知识点笔记
知识点笔记
一、 Java基础
- 暂无
二、Mybatis
1.什么是Mybaits?
从三个出发点介绍了什么是Mybatis,首先Mybatis是一个优秀的持久化框架,它支持自定义SQL查询、存储过程,和很好的一个映射。第二点Mybatis减少了大部分JDBC的代码,避免了手动设置参数和结果集的映射。第三点Mybatis用简单的XML配置文件或注解来配置映射关系,将接口和POJO对象映射到数据库记录中。
在使用传统JDBC时,我们往往需要写很多JDBC代码,需要自己写SQL语句以及自己装配参数,然后自己对结果集进行封装处理,而Mybatis帮我们简化了以上功能,只需要一些配置文件(xml)或是注解的方式即可完成对数据库的查询以及结果的映射封装。
2、Mybatis的优缺点:
1.sql语句与代码分离,存放于xml配置文件中:
优点:便于维护管理,不用在java代码中找这些语句;
缺点: JDBC方式可以用用打断点的方式调试,但是Mybatis不能,需要通过log4j日志输出日志信息帮助调试,然后在配置文件中修改。
2.用逻辑标签控制动态SQL的拼接:
优点:用标签代替编写逻辑代码;
缺点:拼接复杂SQL语句时,没有代码灵活,拼写比较复杂。不要使用变通的手段来应对这种复杂的语句。
3.查询的结果集与java对象自动映射:
优点:保证名称相同,配置好映射关系即可自动映射或者,不配置映射关系,通过配置列名=字段名也可完成自动映射。
缺点:对开发人员所写的SQL依赖很强。
4.编写原声SQL:
优点:接近JDBC,比较灵活。
缺点:对SQL语句依赖程度很高;并且属于半自动,数据库移植比较麻烦,比如mysql数据库编程Oracle数据库,部分的sql语句需要调整。
3、Mybatis中的#{}和${}的区别
- #{}是预编译处理,${}是字符串替换。
- #{}将传入的数据都当成一个字符串,会对自动传入的数据加一个双引号。如:select #{user_id} from user,如果传入的值是18,那么解析成sql时的值为select “18” from user , 如果传入的值是userId,则解析成的sql为select “userId” from user 。
- ${}将传入的数据直接显示生成在sql中。如:select ${user_id} from user 如果传入的值是111,那么解析成sql时的值为select 111 from user, 如果传入的值是id,则解析成的sql为 select id from user.
- #{}方式能够很大程度防止sql注入,${}方式无法防止Sql注入。
4、Mybatis表中和实体类的字段对应不上怎么办?
- 写SQL语句时起别名。
<select id=”selectorder” parametertype=”int” resultetype=”me.gacl.domain.order”>
select order_id as id, order_no as orderno ,order_price as price form orders where order_id=#{id};
select>
- 通过来映射字段名和实体类属性名的一 一对应的关系(resultMap)。
<resultMap type=”cn.soft.entity.order” id=”orderresultmap”>
<!–用id属性来映射主键字段–>
<id property=”id” column=”order_id”>
<!–用result属性来映射非主键字段,property为实体类属性名,column为数据表中的属性–>
<result property = “orderno” column =”order_no”/>
<result property=”price” column=”order_price” />
reslutMap>
<select id="getOrder" parameterType="int" resultMap="orderresultmap">
select * from orders where order_id=#{id}
select>
5、 使用MyBatis的mapper接口调用时有哪些要求?
- Mapper接口方法名和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的id相同;
- Mapper接口方法的输入参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql 的parameterType的类型相同;
- Mapper接口方法的输出参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的resultType的类型相同;
- Mapper.xml文件中的namespace即是mapper接口的类路径。
6、 模糊查询like语句该怎么写?
<select>
select * from user
where userName like #{userName}
select>
7、 在mapper中如何传递多个参数?
(1)第一种:
//DAO层的函数
Public UserselectUser(String name,String area);
//对应的xml,#{0}代表接收的是dao层中的第一个参数,#{1}代表dao层中第二参数,更多参数一致往后加即可。
<select id="selectUser"resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select * fromuser_user_t whereuser_name = #{0} anduser_area=#{1}
</select>
(2)第二种: 使用 @param 注解:
public interface usermapper {
user selectuser(@param(“username”) string username,@param(“hashedpassword”) string hashedpassword);
}
然后,就可以在xml像下面这样使用(推荐封装为一个map,作为单个参数传递给mapper):
<select id=”selectuser” resulttype=”user”>
select id, username, hashedpassword
from some_table
where username = #{username}
and hashedpassword = #{hashedpassword}
</select>
(3)第三种:多个参数封装成map
try{
//映射文件的命名空间.SQL片段的ID,就可以调用对应的映射文件中的SQL
//由于我们的参数超过了两个,而方法中只有一个Object参数收集,因此我们使用Map集合来装载我们的参数
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap();
map.put("start", start);
map.put("end", end);
return sqlSession.selectList("StudentID.pagination", map);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
sqlSession.rollback();
throw e; }
finally{
MybatisUtil.closeSqlSession();
}
8、 一对一、一对多的关联查询 ?
