SpringBoot基于Redisson实现分布式锁并分析其原理
目录
-
- 一、简介
- 二、maven依赖
- 三、配置类
-
- 3.1、属性配置
- 3.2、redis配置
- 3.3、redisson配置
- 四、分布式锁使用
-
- 4.1、service层
- 4.2、controller层
- 五、配置文件application.yml
-
- 5.1、单节点配置
- 5.2、集群节点配置
- 六、测试
-
- 6.1、多实例准备和Nginx配置
- 6.2、jemeter并发测试
-
- 6.2.1、不加锁并发结果
- 6.2.2、使用redisson加锁结果
- 七、redisson原理(注释都在代码里)
-
- 7.1、获取锁对象
-
- 7.1.1、加锁getLock()
- 7.2、加锁lock()
-
- 7.2.1、加锁lock()(重要)
- 7.2.2、tryAcquire()
- 7.2.3、tryAcquireAsync()
- 7.2.4、tryLockInnerAsync()(核心)
- 7.2.5、流程图
- 7.3、释放锁unlock
-
- 7.3.1、unlock()
- 7.3.2、unlockAsync()
- 7.3.3、unlockInnerAsync()(核心)
- 7.3.4、流程图
- 7.4、锁的续期
-
- 7.4.1、scheduleExpirationRenewal()
- 7.4.2、renewExpiration()(重要)
- 7.4.3、renewExpirationAsync()(核心)
- 7.5、lua脚本
一、简介
在分布式系统中,为了保证同一时间只能由一个客户端对共享资源操作,我们通常采用加锁来实现,常见有三种方式:
- 基于数据库实现的分布式锁
- 基于zookeeper实现的分布式锁
- 基于redis实现的分布式锁
而在使用redis实现时Redisson是官方推荐的一种方案也是我们今天的主角。
二、maven依赖
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.5.2version>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<groupId>com.aliangroupId>
<artifactId>redissonartifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
<name>redissonname>
<description>Spring Boot分布式锁之redissondescription>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
<version>${parent.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId>
<version>${parent.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.coregroupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databindartifactId>
<version>2.9.10version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.datatypegroupId>
<artifactId>jackson-datatype-jsr310artifactId>
<version>2.9.10version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>fastjsonartifactId>
<version>1.2.68version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redissongroupId>
<artifactId>redissonartifactId>
<version>3.16.3version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>1.16.14version>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-pluginartifactId>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
今天的主角就是redisson,如果关于redis不知道整合的可以参考我之前的文章:SpringBoot整合redis(redis支持单节点和集群),这里我就不过多的介绍了。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redissongroupId>
<artifactId>redissonartifactId>
<version>3.16.3version>
dependency>
三、配置类
3.1、属性配置
AppProperties.java
package com.alian.redisson.config;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "app.redisson")
public class AppProperties {
/**
* redis地址
*/
private String address;
/**
* redis数据库
*/
private int database;
}
3.2、redis配置
这里使用redis配置只是为了模拟分布式环境下数据库减库存。
RedisConfig.java
package com.alian.redisson.config;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.SerializationFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.JavaTimeModule;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.deser.LocalDateDeserializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.deser.LocalDateTimeDeserializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.deser.LocalTimeDeserializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.ser.LocalDateSerializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.ser.LocalDateTimeSerializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.ser.LocalTimeSerializer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
/**
* redis配置
*
* @param redisConnectionFactory
* @return
*/
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
// 实例化redisTemplate
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
//设置连接工厂
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
// key采用String的序列化
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(keySerializer());
// value采用jackson序列化
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(valueSerializer());
// Hash key采用String的序列化
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(keySerializer());
