sphereface_pytorch
学习记录
matlab_cp2tform.py
Introduction:
numpy implemetation form matlab function CP2TFORM(…) with ‘transformtype’:
1) ‘nonreflective similarity’
2) ‘similarity’
Function findNonreflectiveSimilarity
function [trans, output] = findNonreflectiveSimilarity(uv,xy,options)
根据U和X解出sc,ss,tx,ty,将变换结构T赋予结构变量trans, 其中maketformd的相关信息见matlab中的图像几何操作.
For a nonreflective similarity:
% let sc = s*cos(theta)
% let ss = s*sin(theta)
%
% [ sc -ss
% [u v] = [x y 1] * ss sc
% tx ty]
%
% There are 4 unknowns: sc,ss,tx,ty.
% Or rewriting the above matrix equation:
% U = X * r, where r = [sc ss tx ty]’
% so r = X\U.
Function findSimilarity
function [trans, output] = findSimilarity(uv,xy,options)
% The similarities are a superset of the nonreflective similarities as they may
% also include reflection.% Algorithm:
% 1) Solve for trans1, a nonreflective similarity.
% 2) Reflect the xy data across the Y-axis,
% and solve for trans2r, also a nonreflective similarity.
% 3) Transform trans2r to trans2, undoing the reflection done in step 2.
% 4) Use TFORMFWD to transform uv using both trans1 and trans2,
% and compare the results, Returnsing the transformation corresponding
% to the smaller L2 norm.
% Need to reset options.K to prepare for calls to findNonreflectiveSimilarity.
% This is safe because we already checked that there are enough point pairs.
options.K = 2;
这里不懂,还得继续Python入门
class MatlabCp2tormException(Exception):
def _ _ str _ _(self):
return ‘In File {}:{}’.format(
_ _ file _ , super. _ str _ _(self))
- hstack()函数:
函数原型:hstack(tup) ,参数tup可以是元组,列表,或者numpy数组,返回结果为numpy的数组。
它其实就是水平(按列顺序)把数组给堆叠起来,vstack()函数正好和它相反。 - vstack()函数
函数原型:vstack(tup) ,参数tup可以是元组,列表,或者numpy数组,返回结果为numpy的数组。
它是垂直(按照行顺序)的把数组给堆叠起来。
具体含义见博客 Numpy中stack(),hstack(),vstack()函数详解 :
np.linalg
顾名思义,linalg=linear+algebra
np.linalg.inv():矩阵求逆
np.linalg.norm : 范数
numpy.linalg.lstsq : lstsq 是 LeaST SQuare (最小二乘)的意思 , 它就是用最小二乘法拟合数据得到一个形如y = mx + c的线性方程(参考文档字符串里的原话:Return the least-squares solution to a linear matrix equation)
linalg.matrix_rank :NumPy的主要对象是同种元素的多维数组。这是一个所有的元素都是一种类型、通过一个正整数元组索引的元素表格(通常是元素是数字)。在NumPy中维度(dimensions)叫做轴(axes),轴的个数叫做秩(rank,但是和线性代数中的秩不是一样的,在用python求线代中的秩中,我们用numpy包中的linalg.matrix_rank方法计算矩阵的秩
- numpy中数组和矩阵的区别:
matrix是array的分支,matrix和array在很多时候都是通用的,你用哪一个都一样。但这时候,官方建议大家如果两个可以通用,那就选择array,因为array更灵活,速度更快,很多人把二维的array也翻译成矩阵。
但是matrix的优势就是相对简单的运算符号,比如两个矩阵相乘,就是用符号*,但是array相乘不能这么用,得用方法.dot()
array的优势就是不仅仅表示二维,还能表示3、4、5…维,而且在大部分Python程序里,array也是更常用的。
现在我们讨论numpy的多维数组:
例如,在3D空间一个点的坐标[1, 2, 3]是一个秩为1的数组,因为它只有一个轴。那个轴长度为3.又例如,在以下例子中,数组的秩为2(它有两个维度).第一个维度长度为2,第二个维度长度为3.
