Android系统启动流程分析
前言
写这篇blog背景是项目在做系统启动耗时优化,之前看了两遍罗升阳大神《Android系统源代码情景分析》都只是看了,没有实践,没有运用到项目中,因此借项目在做系统优化的机会,再次将Android系统的启动流程细细的在撸一遍,边撸边思考哪些点可以优化。
**声明:**由于家里面的代码是去年下的,去年还在做Android O(android-8.0.0_r1)的系统项目,如果博客中有方法在你的代码中找不到,要么选择和我一起看Android O的R1版本代码,要么可以尝试找找你下载版本的源码是否有对我博客中的代码进行封装。因为我经常发现google会将代码在不同版本中封装。大致流程肯定是完全一样的。
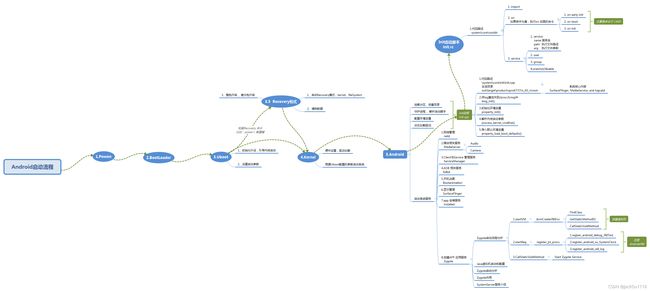
**说明:**这篇博客着实有点长,我本来想分几篇写的,但是感觉分几篇就不完整了,分散了心里始终感觉哪里不对头,所有就没分散。**我不能保证你一定能看完这篇博客,但是我可以保证你看完这篇博客,你肯定会对Android系统启动有更深的理解。**为了方便理解,我先丢两张图,先看图有个直观的认识,再看方法实现了什么功能更容易理解,也更容易在跟踪方法调用迷糊时找到调入的地方。
如果看不清楚,原图下载传送门:系统启动分析
1.Android系统大致启动流程
第一步: 启动电源以及系统启动
当电源按下,引导芯片代码开始从预定义的地方(固化在ROM)开始执行。加载引导程序到RAM,然后 执行引导程序。
第二步:引导程序
引导程序是在Android操作系统开始运行前的一个小程序。引导程序是运行的第一个程序,因此它是针 对特定的主板与芯片的。设备制造商要么使用很受欢迎的引导程序比如redboot、uboot、qi bootloader或者开发自己的引导程序,它不是Android操作系统的一部分。引导程序是OEM厂商或者运 营商加锁和限制的地方。
引导程序分两个阶段执行。
第一个阶段,检测外部的RAM以及加载对第二阶段有用的程序;
第二阶段,引导程序设置网络、内存等等。这些对于运行内核是必要的,为了达到特殊的目标,引导程 序可以根据配置参数或者输入数据设置内核。
Android引导程序可以在\bootable\bootloader\legacy\usbloader找到。传统的加载器包含两个文件, 需要在这里说明:
init.s初始化堆栈,清零BBS段,调用main.c的_main()函数;
main.c初始化硬件(闹钟、主板、键盘、控制台),创建linux标签
第三步:内核
Android内核与桌面linux内核启动的方式差不多。内核启动时,设置缓存、被保护存储器、计划列表, 加载驱动。当内核完成系统设置,它首先在系统文件中寻找”init”文件,然后启动root进程或者系统的第 一个进程
第四步:init进程
init进程是Linux系统中用户空间的第一个进程,进程号固定为1。Kernel启动后,在用户空间启动init进 程,并调用init中的main()方法执行init进程的职责。
第五步:启动zygote进程,通过zygote启动SystemServer,当服务都启动完成之后,启动Lancher App,然后退出开机动画。我们就可以看到桌面应用,此时启动过程就结束了。
2.启动init进程
init进程是Android系统中及其重要的第一个进程,是由内核拉起来的第一个用户进程。
init进程主要完成了三件事情。
- 创建和挂载启动所需要的文件目录
- 初始化和启动属性服务
- 解析init.rc配置文件并启动Zygote进程
// \system\core\init\init.cpp main()
/*
* 1.C++中主函数有两个参数,第一个参数argc表示参数个数,第二个参数是参数列表,也就是具体 的参数
* 2.init的main函数有两个其它入口,一是参数中有ueventd,进入ueventd_main,二是参数中 有watchdogd,进入watchdogd_main
*/
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
/*
* 1.strcmp是String的一个函数,比较字符串,相等返回0
* 2.C++中0也可以表示false
* 3.basename是C库中的一个函数,得到特定的路径中的最后一个'/'后面的内容,
* 比如/sdcard/miui_recovery/backup,得到的结果是backup
*/
if (!strcmp(basename(argv[0]), "ueventd")) {
//当argv[0]的内容为ueventd 时,strcmp的值为0,!strcmp为1
//1表示true,也就执行ueventd_main,ueventd主要是负责设备节点的创建、权限设定等一系列工作
return ueventd_main(argc, argv);
}
if (!strcmp(basename(argv[0]), "watchdogd")) {
//watchdogd俗称看门狗,用于 系统出问题时重启系统
return watchdogd_main(argc, argv);
}
if (REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC) {
//初始化重启系统的处理信号,内部通过sigaction 注册信号,当监听到该信号时重启系统
install_reboot_signal_handlers();
}
add_environment("PATH", _PATH_DEFPATH);
// 查看是否有环境变量INIT_SECOND_STAGE
bool is_first_stage = (getenv("INIT_SECOND_STAGE") == nullptr);
// 1.init的main方法会执行两次,由is_first_stage控制,first_stage就是第一阶段要做的事
if (is_first_stage) {
boot_clock::time_point start_time = boot_clock::now();
// Clear the umask.
//清空文件权限
umask(0);
// Get the basic filesystem setup we need put together in the initramdisk
// on / and then we'll let the rc file figure out the rest.
//mount是用来挂载文件系统的,mount属于Linux系统调用
mount("tmpfs", "/dev", "tmpfs", MS_NOSUID, "mode=0755");
mkdir("/dev/pts", 0755);;//创建目录,第一个参数是目录路径,第二个是读写权限
mkdir("/dev/socket", 0755);
mount("devpts", "/dev/pts", "devpts", 0, NULL);
#define MAKE_STR(x) __STRING(x)
mount("proc", "/proc", "proc", 0, "hidepid=2,gid=" MAKE_STR(AID_READPROC));
// Don't expose the raw commandline to unprivileged processes.
chmod("/proc/cmdline", 0440);//用于修改文件/目录的读写权限
gid_t groups[] = { AID_READPROC };
// 用来将list数组中所标明的组加入到目前进程的组设置中
setgroups(arraysize(groups), groups);
mount("sysfs", "/sys", "sysfs", 0, NULL);
mount("selinuxfs", "/sys/fs/selinux", "selinuxfs", 0, NULL);
//mknod用于创建Linux中的设备文件
mknod("/dev/kmsg", S_IFCHR | 0600, makedev(1, 11));
mknod("/dev/random", S_IFCHR | 0666, makedev(1, 8));
mknod("/dev/urandom", S_IFCHR | 0666, makedev(1, 9));
// Now that tmpfs is mounted on /dev and we have /dev/kmsg, we can actually
// talk to the outside world...
//将标准输入输出重定向到"/sys/fs/selinux/null"
InitKernelLogging(argv);
LOG(INFO) << "init first stage started!";
if (!DoFirstStageMount()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to mount required partitions early ...";
panic();
}
//Avb即Android Verfied boot,功能包括Secure Boot, verfying boot 和dm-verity,
//原理都是对二进制文件进行签名,在系统启动时进行认证,确保系统运行的是合法的二进制镜像文件。
//其中认证的范围涵盖:bootloader,boot.img,system.img
// 通过调用FsManagerAvbHandle::Open()->FsManagerAvbOps::AvbSlotVerify->avb_slot_verify最终去验证每个分区。
// 当验证成功之后,会将版本信息写到环境变量 INIT_AVB_VERSION 中
SetInitAvbVersionInRecovery();
// Set up SELinux, loading the SELinux policy.
//加载SELinux policy,也就是安全策略,
selinux_initialize(true);
// We're in the kernel domain, so re-exec init to transition to the init domain now
// that the SELinux policy has been loaded.
// 我们执行第一遍init的main方法是在kernel domain,所以要重新执行init文件,切换到加载了selinux策略的init domain,
if (restorecon("/init") == -1) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "restorecon failed";
security_failure();
}
// 设置进入第二阶段标志位,进入第二阶段
setenv("INIT_SECOND_STAGE", "true", 1);
static constexpr uint32_t kNanosecondsPerMillisecond = 1e6;
uint64_t start_ms = start_time.time_since_epoch().count() / kNanosecondsPerMillisecond;
setenv("INIT_STARTED_AT", StringPrintf("%" PRIu64, start_ms).c_str(), 1);
char* path = argv[0];
char* args[] = { path, nullptr };
// 重新执行init,由于标志位置为了,因此再次执行init会进入阶段。
execv(path, args);
// execv() only returns if an error happened, in which case we
// panic and never fall through this conditional.
PLOG(ERROR) << "execv(\"" << path << "\") failed";
security_failure();
}
// At this point we're in the second stage of init.
InitKernelLogging(argv);
LOG(INFO) << "init second stage started!";
// Set up a session keyring that all processes will have access to. It
// will hold things like FBE encryption keys. No process should override
// its session keyring.
keyctl(KEYCTL_GET_KEYRING_ID, KEY_SPEC_SESSION_KEYRING, 1);
// Indicate that booting is in progress to background fw loaders, etc.
close(open("/dev/.booting", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_CLOEXEC, 0000));
//初始化属性系统,并从指定文件读取属性
// bionic/libc/bionic/system_properties.c
// __system_property_area_init->map_prop_area_rw->打开/dev/__properties__文件->并且映射128kb空间大小内存来存属性键值对。
property_init();
// If arguments are passed both on the command line and in DT,
// properties set in DT always have priority over the command-line ones.