// Hash value采用jackson序列化
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(valueSerializer());
//执行函数,初始化RedisTemplate
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
/**
* key类型采用String序列化
*
* @return
*/
private RedisSerializer<String> keySerializer() {
return new StringRedisSerializer();
}
/**
* value采用JSON序列化
*
* @return
*/
private RedisSerializer<Object> valueSerializer() {
//设置jackson序列化
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class);
//设置序列化对象
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(getMapper());
return jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
}
/**
* 使用com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper
* 对数据进行处理包括java8里的时间
*
* @return
*/
private ObjectMapper getMapper() {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
//设置可见性
mapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
//默认键入对象
mapper.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
//设置Java 8 时间序列化
JavaTimeModule timeModule = new JavaTimeModule();
timeModule.addSerializer(LocalDateTime.class, new LocalDateTimeSerializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")));
timeModule.addSerializer(LocalDate.class, new LocalDateSerializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd")));
timeModule.addSerializer(LocalTime.class, new LocalTimeSerializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("HH:mm:ss")));
timeModule.addDeserializer(LocalDateTime.class, new LocalDateTimeDeserializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")));
timeModule.addDeserializer(LocalDate.class, new LocalDateDeserializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd")));
timeModule.addDeserializer(LocalTime.class, new LocalTimeDeserializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("HH:mm:ss")));
//禁用把时间转为时间戳
mapper.configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS, false);
mapper.registerModule(timeModule);
return mapper;
}
}
3.3、redisson配置
RedissonConfig.java
package com.alian.redisson.config;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.redisson.Redisson;
import org.redisson.config.Config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class RedissonConfig {
private static final String COMMA = ",";
@Autowired
private AppProperties appProperties;
@Bean
public Redisson redisson() {
//实例化redisson配置实例
Config config = new Config();
//获取配置文件的配置的地址
String address = appProperties.getAddress();
//如果配置项中包含逗号,我们认为是集群模式(也就是相当于内部一个规定,没必要去较真哦,这里哨兵模式就不考虑了)
if (address != null && address.contains(COMMA)) {
//通过逗号分隔为字符数组
String[] nodeAddress = address.split(COMMA);
//集群模式
config.useClusterServers().addNodeAddress(nodeAddress).setScanInterval(5000);
} else {
//单机模式
config.useSingleServer().setAddress(address).setDatabase(appProperties.getDatabase());
}
//设置加锁时间,默认情况下,加锁的时间是30秒,此处单位为毫秒(实际中你还可以设置)
config.setLockWatchdogTimeout(appProperties.getLeaseTime());
return (Redisson) Redisson.create(config);
}
}
四、分布式锁使用
4.1、service层
模拟启动系统初始化库存为1000,要注意的是setIfAbsent方法,表示不存在就设置,存在就不会设置了。
RedisService.java
package com.alian.redisson.service;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.redisson.Redisson;
import org.redisson.api.RLock;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
@Slf4j
@Service
public class RedisService {
private final String stock = "com.alian.redisson.stock";
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
log.info("模拟初始化库存为:1000");
redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(stock, 1000);
log.info("初始化库存完成");
}
}
具体减库存业务实现
RedissonLockService.java
package com.alian.redisson.service;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.redisson.Redisson;
import org.redisson.api.RLock;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Slf4j
@Service
public class RedissonLockService {
private final String stock = "com.alian.redisson.stock";