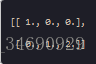
NumPy的数组类被称作ndarray。通常被称作数组。注意numpy.array和标准Python库类array.array并不相同,后者只处理一维数组和提供少量功能。更多重要ndarray对象属性见 Python Numpy的数组array和矩阵matrix:
dataset.py
Python future 模块
原文参考: Python future 模块
从单词含义上猜应该是“未来”的模块。它有下面几个目的:
- 避免和现有分析import工具混淆,并得到你期望的模块
- 确保2.1之前的版本导入future产生运行时异常,因为2.1之前没有这个模块
文档化不兼容的改变,通常这些改变会在新版中强制执行。这类文档以可执行的形式组织,通过导入future进行可编程式的检查。
- Python ctypes 模块
摘要:模块ctypes是Python内建的用于调用动态链接库函数的功能模块,一定程度上可以用于Python与其他语言的混合编程。由于编写动态链接库,使用C/C++是最常见的方式,故ctypes最常用于Python与C/C++混合编程之中。
原文
- multiprocessing
多线程
image.reshape(-1)[0:image.size]中的-1表示模糊概念,自动计算出相应的维数。
Python 字典(Dictionary) get()方法
描述
Python 字典(Dictionary) get() 函数返回指定键的值,如果值不在字典中返回默认值。
语法
get()方法语法:
dict.get(key, default=None)
参数key -- 字典中要查找的键。 default -- 如果指定键的值不存在时,返回该默认值值。返回值
返回指定键的值,如果值不在字典中返回默认值None。
numpy.frombuffer
Interpret a buffer as a 1-dimensional array.
Exampless = ‘hello world’
np.frombuffer(s, dtype=’S1’, count=5, offset=6)
array([‘w’, ‘o’, ‘r’, ‘l’, ‘d’],
dtype=’|S1’)Python endswith()方法
Python endswith() 方法用于判断字符串是否以指定后缀结尾,如果以指定后缀结尾返回True,否则返回False。可选参数”start”与”end”为检索字符串的开始与结束位置。
endswith()方法语法:
string.endswith(obj, beg=0, end=len(string))
以下实例展示了endswith()方法的实例:
str = "this is string example....wow!!!";
suffix = "wow!!!";
print str.endswith(suffix);
print str.endswith(suffix,20);
suffix = "is";
print str.endswith(suffix, 2, 4);
print str.endswith(suffix, 2, 6);以上实例输出结果如下:
True
True
True
Falsepython filename[:-1]
示例:
line = “abcde”
line[:-1]
‘abcd’line[:-1]其实就是去除了这行文本的最后一个字符(换行符)后剩下的部分。
python callback回调函数
原文参考:回调函数(callback)是什么
编程分为两类:系统编程(system programming)和应用编程(application programming)。所谓系统编程,简单来说,就是编写库;而应用编程就是利用写好的各种库来编写具某种功用的程序,也就是应用。系统程序员会给自己写的库留下一些接口,即API(application programming interface,应用编程接口),以供应用程序员使用。所以在抽象层的图示里,库位于应用的底下。当程序跑起来时,一般情况下,应用程序(application program)会时常通过API调用库里所预先备好的函数。但是有些库函数(library function)却要求应用先传给它一个函数,好在合适的时候调用,以完成目标任务。这个被传入的、后又被调用的函数就称为回调函数(callback function)。函数:split()
Python中有split()和os.path.split()两个函数,具体作用如下:- split():拆分字符串。通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片,并返回分割后的字符串列表(list)
- os.path.split():按照路径将文件名和路径分割开
- 函数语法
-
- split()函数
语法:str.split(str=”“,num=string.count(str))[n]
参数说明:
str: 表示为分隔符,默认为空格,但是不能为空(”)。若字符串中没有分隔符,则把整个字符串作为列表的一个元素
num:表示分割次数。如果存在参数num,则仅分隔成 num+1 个子字符串,并且每一个子字符串可以赋给新的变量
[n]: 表示选取第n个分片
注意:当使用空格作为分隔符时,对于中间为空的项会自动忽略
- split()函数
-
- os.path.split()函数
语法:os.path.split(‘PATH’)
参数说明:
1.PATH指一个文件的全路径作为参数:
2.如果给出的是一个目录和文件名,则输出路径和文件名
3.如果给出的是一个目录名,则输出路径和为空文件名
- os.path.split()函数