//接下来的一系列操作都是从各个文件读取一些属性,然后通过property_set设置系统属性
// 1.这句英文的大概意思是,如果参数同时从命令行和DT传过来,DT的优先级总是大于命令行的。
// 2.DT即device-tree,中文意思是设备树,这里面记录自己的硬件配置和系统运行参数,参考http://www.wowotech.net/linux_kenrel/why-dt.html
process_kernel_dt();//处理DT属性
process_kernel_cmdline();//处理命令行属性
// Propagate the kernel variables to internal variables
// used by init as well as the current required properties.
export_kernel_boot_props();//处理其他的一些属性
// Make the time that init started available for bootstat to log.
property_set("ro.boottime.init", getenv("INIT_STARTED_AT"));
property_set("ro.boottime.init.selinux", getenv("INIT_SELINUX_TOOK"));
// Set libavb version for Framework-only OTA match in Treble build.
const char* avb_version = getenv("INIT_AVB_VERSION");
// 将avb版本设置到系统属性中
if (avb_version) property_set("ro.boot.avb_version", avb_version);
// Clean up our environment.
// 清除环境变量
unsetenv("INIT_SECOND_STAGE");
unsetenv("INIT_STARTED_AT");
unsetenv("INIT_SELINUX_TOOK");
unsetenv("INIT_AVB_VERSION");
// Now set up SELinux for second stage.
selinux_initialize(false);
selinux_restore_context();
//创建epoll实例,并返回epoll的文件描述符
epoll_fd = epoll_create1(EPOLL_CLOEXEC);
if (epoll_fd == -1) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "epoll_create1 failed";
exit(1);
}
// 主要是创建handler处理子进程终止信号,创建一个匿名 socket并注册到epoll进行监听
signal_handler_init();
// 从文件中加载一些属性,读取usb配置
// 涉及到的文件,/system/etc/prop.default,/odm/default.prop,/vendor/default.prop
property_load_boot_defaults();
export_oem_lock_status();// 设置ro.boot.flash.locked 属性
start_property_service();//开启一个socket监听系统属性的设置
set_usb_controller();//设置sys.usb.controller 属性
//init.rc文件中方法映射,例如“class_start”-> "do_class_start"
const BuiltinFunctionMap function_map;
Action::set_function_map(&function_map);//将function_map存放到Action中作 为成员属性
// 使用不同的parse解析init.rc文件中的不同字段,并且将service保存在servicelist中
Parser& parser = Parser::GetInstance();
parser.AddSectionParser("service",std::make_unique());
parser.AddSectionParser("on", std::make_unique());
parser.AddSectionParser("import", std::make_unique());
std::string bootscript = GetProperty("ro.boot.init_rc", "");
if (bootscript.empty()) {
// 以下目录的所有rc文件默认都会被解析
parser.ParseConfig("/init.rc");
parser.set_is_system_etc_init_loaded(
parser.ParseConfig("/system/etc/init"));
parser.set_is_vendor_etc_init_loaded(
parser.ParseConfig("/vendor/etc/init"));
parser.set_is_odm_etc_init_loaded(parser.ParseConfig("/odm/etc/init"));
} else {
parser.ParseConfig(bootscript);
parser.set_is_system_etc_init_loaded(true);
parser.set_is_vendor_etc_init_loaded(true);
parser.set_is_odm_etc_init_loaded(true);
}
// Turning this on and letting the INFO logging be discarded adds 0.2s to
// Nexus 9 boot time, so it's disabled by default.
if (false) parser.DumpState();//打印一些当前Parser的信息,默认是不执行的
ActionManager& am = ActionManager::GetInstance();
// QueueEventTrigger用于触发Action,这里触发early-init事件
am.QueueEventTrigger("early-init");
// Queue an action that waits for coldboot done so we know ueventd has set up all of /dev...
//QueueBuiltinAction用于添加Action,第一个参数是 Action要执行的Command,第二个是Trigger
am.QueueBuiltinAction(wait_for_coldboot_done_action, "wait_for_coldboot_done");
// ... so that we can start queuing up actions that require stuff from /dev.
am.QueueBuiltinAction(mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng_action, "mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(set_mmap_rnd_bits_action, "set_mmap_rnd_bits");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(set_kptr_restrict_action, "set_kptr_restrict");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(keychord_init_action, "keychord_init");
am.QueueBuiltinAction(console_init_action, "console_init");
// Trigger all the boot actions to get us started.
am.QueueEventTrigger("init");
// Repeat mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng in case /dev/hw_random or /dev/random
// wasn't ready immediately after wait_for_coldboot_done
am.QueueBuiltinAction(mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng_action, "mix_hwrng_into_linux_rng");
// Don't mount filesystems or start core system services in charger mode.
std::string bootmode = GetProperty("ro.bootmode", "");
if (bootmode == "charger") {
am.QueueEventTrigger("charger");
} else {
am.QueueEventTrigger("late-init");
}
// Run all property triggers based on current state of the properties.
am.QueueBuiltinAction(queue_property_triggers_action, "queue_property_triggers");
while (true) {
// By default, sleep until something happens.
int epoll_timeout_ms = -1; //epoll超时时间,相当于阻塞时间
if (!(waiting_for_prop || ServiceManager::GetInstance().IsWaitingForExec())) {
am.ExecuteOneCommand();//执行一个command
}
if (!(waiting_for_prop || ServiceManager::GetInstance().IsWaitingForExec())) {
restart_processes();
// If there's a process that needs restarting, wake up in time for that.
if (process_needs_restart_at != 0) {
epoll_timeout_ms = (process_needs_restart_at - time(nullptr)) * 1000;
if (epoll_timeout_ms < 0) epoll_timeout_ms = 0;
}
// If there's more work to do, wake up again immediately.
//当还有命令要执行时,将epoll_timeout_ms设置为0
if (am.HasMoreCommands()) epoll_timeout_ms = 0;
}
epoll_event ev;
/*
* 1.epoll_wait与epoll_create1、epoll_ctl是一起使用的
* 2.epoll_create1用于创建epoll的文件描述符,epoll_ctl、epoll_wait都把它创建的fd作为第一个参数传入
* 3.epoll_ctl用于操作epoll,EPOLL_CTL_ADD:注册新的fd到epfd中,
EPOLL_CTL_MOD:修改已经注册的fd的监听事件,EPOLL_CTL_DEL:从epfd中删除一个fd;
* 4.epoll_wait用于等待事件的产生,epoll_ctl调用EPOLL_CTL_ADD时会传入需要监听什么类型的事件,
*比如EPOLLIN表示监听fd可读,当该fd有可读的数据时,调用epoll_wait经过epoll_timeout_ms时间就会把该事件的信息返回给&ev
*/
int nr = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(epoll_wait(epoll_fd, &ev, 1, epoll_timeout_ms));
if (nr == -1) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "epoll_wait failed";
} else if (nr == 1) {
//当有event返回时,取出 ev.data.ptr(之前epoll_ctl注册时的回调函数),直接执行
//在signal_handler_init和start_property_service有注册两个fd的监听,一个用于监听SIGCHLD(子进程结束信号),一个用于监听属性设置
((void (*)()) ev.data.ptr)();
}
}
return 0;
}
3.解析init.rc
init.rc是一个非常重要的配置文件,它是由Android初始化语言(Android Init Language)编写的脚本,它主要包含五种类型语句:Action(Action中包含了一系列的Command)、Commands(init语言中的命令)、Services(由init进程启动的服务)、Options(对服务进行配置的选项)和Import(引入其他配置文件)。init.rc的配置代码如下所示。
# \system\core\rootdir\init.rc
on init # L41
sysclktz 0
# Mix device-specific information into the entropy pool
copy /proc/cmdline /dev/urandom
copy /default.prop /dev/urandom
...
on <trigger> [&& <trigger>]* //设置触发器
<command>
<command> //动作触发之后要执行的命令
service <name> <pathname> [ <argument> ]* #<执行程序路径><传递参数>
<option> #Options是Services的参数配置. 它们影响Service如何运行及运行时机
group <groupname> [ <groupname>\* ] #在启动Service前将group改为第一个 groupname,第一个groupname是必须有的,默认值为root(或许默认值是无),第二个groupname可以不设置,用于追加组(通过 setgroups)
priority <priority> #设置进程优先级. 在-20~19之间,默认值是0,能过 setpriority实现
socket <name> <type> <perm> [ <user> [ <group> [ <seclabel> ] ] ] #创建 一个unix域的socket,名字叫/dev/socket/name , 并将fd返回给Service. type 只能是 "dgram", "stream" or "seqpacket".
3.1 Action
Action: 通过触发器trigger,即以on开头的语句来决定执行相应的service的时机,具体有如下时机:
- on early-init; 在初始化早期阶段触发;
- on init; 在初始化阶段触发;
- on late-init; 在初始化晚期阶段触发;
- on boot/charger: 当系统启动/充电时触发,还包含其他情况,此处不一一列举;
- on property:=: 当属性值满足条件时触发
3.2 Service
服务Service,以 service开头,由init进程启动,一般运行在init的一个子进程,所以启动service前需要判断对应的可执行文件是否存在。init生成的子进程,定义在rc文件,其中每一个service在启动时会通过 fork方式生成子进程。
例如: service servicemanager /system/bin/servicemanager代表的是服务名为 servicemanager,服务执行的路径为/system/bin/servicemanager。
3.3 Command
下面列举常用的命令:
- class_start
: 启动属于同一个class的所有服务; - start
: 启动指定的服务,若已启动则跳过; - stop
: 停止正在运行的服务 - setprop :设置属性值
- mkdir :创建指定目录
- symlink
: 创建连接到的 符号链接; - write : 向文件path中写入字符串;
- exec: fork并执行,会阻塞init进程直到程序完毕;
- exprot:设定环境变量;
- loglevel :设置log级别
3.4 Options
Options是Service的可选项,与service配合使用
- disabled: 不随class自动启动,只有根据service名才启动;
- oneshot: service退出后不再重启;
- user/group: 设置执行服务的用户/用户组,默认都是root;
- class:设置所属的类名,当所属类启动/退出时,服务也启动/停止,默认为default; onrestart:当服务重启时执行相应命令;
- socket: 创建名为 /dev/socket/的socket
- critical: 在规定时间内该service不断重启,则系统会重启并进入恢复模式
- default: 意味着disabled=false,oneshot=false,critical=false。
下面看看zygote的rc脚本
service zygote /system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote -- start-system-server
class main
priority -20
user root
group root readproc reserved_disk
socket zygote stream 660 root system
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart audioserver
onrestart restart cameraserver
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
onrestart restart wificond
writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks
3.5 逐行解析脚本
// system\core\init\init_parser.cpp
void Parser::ParseData(const std::string& filename, const std::string& data) {
//TODO: Use a parser with const input and remove this copy
std::vector<char> data_copy(data.begin(), data.end());
data_copy.push_back('\0');
parse_state state;
state.filename = filename.c_str();
state.line = 0;
state.ptr = &data_copy[0];
state.nexttoken = 0;
SectionParser* section_parser = nullptr;
std::vector<std::string> args;
for (;;) {
switch (next_token(&state)) {
case T_EOF:
if (section_parser) {
// 结束解析
section_parser->EndSection();
}
return;
case T_NEWLINE:
state.line++;
if (args.empty()) {
break;
}
if (section_parsers_.count(args[0])) {
if (section_parser) {
section_parser->EndSection();
}
section_parser = section_parsers_[args[0]].get();
std::string ret_err;
// 逐行解析
if (!section_parser->ParseSection(args, &ret_err)) {
parse_error(&state, "%s\n", ret_err.c_str());
section_parser = nullptr;
}
} else if (section_parser) {
std::string ret_err;
if (!section_parser->ParseLineSection(args, state.filename,
state.line, &ret_err)) {
parse_error(&state, "%s\n", ret_err.c_str());
}
}
args.clear();
break;
case T_TEXT:
args.emplace_back(state.text);
break;
}
}
}
// \system\core\init\service.cpp
Result<Success> ServiceParser::ParseSection(std::vector<std::string>&& args, const std::string& filename, int line) {
if (args.size() < 3) {
return Error() << "services must have a name and a program"; }
const std::string& name = args[1]; if (!IsValidName(name)) {
return Error() << "invalid service name '" << name << "'"; }
Subcontext* restart_action_subcontext = nullptr; if (subcontexts_) {
for (auto& subcontext : *subcontexts_) {
if (StartsWith(filename, subcontext.path_prefix())) {
restart_action_subcontext = &subcontext;
break; }
} }
std::vector<std::string> str_args(args.begin() + 2, args.end());
service_ = std::make_unique<Service>(name, restart_action_subcontext, str_args);//构建出一个service对象
return Success(); }
// \system\core\init\service.cpp
void ServiceParser::EndSection() {
if (service_) {
// 如果上面解析的service不为空,就加入到ServiceManager中
ServiceManager::GetInstance().AddService(std::move(service_));
}
}
上面解析完成后,接下来就是启动Service,这里我们以启动Zygote来分析
# \system\core\rootdir\init.rc L680
on nonencrypted
class_start main #class_start是一个命令,通过do_class_start函数处理
class_start late_start
# system\core\init\builtins.cpp
static Result<Success> do_class_start(const BuiltinArguments& args) {
// Starting a class does not start services which are explicitly disabled.