@Autowired
private Redisson redisson;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
/**
* 使用redisson分布式锁
*
* @return
*/
public int deductInventoryWithLock() {
//简单定义锁对象,实际中可以对订单号(202110141605211234565)或者其他组合(几个条件一起)作为业务的锁
String lockKey = "redisson_lock";
// 获取锁对象
RLock lock = redisson.getLock(lockKey);
try {
// 加锁
lock.lock();
//获取缓存里的库存数量
Integer stockNum = (Integer) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(stock);
if (stockNum != null && stockNum > 0) {
//扣减库存
stockNum--;
//缓存数据
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(stock, stockNum);
//更新数据库等其他操作
log.info("使用redisson锁库存减1,剩余:{}", stockNum);
return stockNum;
} else {
log.info("使用redisson锁,获取库存异常或者已经没有库存了");
return 0;
}
} finally {
try {
// 释放锁
lock.unlock();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("释放锁异常",e);
}
}
}
/**
* 不使用任何锁
*
* @return
*/
public int deductInventoryWithOutLock() {
//获取缓存里的库存数量
Integer stockNum = (Integer) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(stock);
if (stockNum != null && stockNum > 0) {
//扣减库存
stockNum--;
//缓存数据
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(stock, stockNum);
//更新数据库等其他操作
log.info("不加锁库存减1,剩余:{}", stockNum);
return stockNum;
} else {
log.info("不加锁,获取库存异常或者已经没有库存了");
return 0;
}
}
}
4.2、controller层
RedissonController.java
package com.alian.redisson.controller;
import com.alian.redisson.service.RedissonLockService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@Slf4j
@RequestMapping("/test")
@RestController
public class RedissonController {
@Autowired
RedissonLockService redissonLockService;
@RequestMapping("/deductWithLock")
public int deductInventoryWithLock() {
return redissonLockService.deductInventoryWithLock();
}
@RequestMapping("/deductWithOutLock")
public int deductInventoryWithOutLock() {
return redissonLockService.deductInventoryWithOutLock();
}
}
五、配置文件application.yml
如果是使用我的配置类,调用加锁时不传入任何参数,则默认值还是一定要配置的。
否则就会出现
java.lang.IllegalMonitorStateException: attempt to unlock lock, not locked by current thread by node id: c305b4a2-42fe-4384-9e06-309675d21258 thread-id: 86
因为config.setLockWatchdogTimeout();会设置为0,锁设置的时间0小于了被锁程序的执行时间。导致redisson解锁时,锁已经因为超时被释放掉了。故抛出改异常
5.1、单节点配置
server:
port: 8084
servlet:
context-path: /redisson
tomcat:
accept-count: 200
threads:
max: 500
spring:
redis:
database: 0
host: 192.168.0.193
port: 6379
password:
timeout: 1000
jedis:
pool:
max-active: 10
min-idle: 5
max-idle: 10
max-wait: -1
app:
redisson:
database: 0
address: redis://192.168.0.193:6379
lease-time: 30000
5.2、集群节点配置
server:
port: 8084
servlet:
context-path: /redisson
tomcat:
accept-count: 200
threads:
max: 500
spring:
redis:
cluster:
nodes: 192.168.0.111:6379,192.168.0.112:6379,192.168.0.113:6379,192.168.0.101:6379,192.168.0.102:6379,192.168.0.103:6379,192.168.0.114:6379,192.168.0.104:6379
app:
redisson:
database: 0
address: redis://192.168.0.111:6379,redis://192.168.0.112:6379,redis://192.168.0.113:6379,redis://192.168.0.101:6379,redis://192.168.0.102:6379,redis://192.168.0.103:6379,redis://192.168.0.114:6379,redis://192.168.0.104:6379
lease-time: 30000
六、测试
6.1、多实例准备和Nginx配置
既然是分布式,所以我们的请求能通过nginx发送到不同的实例上,在idea下,我们分别启动两个实例,端口分别为8086、8087,如果对于多实例启动及nginx配置这块不懂的可以参考另一篇文章:windows下Nginx配置及负载均衡使用,里面有详细的介绍,linux下也差不多,案例写的是windows而已。
#nginx转发配置
location ~ ^/redisson/ {
proxy_redirect off;
#端口
proxy_set_header Host $host;
#远程地址
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
#程序可获取远程ip地址
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
#此处会用的upstream.conf,此文件在nginx.conf已经引入了
proxy_pass http://redisson-lock;
}
#负载均衡配置
upstream redisson-lock {
server 127.0.0.1:8086 ;
server 127.0.0.1:8087 ;
}
6.2、jemeter并发测试
既然是分布式的并发,所以我们使用测试工具jemeter来进行测试。因为结果太多,我们使用10个线程进行并发测试。
6.2.1、不加锁并发结果
我们请求接口为:http://localhost/redisson/test/deductWithOutLock
-
端口为8086实例输出结果
