的UserServiceImpl
package com.example.datasources.service.impl;
import com.example.datasources.entity.db1.User;
import com.example.datasources.mapper.db1.UserMapper;
import com.example.datasources.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public List selectUserList() {
return this.userMapper.selectUserList();
}
@Transactional
@Override
public void saveUser(User user) {
this.userMapper.saveUser(user);
// throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
3.7.2 db2的RoleServiceImpl
package com.example.datasources.service.impl;
import com.example.datasources.entity.db2.Role;
import com.example.datasources.mapper.db2.RoleMapper;
import com.example.datasources.service.RoleService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class RoleServiceImpl implements RoleService {
@Autowired
private RoleMapper roleMapper;
@Override
public List selectRoleList() {
return this.roleMapper.selectRoleList();
}
// 注:不是主数据源必须要声明其数据源,否则事务不起作用
@Transactional(value = "db2TransactionManager")
@Override
public void saveRole(Role role) {
this.roleMapper.saveRole(role);
// throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
3.8 mapper
3.8.1 db1的UserMapper
package com.example.datasources.mapper.db1;
import com.example.datasources.entity.db1.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserMapper {
List selectUserList();
void saveUser(User user);
}
3.8.2 db2的RoleMapper
package com.example.datasources.mapper.db2;
import com.example.datasources.entity.db2.Role;
import java.util.List;
public interface RoleMapper {
List selectRoleList();
void saveRole(Role role);
}
3.9 mapper.xml
3.9.1 db1的UserMapper.xml
id, `name` INSERT INTO `user` (id, `name`) VALUES ( #{id}, #{name} )
3.9.2 db2的RoleMapper.xml
id, name INSERT INTO `role` (id, `name`) VALUES ( #{id}, #{name} )
3.10 entity
3.10.1 db1的User
package com.example.datasources.entity.db1;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public User() {
}
public User(Integer id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
3.10.2 db2的Role
package com.example.datasources.entity.db2;
public class Role {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Role() {
}
public Role(Integer id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
3.11 启动类
package com.example.datasources;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DatasourcesApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DatasourcesApplication.class, args);
}
}
四. 测试
可以直接在浏览器测试,测试事务的时候可以将异常打开。
需要注意的是: 非主数据源必须要在@Transactional注解中指定数据源,否则事务不起作用。主数据库不需要。
到此这篇关于springboot + mybatis + druid + 多数据源的问题详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springboot druid多数据源内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!