// They must be started individually.
for (const auto& service : ServiceList::GetInstance()) {
if (service->classnames().count(args[1])) {
// 调用刚刚注册的service的StartIfNotDisabled()方法
if (auto result = service->StartIfNotDisabled(); !result) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Could not start service '" << service->name() << "' as part of class '" << args[1] << "': " << result.error();
}
}
}
return Success();
}
// \system\core\init\service.cpp
Result<Success> Service::StartIfNotDisabled() {
if (!(flags_ & SVC_DISABLED)) {
return Start();
} else {
flags_ |= SVC_DISABLED_START; }
return Success();
}
bool Service::Start() {
// Starting a service removes it from the disabled or reset state and
// immediately takes it out of the restarting state if it was in there.
flags_ &= (~(SVC_DISABLED|SVC_RESTARTING|SVC_RESET|SVC_RESTART|SVC_DISABLED_START));
// 如果service已经启动了,就不启动了
if (flags_ & SVC_RUNNING) {
return false;
}
......
struct stat sb;
//判断需要启动的service的对应的执行文件是否存在,不存在则不启动service
if (stat(args_[0].c_str(), &sb) == -1) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "cannot find '" << args_[0] << "', disabling '" << name_ << "'";
flags_ |= SVC_DISABLED;
return false;
}
std::string scon;
if (!seclabel_.empty()) {
scon = seclabel_;
} else {
LOG(INFO) << "computing context for service '" << name_ << "'";
scon = ComputeContextFromExecutable(name_, args_[0]);
if (scon == "") {
return false;
}
}
LOG(INFO) << "starting service '" << name_ << "'...";
//如果子进程没有启动,则调用fork函数创建子进程
pid_t pid = -1;
if (namespace_flags_) {
pid = clone(nullptr, nullptr, namespace_flags_ | SIGCHLD, nullptr);
} else {
pid = fork();
}
if (pid == 0) {
//当期代码逻辑在子进程中运行
umask(077);
if (namespace_flags_ & CLONE_NEWPID) {
// This will fork again to run an init process inside the PID
// namespace.
SetUpPidNamespace(name_);
}
for (const auto& ei : envvars_) {
add_environment(ei.name.c_str(), ei.value.c_str());
}
std::for_each(descriptors_.begin(), descriptors_.end(),
std::bind(&DescriptorInfo::CreateAndPublish, std::placeholders::_1, scon));
// See if there were "writepid" instructions to write to files under /dev/cpuset/.
auto cpuset_predicate = [](const std::string& path) {
return android::base::StartsWith(path, "/dev/cpuset/");
};
auto iter = std::find_if(writepid_files_.begin(), writepid_files_.end(), cpuset_predicate);
if (iter == writepid_files_.end()) {
// There were no "writepid" instructions for cpusets, check if the system default
// cpuset is specified to be used for the process.
std::string default_cpuset = android::base::GetProperty("ro.cpuset.default", "");
if (!default_cpuset.empty()) {
// Make sure the cpuset name starts and ends with '/'.
// A single '/' means the 'root' cpuset.
if (default_cpuset.front() != '/') {
default_cpuset.insert(0, 1, '/');
}
if (default_cpuset.back() != '/') {
default_cpuset.push_back('/');
}
writepid_files_.push_back(
StringPrintf("/dev/cpuset%stasks", default_cpuset.c_str()));
}
}
std::string pid_str = StringPrintf("%d", getpid());
for (const auto& file : writepid_files_) {
if (!WriteStringToFile(pid_str, file)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "couldn't write " << pid_str << " to " << file;
}
}
if (ioprio_class_ != IoSchedClass_NONE) {
if (android_set_ioprio(getpid(), ioprio_class_, ioprio_pri_)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "failed to set pid " << getpid()
<< " ioprio=" << ioprio_class_ << "," << ioprio_pri_;
}
}
if (needs_console) {
setsid();
OpenConsole();
} else {
ZapStdio();
}
// As requested, set our gid, supplemental gids, uid, context, and
// priority. Aborts on failure.
SetProcessAttributes();
std::vector<char*> strs;
//调用execv函数,启动sevice子进程
ExpandArgs(args_, &strs);
if (execve(strs[0], (char**) &strs[0], (char**) ENV) < 0) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "cannot execve('" << strs[0] << "')";
}
_exit(127);
}
......
}
4.zygote启动
上面看到了解析了init.rc之后就可以启动服务。下面我们来看看zygote是如何启动的,启动起来干了什么事情。
4.1 Zygote简述
Zygote是一个C/S模型,Zygote进程作为服务端,它主要负责创建Java虚拟机,加载系统资源,启动SystemServer进程,以及在后续运行过程中启动普通的应用程序,其他进程作为客户端向它发 出“孵化”请求,而Zygote接收到这个请求后就“孵化”出一个新的进程。比如,当点击Launcher里的 应用程序图标去启动一个新的应用程序进程时,这个请求会到达框架层的核心服务 ActivityManagerService中,当AMS收到这个请求后,它通过调用Process类发出一个“孵化”子进 程的Socket请求,而Zygote监听到这个请求后就立刻fork一个新的进程出来。
zygote的启动脚本文件是:init.zygoteXX.rc,在init.rc中会引用该rc文件
import /init.${ro.zygote}.rc
${ro.zygote} 会被替换成 ro.zyogte 的属性值,这个是由不同的硬件厂商自己定制的, 有四个值,
- zygote32: zygote 进程对应的执行程序是 app_process (纯 32bit 模式)
- zygote64: zygote 进程对应的执行程序是 app_process64 (纯 64bit 模式)
- zygote32_64: 启动两个 zygote 进程 (名为 zygote 和 zygote_secondary),对应的执行程序分别 是 app_process32 (主模式)
- zygote64_32: 启动两个 zygote 进程 (名为 zygote 和 zygote_secondary),对应的执行程序分别 是 app_process64 (主模式)、app_process32
4.2 启动runtime
# 位置:system\core\rootdir\init.rc L560
start zygote
# It is recommended to put unnecessary data/ initialization from post-fs- data
# to start-zygote in device's init.rc to unblock zygote start. on zygote-start && property:ro.crypto.state=unencrypted
# A/B update verifier that marks a successful boot. exec_start update_verifier_nonencrypted
start netd
start zygote
start zygote_secondary
on zygote-start && property:ro.crypto.state=unsupported # A/B update verifier that marks a successful boot. exec_start update_verifier_nonencrypted
start netd
start zygote
start zygote_secondary
on zygote-start && property:ro.crypto.state=encrypted && property:ro.crypto.type=file
# A/B update verifier that marks a successful boot. exec_start update_verifier_nonencrypted
start netd
start zygote
start zygote_secondary
无论是否启动FDE/FBE加密,都依赖zygote-start,zygote-start 是在 on late-init 中触发的。
# Mount filesystems and start core system services.
on late-init
trigger early-fs
# Mount fstab in init.{$device}.rc by mount_all command. Optional parameter
# '--early' can be specified to skip entries with 'latemount'.
# /system and /vendor must be mounted by the end of the fs stage,
# while /data is optional.
trigger fs
trigger post-fs
# Mount fstab in init.{$device}.rc by mount_all with '--late' parameter
# to only mount entries with 'latemount'. This is needed if '--early' is
# specified in the previous mount_all command on the fs stage.
# With /system mounted and properties form /system + /factory available,
# some services can be started.
trigger late-fs
# Now we can mount /data. File encryption requires keymaster to decrypt
# /data, which in turn can only be loaded when system properties are present.
trigger post-fs-data
# Now we can start zygote for devices with file based encryption
trigger zygote-start #zygote-start 是在on late-init 中触发的。
# Load persist properties and override properties (if enabled) from /data.
trigger load_persist_props_action
# Remove a file to wake up anything waiting for firmware.
trigger firmware_mounts_complete
trigger early-boot
trigger boot
if (bootmode == "charger") {
am.QueueEventTrigger("charger");
} else {
am.QueueEventTrigger("late-init");
}
不是充电模式,就触发late-init,最后触发start zygote。
app_processXX位置\frameworks\base\cmds\app_process目录下。
4.3 zygote启动代码分析
位置\frameworks\base\cmds\app_process\app_main.cpp
在app_main.cpp的main函数中,主要做的事情就是参数解析. 这个函数有两种启动模式:
- 一种是zygote模式,也就是初始化zygote进程,传递的参数有–start-system-server --socket- name=zygote,前者表示启动SystemServer,后者指定socket的名称
- 一种是application模式,也就是启动普通应用程序,传递的参数有class名字以及class带的参数
两者最终都是调用AppRuntime对象的start函数,加载ZygoteInit或RuntimeInit两个Java类,并将之前 整理的参数传入进去
// \frameworks\base\cmds\app_process\app_main.cpp main() L280
if (strcmp(arg, "--zygote") == 0) {
// 如果rc脚本传入的--zygote参数,就将zygote设置为true。
zygote = true;
niceName = ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--start-system-server") == 0) {
startSystemServer = true;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--application") == 0) {
application = true;
}
......
if (zygote) {
//这些Java的应用都是通过AppRuntime.start(className)开始的
//其实AppRuntime是AndroidRuntime的子类,它主要实现了几个回调函数,而start()方法是实现在AndroidRuntime这个方法类里
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote);
} else if (className) {
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit", args, zygote);
}
// \frameworks\base\core\jni\androidRuntime.cpp
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector<String8>& options, bool zygote)
{
static const String8 startSystemServer("start-system-server");
/*
* 'startSystemServer == true' means runtime is obsolete and not run from
* init.rc anymore, so we print out the boot start event here.