2021-10-16 19:01:36 362 [http-nio-8086-exec-6] INFO :不加锁库存减1,剩余:999
2021-10-16 19:01:36 363 [http-nio-8086-exec-1] INFO :不加锁库存减1,剩余:999
2021-10-16 19:01:36 363 [http-nio-8086-exec-2] INFO :不加锁库存减1,剩余:999
2021-10-16 19:01:36 363 [http-nio-8086-exec-5] INFO :不加锁库存减1,剩余:999
2021-10-16 19:01:36 363 [http-nio-8086-exec-3] INFO :不加锁库存减1,剩余:999 -
端口为8087实例输出结果
2021-10-16 19:01:36 362 [http-nio-8087-exec-1] INFO :不加锁库存减1,剩余:999
2021-10-16 19:01:36 362 [http-nio-8087-exec-2] INFO :不加锁库存减1,剩余:999
2021-10-16 19:01:36 363 [http-nio-8087-exec-3] INFO :不加锁库存减1,剩余:999
2021-10-16 19:01:36 363 [http-nio-8087-exec-4] INFO :不加锁库存减1,剩余:999
2021-10-16 19:01:36 364 [http-nio-8087-exec-5] INFO :不加锁库存减1,剩余:999
从结果我们可以看到当10个线程并发请求时,分别转发到两个实例上了,nginx是没有问题的,为什么是这个结果呢?因为当库存还没有扣减更新时,获取的库存都是1000,然后都做库存减1的操作,变成999,当然也和我机器配置高有关系,你有可能会得到998或997等等。
6.2.2、使用redisson加锁结果
-
端口为8086实例输出结果
2021-10-16 19:11:29 737 [http-nio-8087-exec-9] INFO :使用redisson锁库存减1,剩余:999 2021-10-16 19:11:29 804 [http-nio-8087-exec-5] INFO :使用redisson锁库存减1,剩余:996 2021-10-16 19:11:29 827 [http-nio-8087-exec-3] INFO :使用redisson锁库存减1,剩余:995 2021-10-16 19:11:29 842 [http-nio-8087-exec-1] INFO :使用redisson锁库存减1,剩余:994 2021-10-16 19:11:29 884 [http-nio-8087-exec-6] INFO :使用redisson锁库存减1,剩余:991 -
端口为8087实例输出结果
2021-10-16 19:11:29 772 [http-nio-8086-exec-1] INFO :使用redisson锁库存减1,剩余:998 2021-10-16 19:11:29 787 [http-nio-8086-exec-5] INFO :使用redisson锁库存减1,剩余:997 2021-10-16 19:11:29 855 [http-nio-8086-exec-4] INFO :使用redisson锁库存减1,剩余:993 2021-10-16 19:11:29 866 [http-nio-8086-exec-3] INFO :使用redisson锁库存减1,剩余:992 2021-10-16 19:11:29 901 [http-nio-8086-exec-6] INFO :使用redisson锁库存减1,剩余:990
从结果看到,我们扣减库存是正确的,可能会有小伙伴说
//获取缓存里的库存数量
Integer stockNum = (Integer) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(stock);
//扣减库存
stockNum--;
//缓存数据
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(stock, stockNum);
就不能写成下面这个就解决了问题么?
redisTemplate.opsForValue().decrement(stock);
兄弟,我这里只是一个模拟业务的过程,比如你的业务里可能还有会有对数据库的操作等以及key的超时等,分多步执行,每一步都会有并发的情况,也可能每一步都可能出现异常。我们的着重点在用分布式锁,也就是三步。
- 获取锁
- 加锁
- 释放锁
七、redisson原理(注释都在代码里)
每个版本源码都有不同,我这里redisson版本是3.16.3
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redissongroupId>
<artifactId>redissonartifactId>
<version>3.16.3version>
dependency>
7.1、获取锁对象
7.1.1、加锁getLock()
首先是:RLock lock = redisson.getLock(lockKey);
public RLock getLock(String name) {
return new RedissonLock(commandExecutor, name);
}
从这里我们知道默认实现是用的:org.redisson.RedissonLock
7.2、加锁lock()
7.2.1、加锁lock()(重要)
然后是加锁方法:lock.lock();
public void lock() {
try {
lock(-1, null, false);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
}
private void lock(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, boolean interruptibly) throws InterruptedException {
//获取线程Id
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
//尝试获取锁
Long ttl = tryAcquire(-1, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired即获取锁
if (ttl == null) {
return;
}
// 异步订阅redis chennel
RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = subscribe(threadId);
if (interruptibly) {
//同步订阅中断
commandExecutor.syncSubscriptionInterrupted(future);
} else {
// 同步订阅
commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future);
}
try {
while (true) {
// 循环尝试获取锁
ttl = tryAcquire(-1, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired,也就是获取到了锁
if (ttl == null) {
break;
}
// waiting for message
if (ttl >= 0) {
try {
future.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
if (interruptibly) {
throw e;
}
future.getNow().getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
} else {
if (interruptibly) {
future.getNow().getLatch().acquire();
} else {
future.getNow().getLatch().acquireUninterruptibly();
}
}
}
} finally {
// 取消订阅
unsubscribe(future, threadId);
}
// get(lockAsync(leaseTime, unit));
}
7.2.2、tryAcquire()
接下里我们看tryAcquire方法,意思是尝试获取锁。