<mapper namespace="com.lcb.mapping.userMapper">
<!--association 一对一关联查询 -->
<select id="getClass" parameterType="int" resultMap="ClassesResultMap">
select * from class c,teacher t where c.teacher_id=t.t_id and c.c_id=#{id}
</select>
<resultMap type="com.lcb.user.Classes" id="ClassesResultMap">
<!-- 实体类的字段名和数据表的字段名映射 -->
<id property="id" column="c_id"/>
<result property="name" column="c_name"/>
<association property="teacher" javaType="com.lcb.user.Teacher">
<id property="id" column="t_id"/>
<result property="name" column="t_name"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<!--collection 一对多关联查询 -->
<select id="getClass2" parameterType="int" resultMap="ClassesResultMap2">
select * from class c,teacher t,student s where c.teacher_id=t.t_id and c.c_id=s.class_id and c.c_id=#{id}
</select>
<resultMap type="com.lcb.user.Classes" id="ClassesResultMap2">
<id property="id" column="c_id"/>
<result property="name" column="c_name"/>
<association property="teacher" javaType="com.lcb.user.Teacher">
<id property="id" column="t_id"/>
<result property="name" column="t_name"/>
</association>
<collection property="student" ofType="com.lcb.user.Student">
<id property="id" column="s_id"/>
<result property="name" column="s_name"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
</mapper>
9、 Mybatis 中一级缓存与二级缓存的区别?
缓存:合理使用缓存是优化中最常见的方法之一,将从数据库中查询出来的数据放入缓存中,下次使用时不必从数据库查询,而是直接从缓存中读取,避免频繁操作数据库,减轻数据库的压力,同时提高系统性能。
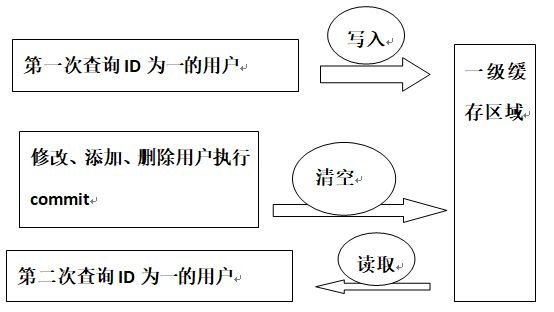
- 一级缓存是SqlSession级别的缓存:
Mybatis对缓存提供支持,但是在没有配置的默认情况下,它只开启一级缓存。一级缓存在操作数据库时需要构造sqlSession对象,在对象中有一个数据结构用于存储缓存数据。不同的sqlSession之间的缓存数据区域是互相不影响的。也就是他只能作用在同一个sqlSession中,不同的sqlSession中的缓存是互相不能读取的。
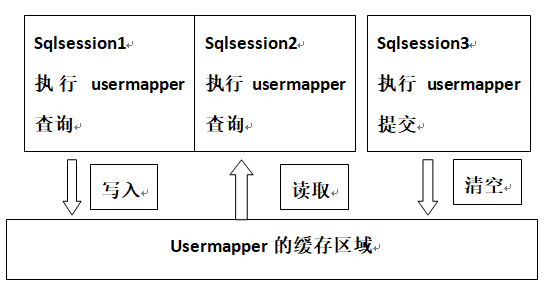
- 二级缓存是mapper级别的缓存:
MyBatis的二级缓存是mapper级别的缓存,它可以提高对数据库查询的效率,以提高应用的性能。多个SqlSession去操作同一个Mapper的sql语句,多个SqlSession可以共用二级缓存,二级缓存是跨SqlSession的。
开启二级缓存:
A.mybatis.xml配置文件中加入:
<span style="font-size:18px;"><settings>
<!--开启二级缓存-->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings> </span>
B.在需要开启二级缓存的mapper.xml中加入caceh标签
<span style="font-size:18px;"><cache/></span>
···
C.让使用二级缓存的POJO类实现Serializable接口
```sql
<span style="font-size:18px;">public class User implements Serializable {}</span>
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/yuluoxingkong/p/8205858.html
10、Mybatis动态sql是什么意思?常用的标签有哪些和用途?
传统jdbc方法中,在写组合的多表复杂sql语句时,需要去拼接sql语句,稍不注意少写一个空格或“”,就会导致报错。
这个Mybatis动态sql的功能,就拥有有效的解决了这个问题,Mybatis动态sql语言可以被用在任意的sql语句映射中。
Mybatis采用强大的功能基于OGNL的表达式消除其他元素。
- 常用的标签:
1. if:非空验证 如id为空时,if标签里的代码,则不会执行。反之,就会if标签里的代码。
<select id = "getByCon">
select * from user where userName = 'zhangsan'
<if test="password != null and title != null">
and password = #{password} and title = #{title}
<if/>
</select>
2. choose:choose(when,otherwise)标签相当于switch(case,default),如title为空时,when标签里的代码,则不执行。默认会执行otherwise表签里的代码。
select * from user where userName = 'zhangsan'
<choose>
<when test="title != null"> <!--如果符合条件不会执行otherwise-->
and title like #{title}
</when>
<otherwise> <!--如果when条件不符合默认执行otherwise-->
and password = #{password}
</otherwise>
</choose>
3. set:set标签功能和where标签差不多,sql标签代表了sql中的关键字,set表签可以自动去除sql中多余的“,”。
<update id = "">
update user
<set>
<if test = "userName != null">
userName = #{userName}
</if>
</set>
<where>
<if test = "id != null">
id = #{id}
</if>
</where>
</update>
11、 为什么说 Mybatis 是半自动 ORM 映射工具?它与全自动的区别在哪里
规范化Hibernate 属于全自动 ORM 映射工具,使用 Hibernate 查询关联对象或者关联集合对象 时,可以根据对象关系模型直接获取,所以它是全自动的。而 Mybatis 在查询关联对象或 关联集合对象时,需要手动编写 sql 来完成,所以,称之为半自动 ORM 映射工具。