*/
for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i) {
if (options[i] == startSystemServer) {
/* track our progress through the boot sequence */
const int LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START = 3000;
LOG_EVENT_LONG(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_START, ns2ms(systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC)));
}
}
// 获取环境变量,确认系统根目录
const char* rootDir = getenv("ANDROID_ROOT");
if (rootDir == NULL) {
rootDir = "/system";
if (!hasDir("/system")) {
LOG_FATAL("No root directory specified, and /android does not exist.");
return;
}
setenv("ANDROID_ROOT", rootDir, 1);
}
/* start the virtual machine */
JniInvocation jni_invocation;
jni_invocation.Init(NULL);
JNIEnv* env;
// 启动虚拟机
//startVM的前半部分是在处理虚拟机的启动参数,处理完配置参数后,会调用libart.so提供 的一个接口:JNI_CreateJavaVM函数
// 在创建虚拟机的时候,首先会通过Runtime的create方法创建单例的Runtime对象,runtime负责提供art虚拟机的运行时环境,然后调用其init方法来初始化虚拟机。
// 创建虚拟机一共做了五个事情:
// 1.new gc::heap(),创建Heap对象,这是虚拟机管理对内存的起点。
// 2.new JavaVmExt(),创建Java虚拟机实例。
// 3.Thread::attach(),attach主线程
// 4.创建ClassLinker
// 5.初始化ClassLinker,成功attach到runtime环境后,创建ClassLinker实例负责管理java class
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env, zygote) != 0) {
return;
}
// 回调虚拟机创建成功,解析类名,并且找到对应的Class对象。
onVmCreated(env);
/*
* Register android functions.
*/
// 注册jni方法,以便java层可以调用
if (startReg(env) < 0) {
ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
return;
}
/*
* We want to call main() with a String array with arguments in it.
* At present we have two arguments, the class name and an option string.
* Create an array to hold them.
*/
// 创建main方法中的两个参数
jclass stringClass;
jobjectArray strArray;
jstring classNameStr;
stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String");
assert(stringClass != NULL);
strArray = env->NewObjectArray(options.size() + 1, stringClass, NULL);
assert(strArray != NULL);
classNameStr = env->NewStringUTF(className);
assert(classNameStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 0, classNameStr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i) {
jstring optionsStr = env->NewStringUTF(options.itemAt(i).string());
assert(optionsStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, i + 1, optionsStr);
}
/*
* Start VM. This thread becomes the main thread of the VM, and will
* not return until the VM exits.
*/
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className);
jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
if (startClass == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
/* keep going */
} else {
// 调用main()启动对应的进程,如果是zygoteinit就调用zygoteinit的main方法启动zygote
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
"([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
if (startMeth == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
/* keep going */
} else {
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
#if 0
if (env->ExceptionCheck())
threadExitUncaughtException(env);
#endif
}
}
free(slashClassName);
......
}
// \frameworks\base\core\java\com\android\internal\os\RuntimeInit.java
// 虚拟机创建好之后,创建java Runtime.
public static final void main(String[] argv) {
enableDdms();
if (argv.length == 2 && argv[1].equals("application")) {
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application");
//将System.out 和 System.err 输出重定向到Android 的Log系统(定义在android.util.Log)
redirectLogStreams();
} else {
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting tool");
}
// commonInit(): 初始化了一下系统属性,其中最重要的一点就是设置了一个未捕捉异常的 handler,当代码有任何未知异常,就会执行它,
commonInit();
/*
* Now that we're running in interpreted code, call back into native code
* to run the system.
*/
// 回调native java Runtime已经启动完毕
nativeFinishInit();
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "Leaving RuntimeInit!");
}
// \frameworks\base\core\jni\androidRuntime.cpp nativeFinishInit() L225
/** Code written in the Java Programming Language calls here from main(). */
static void com_android_internal_os_RuntimeInit_nativeFinishInit(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz){
// 调到要启动的进程中
gCurRuntime->onStarted();
}
// \frameworks\base\cmds\app_process\app_main.cpp
virtual void onStarted()
{
sp<ProcessState> proc = ProcessState::self();
ALOGV("App process: starting thread pool.\n");
proc->startThreadPool();
AndroidRuntime* ar = AndroidRuntime::getRuntime();
// 调用ZygoteInit的main方法.回应到runtime.start("...ZygoteInit")
ar->callMain(mClassName, mClass, mArgs);
IPCThreadState::self()->stopProcess();
hardware::IPCThreadState::self()->stopProcess();
}
4.3 启动zygote
public static void main(String argv[]) {
// 创建一个LocalServerSocket,等待AMS发起fork子进程通知
ZygoteServer zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer();
// Mark zygote start. This ensures that thread creation will throw
// an error.
ZygoteHooks.startZygoteNoThreadCreation();
// Zygote goes into its own process group.
try {
Os.setpgid(0, 0);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to setpgid(0,0)", ex);
}
try {
// Report Zygote start time to tron unless it is a runtime restart
if (!"1".equals(SystemProperties.get("sys.boot_completed"))) {
MetricsLogger.histogram(null, "boot_zygote_init",
(int) SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());
}
String bootTimeTag = Process.is64Bit() ? "Zygote64Timing" : "Zygote32Timing";
BootTimingsTraceLog bootTimingsTraceLog = new BootTimingsTraceLog(bootTimeTag,
Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygoteInit");
RuntimeInit.enableDdms();
// Start profiling the zygote initialization.
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
boolean startSystemServer = false;
String socketName = "zygote";
String abiList = null;
boolean enableLazyPreload = false;
for (int i = 1; i < argv.length; i++) {
// zygote.rc脚本传参启动systemserver
if ("start-system-server".equals(argv[i])) {
startSystemServer = true;
} else if ("--enable-lazy-preload".equals(argv[i])) {
// 在zygoteXX.rc脚本可以加--enable-lazy-preload参数来懒加载资源和class类
enableLazyPreload = true;
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG)) {
abiList = argv[i].substring(ABI_LIST_ARG.length());
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG)) {
socketName = argv[i].substring(SOCKET_NAME_ARG.length());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);
}
}
if (abiList == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No ABI list supplied.");
}
zygoteServer.registerServerSocket(socketName);
// In some configurations, we avoid preloading resources and classes eagerly.
// In such cases, we will preload things prior to our first fork.
// 如果没有懒加载,就加载class和资源
if (!enableLazyPreload) {
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygotePreload");
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
preload(bootTimingsTraceLog);
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygotePreload
} else {
Zygote.resetNicePriority();
}
// Finish profiling the zygote initialization.
SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeZygoteSnapshot();
// Do an initial gc to clean up after startup
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("PostZygoteInitGC");
//主动进行一次资源GC
gcAndFinalize();
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // PostZygoteInitGC
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygoteInit
// Disable tracing so that forked processes do not inherit stale tracing tags from
// Zygote.
Trace.setTracingEnabled(false);
// Zygote process unmounts root storage spaces.
Zygote.nativeUnmountStorageOnInit();
// Set seccomp policy
Seccomp.setPolicy();
ZygoteHooks.stopZygoteNoThreadCreation();
if (startSystemServer) {
// 启动systemserver
startSystemServer(abiList, socketName, zygoteServer);
}
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
// 死循环等待socket有数据读入
zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
} catch (Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
// 通过抛异常的方式来调用子进程的main可以清空调用栈。
caller.run();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
throw ex;
}
}
我们可以看到Zygote启动一共干了如下几个事情:
- 启动LocalServerSocket
- 加载class和各种资源
- 启动systemserver
- runSelectLoop中epoll等待客户端socket连接
- 根据客户端传过来的参数,在run()中反射调用ActivityThread的main()方法来启动app进程。
下面我们来分别看一下以上几个方法中做了什么。
4.3.1 加载class和各种资源
static void preload(BootTimingsTraceLog bootTimingsTraceLog) {
Log.d(TAG, "begin preload");
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("BeginIcuCachePinning");
// 将ICU数据通常由软引用保存固定在内存中。如果没有这一点,那么当Zygote GC在gcAndFinalize()中运行时,将收集在类预加载过程中直接创建的引用。
beginIcuCachePinning();
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // BeginIcuCachePinning
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("PreloadClasses");
// 加载类
preloadClasses();
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // PreloadClasses
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("PreloadResources");
// 加载资源
preloadResources();
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // PreloadResources
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK, "PreloadOpenGL");
// 加载OpenGL
preloadOpenGL();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
// 加载共享库
preloadSharedLibraries();
// 加载内置字体
preloadTextResources();
// Ask the WebViewFactory to do any initialization that must run in the zygote process,
// for memory sharing purposes.