private Long tryAcquire(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
// get(future)实现同步,通过异步获取锁tryAcquireAsync
return get(tryAcquireAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId));
}
7.2.3、tryAcquireAsync()
接下里是tryAcquireAsync方法,尝试异步方式获取锁。
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture;
if (leaseTime != -1) {
//1 如果设置了超时时间,直接调用 tryLockInnerAsync
ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
} else {
//如果leaseTime==-1,则默认超时时间为30s,本文中的配置类可修改默认值:config.setLockWatchdogTimeout()
ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, internalLockLeaseTime,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
}
//监听Future,获取Future返回值ttlRemaining(剩余过期时间),获取锁成功,且ttlRemaining为空leaseTime为-1,则刷新过期时间
ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
return;
}
// lock acquired,也就是获取到了锁
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
if (leaseTime != -1) {
//过期时间转为毫秒
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
} else {
//计划到期续期,也就是刷新过期时间(重要)
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
});
return ttlRemainingFuture;
}
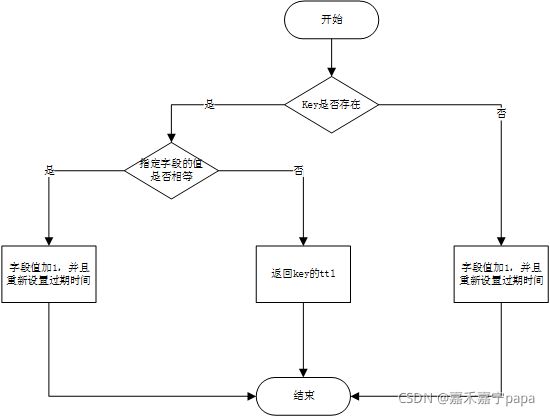
7.2.4、tryLockInnerAsync()(核心)
下面就是最重要的方法:tryLockInnerAsync,意思是尝试异步方式获取内部锁
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
return evalWriteAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
//此处是判断key是否存在,这里的KEYS[1]是我们传入的锁的名字
"if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
//ARGV[2]值是getLockName(threadId),得到类型UUID+线程Id的字段
//key不存在,则在redis中key为KEYS[1],字段ARGV[2]设置值为1,(数据结构为Hash)
//相当于Hash类型, redisTemplate.opsForHash().increment(key,字段,字段的值)
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
//设置key的过期日期
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
//key存在,则判断ARGV[2]的值是否相等,也就是1
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
//值相等,设置一个字段ARGV[2]的值为1
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
//重新设置过期时间
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " +
//返回key的生存时间,后续监听用
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
Collections.singletonList(getRawName()), unit.toMillis(leaseTime), getLockName(threadId));
}
其中KEYS[]和ARGV[]实际是个占位符,具体的参数得看下面这个单位
Collections.singletonList(getRawName()), unit.toMillis(leaseTime), getLockName(threadId));
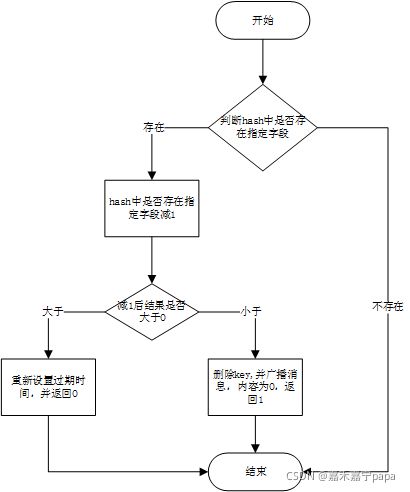
7.2.5、流程图
7.3、释放锁unlock
7.3.1、unlock()
首先我们看下lock.unlock(),
public void unlock() {
try {
//同步get(future),里面通过异步释放锁实现
get(unlockAsync(Thread.currentThread().getId()));
} catch (RedisException e) {
if (e.getCause() instanceof IllegalMonitorStateException) {
throw (IllegalMonitorStateException) e.getCause();
} else {
throw e;
}
}
// Future future = unlockAsync();
// future.awaitUninterruptibly();
// if (future.isSuccess()) {
// return;
// }
// if (future.cause() instanceof IllegalMonitorStateException) {
// throw (IllegalMonitorStateException)future.cause();
// }
// throw commandExecutor.convertException(future);
}
7.3.2、unlockAsync()
接下里看下unlockAsync方法
@Override
public RFuture<Void> unlockAsync(long threadId) {
//给redisson一个承诺
RPromise<Void> result = new RedissonPromise<>();
//异步方式释放内部锁
RFuture<Boolean> future = unlockInnerAsync(threadId);
//取消看门狗机制
future.onComplete((opStatus, e) -> {
//取消到期续约
cancelExpirationRenewal(threadId);
if (e != null) {
result.tryFailure(e);
return;
}
if (opStatus == null) {
IllegalMonitorStateException cause = new IllegalMonitorStateException("attempt to unlock lock, not locked by current thread by node id: "
+ id + " thread-id: " + threadId);
result.tryFailure(cause);
return;
}
result.trySuccess(null);
});
return result;
}
protected abstract RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId);
7.3.3、unlockInnerAsync()(核心)
释放锁最重要的方法unlockInnerAsync
protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) {
return evalWriteAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