WebViewFactory.prepareWebViewInZygote();
endIcuCachePinning();
// 注册AndroidKeysReprovider并预热已注册的程序。
warmUpJcaProviders();
Log.d(TAG, "end preload");
sPreloadComplete = true;
}
其中只有类加载、资源和字体加载有必要分析一下,因为在做精细系统启动优化的时候可能会涉及到该部分内容。其他的就预加载就是单纯的加载。
4.3.1.1 preloadClasses();
// 预加载类的路径
private static final String PRELOADED_CLASSES = "/system/etc/preloaded-classes";
private static void preloadClasses() {
final VMRuntime runtime = VMRuntime.getRuntime();
InputStream is;
try {
// 通过流读入需要预加载的类
is = new FileInputStream(PRELOADED_CLASSES);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Couldn't find " + PRELOADED_CLASSES + ".");
return;
}
......
try {
BufferedReader br
= new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is), 256);
// 一下代码解析并且加载类
int count = 0;
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
// Skip comments and blank lines.
line = line.trim();
if (line.startsWith("#") || line.equals("")) {
continue;
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK, line);
try {
if (false) {
Log.v(TAG, "Preloading " + line + "...");
}
// Load and explicitly initialize the given class. Use
// Class.forName(String, boolean, ClassLoader) to avoid repeated stack lookups
// (to derive the caller's class-loader). Use true to force initialization, and
// null for the boot classpath class-loader (could as well cache the
// class-loader of this class in a variable).
// null代表使用Bootstrap ClassLoader最高级引导类加载器加载,加载后的类保存在该类加载器中。之后的类加载都会依托双亲委托机制,不重复加载相同的类。
Class.forName(line, true, null);
count++;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
......
}
4.3.1.2 preloadResources();
private static void preloadResources() {
final VMRuntime runtime = VMRuntime.getRuntime();
try {
mResources = Resources.getSystem();
mResources.startPreloading();
if (PRELOAD_RESOURCES) {
Log.i(TAG, "Preloading resources...");
long startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
TypedArray ar = mResources.obtainTypedArray(
com.android.internal.R.array.preloaded_drawables);
// 更具索引id加载图片资源
int N = preloadDrawables(ar);
ar.recycle();
......
}
4.3.1.3 preloadTextResources();
private static void preloadTextResources() {
// 加载字体到map中
Hyphenator.init();
// 创建画笔,设置默认字体
TextView.preloadFontCache();
}
// frameworks\base\core\java\android\text\Hyphenator.java
public static void init() {
sMap.put(null, null);
// 需要支持的语言
for (int i = 0; i < AVAILABLE_LANGUAGES.length; i++) {
HyphenationData data = AVAILABLE_LANGUAGES[i];
// 加载对应语言的字体
Hyphenator h = loadHyphenator(data);
if (h != null) {
sMap.put(Locale.forLanguageTag(data.mLanguageTag), h);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < LOCALE_FALLBACK_DATA.length; i++) {
String language = LOCALE_FALLBACK_DATA[i][0];
String fallback = LOCALE_FALLBACK_DATA[i][1];
// 解析后的语言保存到map中
sMap.put(Locale.forLanguageTag(language), sMap.get(Locale.forLanguageTag(fallback)));
}
}
private static final HyphenationData[] AVAILABLE_LANGUAGES = {
new HyphenationData("as", INDIC_MIN_PREFIX, INDIC_MIN_SUFFIX), // Assamese
new HyphenationData("bg", 2, 2), // Bulgarian
new HyphenationData("bn", INDIC_MIN_PREFIX, INDIC_MIN_SUFFIX), // Bengali
new HyphenationData("cu", 1, 2), // Church Slavonic
......
new HyphenationData("pt", 2, 3), // Portuguese
new HyphenationData("sl", 2, 2), // Slovenian
new HyphenationData("ta", INDIC_MIN_PREFIX, INDIC_MIN_SUFFIX), // Tamil
new HyphenationData("te", INDIC_MIN_PREFIX, INDIC_MIN_SUFFIX), // Telugu
new HyphenationData("tk", 2, 2), // Turkmen
new HyphenationData("und-Ethi", 1, 1), // Any language in Ethiopic script
};
4.3.2 启动systemserver
private static boolean startSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName, ZygoteServer zygoteServer) throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller, RuntimeException {
......
/* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */
// 设置systemserver启动参数
String args[] = {
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1023,1032,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,3009,3010",
"--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,
"--nice-name=system_server",
"--runtime-args",
"com.android.server.SystemServer",
};
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null;
int pid;
try {
parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args);
ZygoteConnection.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
ZygoteConnection.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
/* Request to fork the system server process */
// 创建子进程
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
/* For child process */
if (pid == 0) {
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
}
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
// 在子进程中执行SystemServer代码
handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
return true;
}
private static void handleSystemServerProcess(
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs)
throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
......
// 如果systemserver类已经被加载了,命中if;否则创建类加载器并且启动参数传给systemserver进程,首次我们分析SystemServer没有被夹在的情况
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
String[] args = parsedArgs.remainingArgs;
// If we have a non-null system server class path, we'll have to duplicate the
// existing arguments and append the classpath to it. ART will handle the classpath
// correctly when we exec a new process.
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
String[] amendedArgs = new String[args.length + 2];
amendedArgs[0] = "-cp";
amendedArgs[1] = systemServerClasspath;
System.arraycopy(args, 0, amendedArgs, 2, args.length);
args = amendedArgs;
}
WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.invokeWith,
parsedArgs.niceName, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
VMRuntime.getCurrentInstructionSet(), null, args);
} else {
ClassLoader cl = null;
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
// 创建类加载器
cl = createPathClassLoader(systemServerClasspath, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion);
// 将当前执行的线程与类加载器绑定,即设成主线程
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl);
}
/*
* Pass the remaining arguments to SystemServer.
*/
// 将剩余的参数传给Systemserver线程
ZygoteInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion, parsedArgs.remainingArgs, cl);
}
/* should never reach here */
}
public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv,
ClassLoader classLoader) throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
if (RuntimeInit.DEBUG) {
Slog.d(RuntimeInit.TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ZygoteInit");
RuntimeInit.redirectLogStreams();
RuntimeInit.commonInit();
ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit();
// 此方法中就会去通过反射调用main方法了,留一下点悬念,待会儿启动APP分析的时候详细看下面的调用,此处我们理解就是调用了SystemServer的main(),在新的进程中拉起了systemserver。具体SystemServer中干了什么,专门用一章来分析。
RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
}
4.3.3 runSelectLoop()
void runSelectLoop(String abiList) throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
ArrayList<FileDescriptor> fds = new ArrayList<FileDescriptor>();
ArrayList<ZygoteConnection> peers = new ArrayList<ZygoteConnection>();
// 增加Zygote的socket服务端的fd为监听对象。
fds.add(mServerSocket.getFileDescriptor());
peers.add(null);
while (true) {
StructPollfd[] pollFds = new StructPollfd[fds.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < pollFds.length; ++i) {
pollFds[i] = new StructPollfd();
pollFds[i].fd = fds.get(i);
pollFds[i].events = (short) POLLIN;
}
try {
Os.poll(pollFds, -1);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("poll failed", ex);
}
for (int i = pollFds.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if ((pollFds[i].revents & POLLIN) == 0) {
continue;
}
// 如果有POLLIN事件,并且遍历的不是最后一个ZygoteConnection进入else
if (i == 0) {
ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList);
peers.add(newPeer);
fds.add(newPeer.getFileDesciptor());
} else {
// 获取ZygoteConnection,其实ZygoteConnection就可以理解成一个socket客户端,因为在创建的时候持有一个socket。
// 执行ZygoteConnection的runOnce()方法
boolean done = peers.get(i).runOnce(this);
if (done) {
peers.remove(i);
fds.remove(i);
}
}
}
}
}
// frameworks\base\core\java\com\android\internal\os\ZygoteConnection.java
boolean runOnce(ZygoteServer zygoteServer) throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
......
// 该方法前面的都不用管,就是获取启动参数和一些权限校验
// fork一个子进程
pid = Zygote.forkAndSpecialize(parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid, parsedArgs.gids, parsedArgs.debugFlags, rlimits, parsedArgs.mountExternal, parsedArgs.seInfo, parsedArgs.niceName, fdsToClose, fdsToIgnore, parsedArgs.instructionSet, parsedArgs.appDataDir);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Exception creating pipe", ex);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Invalid zygote arguments", ex);
} catch (ZygoteSecurityException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr,
"Zygote security policy prevents request: ", ex);
}
try {
if (pid == 0) {
// in child
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
serverPipeFd = null;
// 处理子进程预启动的事务,关闭客户端socket,并且重新开启标准io
handleChildProc(parsedArgs, descriptors, childPipeFd, newStderr);
// should never get here, the child is expected to either
// throw Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller or exec().
return true;
} else {
// in parent...pid of < 0 means failure
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
childPipeFd = null;
return handleParentProc(pid, descriptors, serverPipeFd, parsedArgs);
}
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
}
}
// frameworks\base\core\java\com\android\internal\os\ZygoteConnection.java
private void handleChildProc(Arguments parsedArgs,
FileDescriptor[] descriptors, FileDescriptor pipeFd, PrintStream newStderr)
throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
/**
* By the time we get here, the native code has closed the two actual Zygote
* socket connections, and substituted /dev/null in their place. The LocalSocket
* objects still need to be closed properly.
*/
// 关闭客户端socket
closeSocket();
......
if (parsedArgs.niceName != null) {
Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.niceName);
}
// End of the postFork event.
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.invokeWith,
parsedArgs.niceName, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
VMRuntime.getCurrentInstructionSet(),
pipeFd, parsedArgs.remainingArgs);
} else {
// 通过zygote进程启动的进程,在此方法中调用待启动进程的main方法
ZygoteInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
parsedArgs.remainingArgs, null /* classLoader */);
}
}
// frameworks\base\core\java\com\android\internal\os\ZygoteInit.java
public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv,
ClassLoader classLoader) throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
if (RuntimeInit.DEBUG) {
Slog.d(RuntimeInit.TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ZygoteInit");
RuntimeInit.redirectLogStreams();
RuntimeInit.commonInit();
ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit();
// 设置一些runtime参数,并且调用带启动进程的main方法
RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
}
// frameworks\base\core\java\com\android\internal\os\RuntimeInit.java
protected static void applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
// If the application calls System.exit(), terminate the process
// immediately without running any shutdown hooks. It is not possible to
// shutdown an Android application gracefully. Among other things, the
// Android runtime shutdown hooks close the Binder driver, which can cause
// leftover running threads to crash before the process actually exits.
nativeSetExitWithoutCleanup(true);
// We want to be fairly aggressive about heap utilization, to avoid
// holding on to a lot of memory that isn't needed.
// 让带启动的进程堆大小最大只能占0.75 * 最大堆内存
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.75f);
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetSdkVersion(targetSdkVersion);
final Arguments args;
try {
args = new Arguments(argv);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
Slog.e(TAG, ex.getMessage());
// let the process exit
return;
}
// The end of of the RuntimeInit event (see #zygoteInit).
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
// Remaining arguments are passed to the start class's static main
// 反射得到待执行的类和得到其中的main(),最终通过抛异常的方式,回到zygoteInit的main方法中
invokeStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader);
}
反射得到待执行的类和得到其中的main(),最终通过抛异常的方式,回到zygoteInit的main方法中!!
反射得到待执行的类和得到其中的main(),最终通过抛异常的方式,回到zygoteInit的main方法中!!
反射得到待执行的类和得到其中的main(),最终通过抛异常的方式,回到zygoteInit的main方法中!!
重要的事情说三遍!
private static void invokeStaticMain(String className, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
Class<?> cl;
try {
cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing class when invoking static main " + className,
ex);
}
Method m;
try {
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] {
String[].class });
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing static main on " + className, ex);
} catch (SecurityException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Problem getting static main on " + className, ex);
}
int modifiers = m.getModifiers();
if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Main method is not public and static on " + className);
}
/*
* This throw gets caught in ZygoteInit.main(), which responds
* by invoking the exception's run() method. This arrangement
* clears up all the stack frames that were required in setting
* up the process.
*/
throw new Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
}
以上代码没什么好说的,一眼就可以看懂,返回得到main方法之后,将main()和参数封装到MethodAndArgsCaller中,清栈返回ZygoteInit.main()。
4.3.4 caller.run();
从4.3.3小节我们拿到了待执行应用的main()和启动参数。然后经过caller.run()真正的来调用main()执行带启动应用的代码。
// frameworks\base\core\java\com\android\internal\os\Zygote.java
public static class MethodAndArgsCaller extends Exception
implements Runnable {
/** method to call */
private final Method mMethod;
/** argument array */
private final String[] mArgs;
public MethodAndArgsCaller(Method method, String[] args) {
mMethod = method;
mArgs = args;
}
public void run() {
try {
// 反射调用main方法
mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] {
mArgs });
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
Throwable cause = ex.getCause();
if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) cause;
} else if (cause instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) cause;
}
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
应用启动的真相终于被挖出来了,此处ActivityThread的main方法被调用,一个应用就正式被启动起来了!!!!
此处并没有完,我们上面讲到了SystemServer启动过程还没有将,需要单独拿一章来讲,本来想单独开一篇帖子来叙述,但是单独开一篇就感觉这篇启动分析的文章断了。所以还是继续往下分析吧。
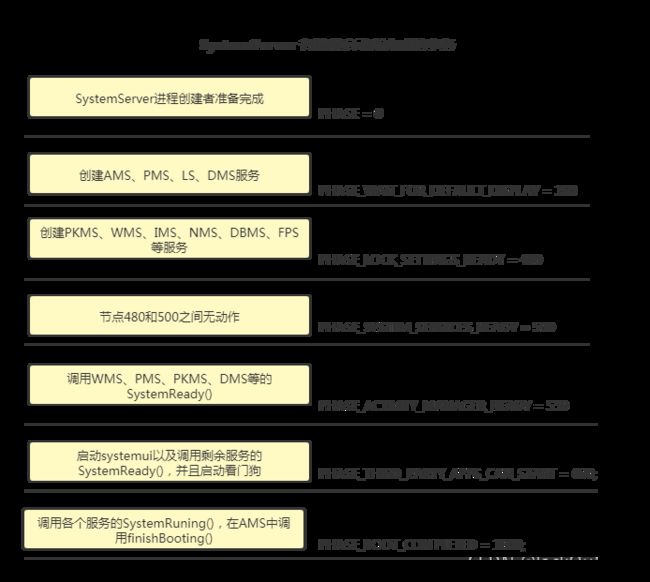
5. SystemServer启动
System Server 是Zygote fork 的第一个Java 进程, 这个进程非常重要,因为他们有很多的系统线程, 提供所有核心的系统服务。它们都是运行在system_server的进程 里。还有很多“Binder-x”的线程,它们是各个Service为了响应应用程序远程调用请求而创建的。除此之 外,还有很多内部的线程,比如 ”UI thread”, “InputReader”, “InputDispatch” 等等。
从4.3.2小节我们看到了Zygote调用了StartSystemServer来启动SystemServer,我们只分析到了调用到SystemServer的main方法就没有分析了,因此,我们在该章专门叙述调用main()之后发生了什么故事。
// frameworks\base\services\java\com\android\server\SystemServer.java
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}
public SystemServer() {
// Check for factory test mode.
mFactoryTestMode = FactoryTest.getMode();
// Remember if it's runtime restart(when sys.boot_completed is already set) or reboot
// 正常启动mRuntimeRestart为false
mRuntimeRestart = "1".equals(SystemProperties.get("sys.boot_completed"));
}
main()中方法很简单,真正有内容的在run()中。其中run()方法中重点干了四个事情:
- 初始化必要的SystemServer环境参数
- 启动引导服务
- 启动核心服务
- 启动其他服务
private void run() {
try {
traceBeginAndSlog("InitBeforeStartServices");
// If a device's clock is before 1970 (before 0), a lot of
// APIs crash dealing with negative numbers, notably
// java.io.File#setLastModified, so instead we fake it and
// hope that time from cell towers or NTP fixes it shortly.
// 初始化系统时间
if (System.currentTimeMillis() < EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME) {
Slog.w(TAG, "System clock is before 1970; setting to 1970.");
SystemClock.setCurrentTimeMillis(EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME);
}
//
// Default the timezone property to GMT if not set.
//
// 设置时区
String timezoneProperty = SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.timezone");
if (timezoneProperty == null || timezoneProperty.isEmpty()) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Timezone not set; setting to GMT.");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.timezone", "GMT");
}
// If the system has "persist.sys.language" and friends set, replace them with
// "persist.sys.locale". Note that the default locale at this point is calculated
// using the "-Duser.locale" command line flag. That flag is usually populated by
// AndroidRuntime using the same set of system properties, but only the system_server
// and system apps are allowed to set them.
//
// NOTE: Most changes made here will need an equivalent change to
// core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
// 设置语言
if (!SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.language").isEmpty()) {
final String languageTag = Locale.getDefault().toLanguageTag();
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.locale", languageTag);
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.language", "");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.country", "");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.localevar", "");
}
// The system server should never make non-oneway calls
Binder.setWarnOnBlocking(true);
// Here we go!
Slog.i(TAG, "Entered the Android system server!");
int uptimeMillis = (int) SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_SYSTEM_RUN, uptimeMillis);
if (!mRuntimeRestart) {
MetricsLogger.histogram(null, "boot_system_server_init", uptimeMillis);
}
// In case the runtime switched since last boot (such as when
// the old runtime was removed in an OTA), set the system
// property so that it is in sync. We can | xq oqi't do this in
// libnativehelper's JniInvocation::Init code where we already
// had to fallback to a different runtime because it is
// running as root and we need to be the system user to set
// the property. http://b/11463182
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.dalvik.vm.lib.2", VMRuntime.getRuntime().vmLibrary());
// Enable the sampling profiler.
if (SamplingProfilerIntegration.isEnabled()) {
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
mProfilerSnapshotTimer = new Timer();
mProfilerSnapshotTimer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
SamplingProfilerIntegration.writeSnapshot("system_server", null);
}
}, SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL, SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL);
}
// Mmmmmm... more memory!
VMRuntime.getRuntime().clearGrowthLimit();
// The system server has to run all of the time, so it needs to be
// as efficient as possible with its memory usage.
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.8f);
// Some devices rely on runtime fingerprint generation, so make sure
// we've defined it before booting further.
Build.ensureFingerprintProperty();
// Within the system server, it is an error to access Environment paths without
// explicitly specifying a user.
Environment.setUserRequired(true);
// Within the system server, any incoming Bundles should be defused
// to avoid throwing BadParcelableException.
BaseBundle.setShouldDefuse(true);
// Ensure binder calls into the system always run at foreground priority.
BinderInternal.disableBackgroundScheduling(true);
// Increase the number of binder threads in system_server
BinderInternal.setMaxThreads(sMaxBinderThreads);
// Prepare the main looper thread (this thread).
android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(
android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND);
android.os.Process.setCanSelfBackground(false);
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
// Initialize native services.
System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
// Check whether we failed to shut down last time we tried.
// This call may not return.
performPendingShutdown();
//=======以上方法就是初始化系统的一些环境,看方法名都知道干了什么====
//=======以下开始实际干活了=====================================
// Initialize the system context.
// 创建系统句柄,有了该句柄后面的服务才能拿到系统资源
createSystemContext();
// Create the system service manager.
mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
mSystemServiceManager.setRuntimeRestarted(mRuntimeRestart);
LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
// Prepare the thread pool for init tasks that can be parallelized
SystemServerInitThreadPool.get();
} finally {
traceEnd(); // InitBeforeStartServices
}
// Start services.
try {
traceBeginAndSlog("StartServices");
// 启动引导服务
startBootstrapServices();
// 启动核心服务
startCoreServices();
// 启动其他服务
startOtherServices();
SystemServerInitThreadPool.shutdown();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
traceEnd();
}
// For debug builds, log event loop stalls to dropbox for analysis.
if (StrictMode.conditionallyEnableDebugLogging()) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Enabled StrictMode for system server main thread.");
}
if (!mRuntimeRestart && !isFirstBootOrUpgrade()) {
int uptimeMillis = (int) SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
MetricsLogger.histogram(null, "boot_system_server_ready", uptimeMillis);
final int MAX_UPTIME_MILLIS = 60 * 1000;
if (uptimeMillis > MAX_UPTIME_MILLIS) {
Slog.wtf(SYSTEM_SERVER_TIMING_TAG,
"SystemServer init took too long. uptimeMillis=" + uptimeMillis);
}
}
// Loop forever.