//判断是否存在key,也就是我们锁的名字,此ARGV[3]值是getLockName(threadId),得到类型UUID+线程Id的字段
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then " +
"return nil;" +
"end; " +
//存在key,则设置一个字段ARGV[3]的值减1
"local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); " +
//判断结果是否大于0
"if (counter > 0) then " +
//ARGV[2]过期时间
//大于0,则重新设置过期时间
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); " +
//返回0
"return 0; " +
"else " +
//小于0则删除key
"redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); " +
//KEYS[2]为getChannelName(),也就是:KEYS[1]__channel:{KEYS[1]}
//ARGV[1]为LockPubSub.unlckMessage,也就是0
//想通道中广播一个消息ARGV[1],内容也就是0
"redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
//返回1
"return 1; " +
"end; " +
"return nil;",
Arrays.asList(getRawName(), getChannelName()), LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
同样的参数KEYS[]和ARGV[],主要还是看下面这个
Arrays.asList(getRawName(), getChannelName()), LockPubSub.UNLOCK_MESSAGE, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
7.3.4、流程图
7.4、锁的续期
在tryAcquireAsync方法中有个看门狗,里面有段代码如下:
ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
return;
}
// lock acquired
if (ttlRemaining == null) {
if (leaseTime != -1) {
//过期时间转为毫秒
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
} else {
//计划到期续期,也就是刷新过期时间(重要)
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
});
7.4.1、scheduleExpirationRenewal()
这里的scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);就是实现了锁的续期,我们进去看看
protected void scheduleExpirationRenewal(long threadId) {
ExpirationEntry entry = new ExpirationEntry();
ExpirationEntry oldEntry = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.putIfAbsent(getEntryName(), entry);
if (oldEntry != null) {
oldEntry.addThreadId(threadId);
} else {
entry.addThreadId(threadId);
try {
//续期(重要)
renewExpiration();
} finally {
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
cancelExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
}
}
7.4.2、renewExpiration()(重要)
我们看下renewExpiration方法。
private void renewExpiration() {
ExpirationEntry ee = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());
if (ee == null) {
return;
}
//timeTask() 任务,过期时间的三分之一的时间开始执行,
//如果说起时间是30秒,那么第10秒的时候执行,再次设置为30秒,实际上对于这个key过期时间就变成了10秒+30秒=40秒
Timeout task = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
ExpirationEntry ent = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());
if (ent == null) {
return;
}
Long threadId = ent.getFirstThreadId();
if (threadId == null) {
return;
}
RFuture<Boolean> future = renewExpirationAsync(threadId);
future.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
log.error("Can't update lock " + getRawName() + " expiration", e);
EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.remove(getEntryName());
return;
}
if (res) {
// reschedule itself 也就是执行成功再次调用
renewExpiration();
} else {
//取消到期续期
cancelExpirationRenewal(null);
}
});
}
}, internalLockLeaseTime / 3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
ee.setTimeout(task);
}
7.4.3、renewExpirationAsync()(核心)
重要方法
protected RFuture<Boolean> renewExpirationAsync(long threadId) {
return evalWriteAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
//KEYS[1]是锁的名字, ARGV[2]是getLockName(threadId),得到类型UUID+线程Id的字段
//是否存在一个KEYS[1]对象,它的字段ARGV[2]的值为1
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
//存在则设置过期时间,ARGV[1]为过期时间
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return 1; " +
"end; " +
"return 0;",
Collections.singletonList(getRawName()),
internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
7.5、lua脚本
上面的锁的实现都用到了lua脚本,因为redis执行时是单线程的,redis会保证这个lua脚本的原子性,他会把这个lua脚本当成一行代码去执行,要么全部成功,要么全部失败。其中nil 类型表示一种没有任何有效值,它只有一个值nil,关于lua脚本大家可以去相关教程学习,我这里就简单写本文里见到的两个语法。
if(布尔表达式)
then
--[ 在布尔表达式为 true 时执行的语句 --]
end
if(布尔表达式)
then
--[ 布尔表达式为 true 时执行该语句块 --]
else
--[ 布尔表达式为 false 时执行该语句块 --]
end