// 死循环等待其他客户端来获取服务,响应客户端请求。
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
5.1 createSystemContext()
初始化必要的SystemServer环境参数,比如系统时间、默认时区、语言、load一些Library等等, 初始化Looper,我们在主线程中使用到的looper就是在SystemServer中进行初始化的
初始化Context,只有初始化一个Context才能进行启动Service等操作
private void createSystemContext() {
ActivityThread activityThread = ActivityThread.systemMain();
mSystemContext = activityThread.getSystemContext();
mSystemContext.setTheme(DEFAULT_SYSTEM_THEME);
final Context systemUiContext = activityThread.getSystemUiContext();
systemUiContext.setTheme(DEFAULT_SYSTEM_THEME);
}
ActivitThread是在这里创建的,此处的Activitythread是系统的ActivityThread,和应用的ActivityThread有区别,下面给出区别。创建了ActivitThread就获得了ResourcesManager,就可以获得各种资源。
// frameworks\base\core\java\android\app\ActivityThread.java
public static ActivityThread systemMain() {
// The system process on low-memory devices do not get to use hardware
// accelerated drawing, since this can add too much overhead to the
// process.
if (!ActivityManager.isHighEndGfx()) {
ThreadedRenderer.disable(true);
} else {
ThreadedRenderer.enableForegroundTrimming();
}
// 创建ActivityThread,在ActivityThread中其实就是去获取ResourcesManager,不在赘述。
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
// 此处就体现了SystemServer的ActivityThread和应用的ActivityThread不同之处。
// 系统的attch传入的是true, 而应用的是传入的false
thread.attach(true);
return thread;
}
private void attach(boolean system) {
sCurrentActivityThread = this;
mSystemThread = system;
// 如果是应用走if,系统走else
if (!system) {
ViewRootImpl.addFirstDrawHandler(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ensureJitEnabled();
}
});
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("" ,
UserHandle.myUserId());
RuntimeInit.setApplicationObject(mAppThread.asBinder());
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManager.getService();
try {
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
// Watch for getting close to heap limit.
BinderInternal.addGcWatcher(new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
if (!mSomeActivitiesChanged) {
return;
}
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
long dalvikMax = runtime.maxMemory();
long dalvikUsed = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
if (dalvikUsed > ((3*dalvikMax)/4)) {
if (DEBUG_MEMORY_TRIM) Slog.d(TAG, "Dalvik max=" + (dalvikMax/1024) + " total=" + (runtime.totalMemory()/1024) + " used=" + (dalvikUsed/1024));
mSomeActivitiesChanged = false;
try {
mgr.releaseSomeActivities(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
}
});
} else {
// Don't set application object here -- if the system crashes,
// we can't display an alert, we just want to die die die.
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("system_process",
UserHandle.myUserId());
try {
mInstrumentation = new Instrumentation();
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(
this, getSystemContext().mPackageInfo);
mInitialApplication = context.mPackageInfo.makeApplication(true, null);
mInitialApplication.onCreate();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate Application():" + e.toString(), e);
}
}
// add dropbox logging to libcore
// 打印应用或者系统崩溃日志
DropBox.setReporter(new DropBoxReporter());
......
}
从上面可以看出:
- 如果是应用,系统会监控应用的内存是否在于堆内存的3/4,如果大于3/4了,ActivityThread就会通知AMS,销毁一些当前进程的activity。
- 如果是系统,仅仅创建Context并且调用Application.onCreate()方法。
下面继续分析Context的创建过程。
// 单例创建ContextImpl
public ContextImpl getSystemContext() {
synchronized (this) {
if (mSystemContext == null) {
mSystemContext = ContextImpl.createSystemContext(this);
}
return mSystemContext;
}
}
// frameworks\base\core\java\android\app\ContextImpl.java
static ContextImpl createSystemContext(ActivityThread mainThread) {
// 获取系统包信息
LoadedApk packageInfo = new LoadedApk(mainThread);
// 封装系统ContextImpl
ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl(null, mainThread, packageInfo, null, null, null, 0, null);
// 设置系统资源
context.setResources(packageInfo.getResources());
// 更新配置信息
context.mResources.updateConfiguration(context.mResourcesManager. getConfiguration(), context.mResourcesManager.getDisplayMetrics());
return context;
}
LoadedApk()一看名字就知道是封装Apk信息的,他有两个构造方法,如下:
// 封装应用apk信息
public LoadedApk(ActivityThread activityThread, ApplicationInfo aInfo,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, ClassLoader baseLoader,
boolean securityViolation, boolean includeCode, boolean registerPackage) {
mActivityThread = activityThread;
setApplicationInfo(aInfo);
mPackageName = aInfo.packageName;
mBaseClassLoader = baseLoader;
mSecurityViolation = securityViolation;
mIncludeCode = includeCode;
mRegisterPackage = registerPackage;
mDisplayAdjustments.setCompatibilityInfo(compatInfo);
}
// 封装系统apk信息
LoadedApk(ActivityThread activityThread) {
mActivityThread = activityThread;
mApplicationInfo = new ApplicationInfo();
mApplicationInfo.packageName = "android";
mPackageName = "android";
mAppDir = null;
mResDir = null;
mSplitAppDirs = null;
mSplitResDirs = null;
mOverlayDirs = null;
mSharedLibraries = null;
mDataDir = null;
mDataDirFile = null;
mDeviceProtectedDataDirFile = null;
mCredentialProtectedDataDirFile = null;
mLibDir = null;
mBaseClassLoader = null;
mSecurityViolation = false;
mIncludeCode = true;
mRegisterPackage = false;
mClassLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
mResources = Resources.getSystem();
}
至此,系统资源的句柄已经创建完成了,那我们来看看该句柄提供了哪些常用的方法,供外部调用来获取系统资源。
// frameworks\base\core\java\android\app\ContextImpl.java
// 获取系统的context
static ContextImpl createSystemContext(ActivityThread mainThread) {
LoadedApk packageInfo = new LoadedApk(mainThread);
ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl(null, mainThread, packageInfo, null, null, null, 0, null);
context.setResources(packageInfo.getResources());
context.mResources.updateConfiguration(context.mResourcesManager. getConfiguration(),context.mResourcesManager.getDisplayMetrics());
return context;
}
// 该Context是包含了系统主题资源,主要用于UI,在使用的时候,需要确保创建的系统ui Context是在相同的LoadedApk的context中
static ContextImpl createSystemUiContext(ContextImpl systemContext) {
final LoadedApk packageInfo = systemContext.mPackageInfo;
ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl(null, systemContext.mMainThread, packageInfo, null, null, null, 0, null);
context.setResources(createResources(null, packageInfo, null, Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY, null, packageInfo.getCompatibilityInfo()));
return context;
}
// app的Context
static ContextImpl createAppContext(ActivityThread mainThread, LoadedApk packageInfo) {
if (packageInfo == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("packageInfo");
ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl(null, mainThread, packageInfo, null, null, null, 0, null);
context.setResources(packageInfo.getResources());
return context;
}
// Activity的context
static ContextImpl createActivityContext(ActivityThread mainThread, LoadedApk packageInfo, ActivityInfo activityInfo, IBinder activityToken, int displayId, Configuration overrideConfiguration) {
......
return context;
}
至此,系统资源的创建和提供的接口已经叙述完毕,下面可以开始启动服务了。
5.2 启动引导服务
从方法名字就可以看出来该阶段启动的是其他服务依赖的关键服务。包含:安装器、AMS、PMS、LightService、DMS、PKMS、UMS、OMS等,具体某个服务的启动,后面写Blog分析。
private void startBootstrapServices() {
......
// Wait for installd to finish starting up so that it has a chance to
// create critical directories such as /data/user with the appropriate
// permissions. We need this to complete before we initialize other services.
traceBeginAndSlog("StartInstaller");
// 安装器
Installer installer = mSystemServiceManager.startService(Installer.class);
traceEnd();
// In some cases after launching an app we need to access device identifiers,
// therefore register the device identifier policy before the activity manager.
traceBeginAndSlog("DeviceIdentifiersPolicyService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(DeviceIdentifiersPolicyService.class);
traceEnd();
// Activity manager runs the show.
traceBeginAndSlog("StartActivityManager");
// 启动AMS
mActivityManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(
ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.class).getService();
mActivityManagerService.setSystemServiceManager(mSystemServiceManager);
mActivityManagerService.setInstaller(installer);
traceEnd();
// Power manager needs to be started early because other services need it.
// Native daemons may be watching for it to be registered so it must be ready
// to handle incoming binder calls immediately (including being able to verify
// the permissions for those calls).
traceBeginAndSlog("StartPowerManager");
// 启动PMS
mPowerManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(PowerManagerService.class);
traceEnd();
// Now that the power manager has been started, let the activity manager
// initialize power management features.
traceBeginAndSlog("InitPowerManagement");
mActivityManagerService.initPowerManagement();
traceEnd();
// Bring up recovery system in case a rescue party needs a reboot
if (!SystemProperties.getBoolean("config.disable_noncore", false)) {
traceBeginAndSlog("StartRecoverySystemService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(RecoverySystemService.class);
traceEnd();
}
// Now that we have the bare essentials of the OS up and running, take
// note that we just booted, which might send out a rescue party if
// we're stuck in a runtime restart loop.
RescueParty.noteBoot(mSystemContext);
// Manages LEDs and display backlight so we need it to bring up the display.
traceBeginAndSlog("StartLightsService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(LightsService.class);
traceEnd();
// Display manager is needed to provide display metrics before package manager
// starts up.
traceBeginAndSlog("StartDisplayManager");
// 显示服务
mDisplayManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(DisplayManagerService.class);
traceEnd();
// We need the default display before we can initialize the package manager.
traceBeginAndSlog("WaitForDisplay");
// 等待显示阶段
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(SystemService. PHASE_WAIT_FOR_DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
traceEnd();
// Only run "core" apps if we're encrypting the device.
String cryptState = SystemProperties.get("vold.decrypt");
if (ENCRYPTING_STATE.equals(cryptState)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Detected encryption in progress - only parsing core apps");
mOnlyCore = true;
} else if (ENCRYPTED_STATE.equals(cryptState)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Device encrypted - only parsing core apps");
mOnlyCore = true;
}
// Start the package manager.
if (!mRuntimeRestart) {
MetricsLogger.histogram(null, "boot_package_manager_init_start",
(int) SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());
}
traceBeginAndSlog("StartPackageManagerService");
// 启动PKMS
mPackageManagerService = PackageManagerService.main(mSystemContext, installer,
mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_OFF, mOnlyCore);
mFirstBoot = mPackageManagerService.isFirstBoot();
mPackageManager = mSystemContext.getPackageManager();
traceEnd();
if (!mRuntimeRestart && !isFirstBootOrUpgrade()) {
MetricsLogger.histogram(null, "boot_package_manager_init_ready",
(int) SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());
}
// Manages A/B OTA dexopting. This is a bootstrap service as we need it to rename
// A/B artifacts after boot, before anything else might touch/need them.
// Note: this isn't needed during decryption (we don't have /data anyways).
if (!mOnlyCore) {
boolean disableOtaDexopt = SystemProperties.getBoolean("config.disable_otadexopt",
false);
if (!disableOtaDexopt) {
traceBeginAndSlog("StartOtaDexOptService");
try {
OtaDexoptService.main(mSystemContext, mPackageManagerService);
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("starting OtaDexOptService", e);
} finally {
traceEnd();
}
}
}
traceBeginAndSlog("StartUserManagerService");
// 启动UMS
mSystemServiceManager.startService(UserManagerService.LifeCycle.class);
traceEnd();
// Initialize attribute cache used to cache resources from packages.
traceBeginAndSlog("InitAttributerCache");
AttributeCache.init(mSystemContext);
traceEnd();
// Set up the Application instance for the system process and get started.
traceBeginAndSlog("SetSystemProcess");
//启动AMS系统进程的应用实例
mActivityManagerService.setSystemProcess();
traceEnd();
// DisplayManagerService needs to setup android.display scheduling related policies
// since setSystemProcess() would have overridden policies due to setProcessGroup
mDisplayManagerService.setupSchedulerPolicies();
// Manages Overlay packages
traceBeginAndSlog("StartOverlayManagerService");
// 启动OMS
mSystemServiceManager.startService(new OverlayManagerService(mSystemContext, installer));
traceEnd();
// The sensor service needs access to package manager service, app ops
// service, and permissions service, therefore we start it after them.
// Start sensor service in a separate thread. Completion should be checked
// before using it.
mSensorServiceStart = SystemServerInitThreadPool.get().submit(() -> {
BootTimingsTraceLog traceLog = new BootTimingsTraceLog(
SYSTEM_SERVER_TIMING_ASYNC_TAG, Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
traceLog.traceBegin(START_SENSOR_SERVICE);
startSensorService();
traceLog.traceEnd();
}, START_SENSOR_SERVICE);
}
5.3 startCoreServices()
启动核心服务比较简单,主要启动DropBoxManagerService、BatteryService、UsageStatsService和WebViewUpdateService。
private void startCoreServices() {
// Records errors and logs, for example wtf()
traceBeginAndSlog("StartDropBoxManager");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(DropBoxManagerService.class);
traceEnd();
traceBeginAndSlog("StartBatteryService");
// Tracks the battery level. Requires LightService.
mSystemServiceManager.startService(BatteryService.class);
traceEnd();
// Tracks application usage stats.
traceBeginAndSlog("StartUsageService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(UsageStatsService.class);
mActivityManagerService.setUsageStatsManager(
LocalServices.getService(UsageStatsManagerInternal.class));
traceEnd();
// Tracks whether the updatable WebView is in a ready state and watches for update installs.
traceBeginAndSlog("StartWebViewUpdateService");
mWebViewUpdateService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(WebViewUpdateService.class);
traceEnd();
}
5.4 startOtherServices()
启动其他服务就不细说了,太多了,套路都一样。主要来分析一下其他服务启动完成之后,又干了什么,Launcher是如何被拉起来的。
private void startOtherServices() {
......
// 前面象征性的放一点启动其他服务代码
traceBeginAndSlog("StartKeyChainSystemService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(KeyChainSystemService.class);
traceEnd();
traceBeginAndSlog("StartSchedulingPolicyService");
ServiceManager.addService("scheduling_policy", new SchedulingPolicyService());
traceEnd();
traceBeginAndSlog("StartTelecomLoaderService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(TelecomLoaderService.class);
traceEnd();
......
// 接下来会回调各个服务启动完成的回调,在各个服务中可以执行响应的操作
traceBeginAndSlog("MakeWindowManagerServiceReady");
try {
// WMS启动结束回调
wm.systemReady();
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("making Window Manager Service ready", e);
}
// 方法最后!!!!
// 方法最后!!!!
// 方法最后!!!!
// 在方法最后回调AMS.SystemReady(),然后第一个参数传入的是一个Runnable。
mActivityManagerService.systemReady(() -> {
Slog.i(TAG, "Making services ready");
traceBeginAndSlog("StartActivityManagerReadyPhase");
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(
SystemService.PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY);
traceEnd();
traceBeginAndSlog("StartObservingNativeCrashes");
try {
mActivityManagerService.startObservingNativeCrashes();
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("observing native crashes", e);
}
traceEnd();
// No dependency on Webview preparation in system server. But this should
// be completed before allowring 3rd party
final String WEBVIEW_PREPARATION = "WebViewFactoryPreparation";
Future<?> webviewPrep = null;
if (!mOnlyCore) {
webviewPrep = SystemServerInitThreadPool.get().submit(() -> {
Slog.i(TAG, WEBVIEW_PREPARATION);
BootTimingsTraceLog traceLog = new BootTimingsTraceLog(
SYSTEM_SERVER_TIMING_ASYNC_TAG, Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
traceLog.traceBegin(WEBVIEW_PREPARATION);
ConcurrentUtils.waitForFutureNoInterrupt(mZygotePreload, "Zygote preload");
mZygotePreload = null;
mWebViewUpdateService.prepareWebViewInSystemServer();
traceLog.traceEnd();
}, WEBVIEW_PREPARATION);
}
traceBeginAndSlog("StartSystemUI");
try {
// 启动systemui
startSystemUi(context, windowManagerF);
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("starting System UI", e);
}
traceEnd();
traceBeginAndSlog("MakeNetworkScoreReady");
try {
// 启动网络评分机制
if (networkScoreF != null) networkScoreF.systemReady();
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("making Network Score Service ready", e);
}
traceEnd();
traceBeginAndSlog("MakeNetworkManagementServiceReady");
try {
if (networkManagementF != null) networkManagementF.systemReady();
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("making Network Managment Service ready", e);
}
......
// 设置启动阶段
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(
SystemService.PHASE_THIRD_PARTY_APPS_CAN_START);
traceEnd();
......
}, BOOT_TIMINGS_TRACE_LOG);
}
ok, 继续分析AMS ready之后干了什么。
// frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\am\ActivityManagerService.java
public void systemReady(final Runnable goingCallback, BootTimingsTraceLog traceLog) {
traceLog.traceBegin("PhaseActivityManagerReady");
synchronized(this) {
// 由于goingCallback中还有服务没有回调systemReady,所以此处为false,继续往下走。
if (mSystemReady) {
// If we're done calling all the receivers, run the next "boot phase" passed in by the SystemServer
if (goingCallback != null) {
goingCallback.run();
}
return;
}
......
retrieveSettings();
final int currentUserId;
synchronized (this) {
// 获取当前用户id,之后启动launcher之前会判断该用户是否解锁
currentUserId = mUserController.getCurrentUserIdLocked();
readGrantedUriPermissionsLocked();
}
// 回调systemserver中的run(),通知其他服务SystemReady()
if (goingCallback != null) goingCallback.run();
......
synchronized (this) {
// Only start up encryption-aware persistent apps; once user is
// unlocked we'll come back around and start unaware apps
// 启动Manifest中配置了Persistent属性的App
startPersistentApps(PackageManager.MATCH_DIRECT_BOOT_AWARE);
// Start up initial activity.
mBooting = true;
// 启动HomeActivity,此处其实是启动的FallbcakHome Activity
startHomeActivityLocked(currentUserId, "systemReady");
......
}
6 启动FallbcakHome和Launcher
可以看到FallbcakHome的category配置也是HOME,当系统开启了FBE之后,SystemServer首先会启动FallbackHome,在FallbackHome中检查用户是否解锁。
<activity android:name=".FallbackHome"
android:excludeFromRecents="true"
android:screenOrientation="nosensor"
android:theme="@style/FallbackHome">
<intent-filter android:priority="-1000">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.HOME" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
intent-filter>
activity>
public class FallbackHome extends Activity {
private static final String TAG = "FallbackHome";
private static final int PROGRESS_TIMEOUT = 2000;
......
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// 注册解锁广播
registerReceiver(mReceiver, new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_USER_UNLOCKED));
maybeFinish();
}
......
private void maybeFinish() {
// 如果用户已经解锁
if (getSystemService(UserManager.class).isUserUnlocked()) {
// 构建launcher的Intent
final Intent homeIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MAIN)
.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME);
final ResolveInfo homeInfo = getPackageManager().resolveActivity(homeIntent, 0);
if (Objects.equals(getPackageName(), homeInfo.activityInfo.packageName)) {
if (UserManager.isSplitSystemUser()
&& UserHandle.myUserId() == UserHandle.USER_SYSTEM) {
return;
}
Log.d(TAG, "User unlocked but no home; let's hope someone enables one soon?");
mHandler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(0, 500);
} else {
Log.d(TAG, "User unlocked and real home found; let's go!");
// 如果用户已经解锁,并且找到了Launcher的主界面,退出FallbackHome界面。
getSystemService(PowerManager.class).userActivity(
SystemClock.uptimeMillis(), false);
finish();
}
}
}
......
}
FallbackHome请求finish自己,当然会请求执行onPasue方法: ActivityManagerService.activityPaused --》触发调用到ActivityStack.activityPausedLocked --》 调用到 ActivityStack.completePauseLocked —》 调用到 ActivityStack.finishCurrentActivityLocked --》调用到 ActivityStackSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked --》ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityUncheckedLocked -》 ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityInnerLocked -》 ActivityStack.resumeTopActivityInNextFocusableStack -》 ActivityStackSupervisor.resumeHomeStackTask -》最后调用到了ActivityManagerService.startHomeActivityLocked。
跟踪调用栈会发现,如果当category是HOME被销毁之后,最终又会调用到startHomeActivityLocked中。
此处调用startHomeActivityLocked的reason是noMoreActivities resumeHomeStackTask,没有找到可返回的Home主页,然后mActivityStarter.startHomeActivityLocked再起启动Home Activity就是启动的Launcher的启动页了。
此次,Launcher界面终于启动起来了,此篇分析系统启动的过程的帖子终于写完了。
后记
此帖子最初的学习资源来自罗升阳大神《Android系统源代码情景分析(第三版)》。回顾写此篇文章主要是工作需要用到了,再次翻读此书,结合Android O的源码,更细,更深入的理解了源码的调用栈和方法含义。
**建议:**如果第一次看系统启动流程,最好看低版本系统的源码,因为高版本的代码google用了很多设计模式进行封装和重构了,很多看着看着就不知道跳到哪里去了,低版本的代码还是很容易看懂的。
参考文章:
罗升阳大神《Android系统源代码情景分析(第三版)》(至于第几版,最好买最新的吧,第三版分析的源码在当前项目Andorid P和Q源码中很多都被重构了)