详解优先级队列(堆)
目录
一、堆的概念以及堆的创建
1、堆的概念
2、堆的创建
二、堆的方法的构建
2.1 入队列操作
2.2出队列操作
2.3查看头元素
三、优先级队列(堆)方法的使用
3.1堆的初始化(大堆和小堆的创建)
四、堆排序(大堆)
五、查找和最小的K对数字
5.1利用小堆来实现
5.2利用大堆来实现
一、堆的概念以及堆的创建
1、堆的概念
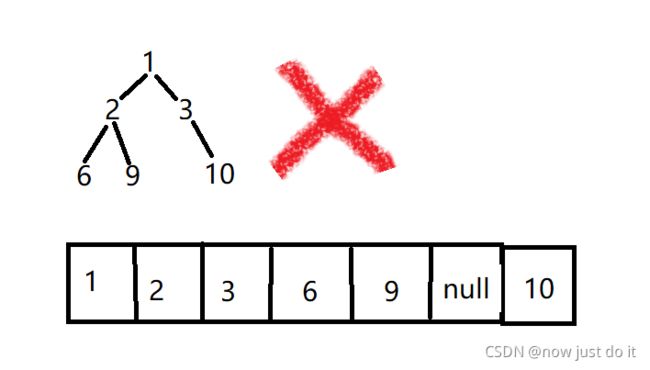
什么是堆?(堆的逻辑上是一个完全二叉树,实际上是保存在数组中)
我们把一个完全二叉树通过层序遍历存储到数组当中,这个数组就叫做堆。
注意:堆中的元素不能为空。(浪费大量空间)
什么是大根堆和小根堆?
大根堆:所有结点的值都大于其子结点的值,我们称为大根堆。
小根堆:所有结点的值都小于其子结点的值,我们称为小根堆。
注意:父亲结点为i时,左孩子的结点为i*2+1,右孩子的结点为i*2+2;
孩子结点为i时,父亲结点为(i-1)/2;
2、堆的创建
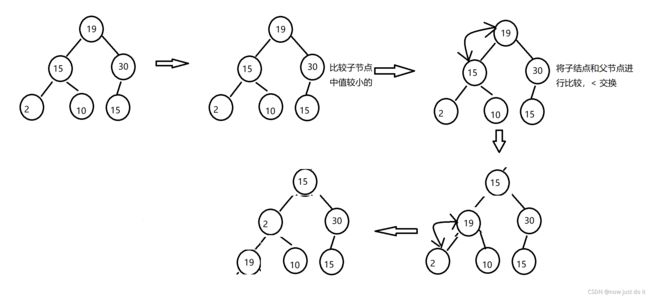
2.1向下遍历
对于堆中的排序我们可以采用向下遍历的方法,我们就拿小堆的向下遍历来做例子。
2.2建堆操作
由于堆的底层是数组,我们开始要创建一个数组并且初始化。
public class TestHeap {
public int[] elem;
public int uesdSize;
public TestHeap(){
this.elem=new int[10];
}
}接下来我们要将一段无序的数组放进去,并且通过elem数组拷贝进来,同时我们通过由下向上不断遍历由上向下的函数。
public void createBigHeap(int[] array){
for(int i=0;i=0;i--){
shiftDown(i);
}
} 接下来我们编写由上向下的函数shiftDown(i);
public void shiftDown(int parent){
int child=parent*2+1;
while (childthis.elem[child]){
int temp=this.elem[parent];
this.elem[child]=this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent]=temp;
parent=child;
child=child*2+1;
}else {
break;
}
}
} 注意:一般来说for循环的时间复杂度为N,shiftDown的时间复杂度为logN,所以为O(N*logN),但是实际上为O(N);
二、堆的方法的构建
2.1 入队列操作
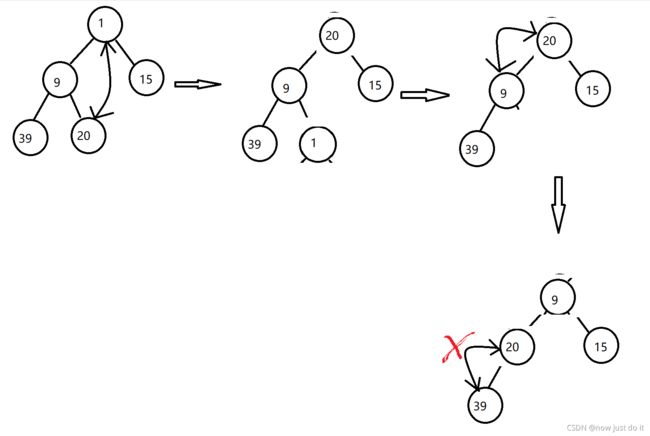
对于入队列操作我们采用向上遍历的方法。
我们入队列时,先判断是否满了,然后我们将入队列的值放入数组的最后一个,将它和他的父亲节点进行比较,若小于进行交换,一直循环到父亲节点小于0;
public boolean isFull(){
return this.elem.length==this.usedSize;
}
public void push(int val){
if(isFull()){
this.elem=Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
this.elem[this.usedSize]=val;
this.usedSize++;
shiftUp(this.usedSize-1);
}
public void shiftUp(int child){
int parent=(child-1)/2;
while (parent>=0){
if(this.elem[parent]>this.elem[child]){
int temp=this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent]=this.elem[child];
this.elem[child]=temp;
child=parent;
parent=(parent-1)/2;
}else{
break;
}
}
}2.2出队列操作
对于出队列的操作时,我们先让头和尾互换,然后将头向下遍历就行了。
public int pop(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("为空不能取出");
}
int temp=this.elem[0];
this.elem[0]=this.elem[this.usedSize-1];
this.elem[this.usedSize-1]=temp;
this.usedSize--;
shiftDown(0);
return temp;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.usedSize==0;
}2.3查看头元素
和出队列操作差不多,不用交换和去除。
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.usedSize==0;
}
public int peek(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("为空不能取出");
}
return this.elem[0];
}三、优先级队列(堆)方法的使用
PriorityQueue是优先级队列
下面的它的方法和使用:
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue pq=new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.offer(1);
pq.offer(2);
pq.offer(3);
System.out.println(pq.poll());
System.out.println(pq.poll());
System.out.println(pq.poll());
//1 2 3
} 我们可以看出PriorityQueue使用时是一个小堆。
3.1堆的初始化(大堆和小堆的创建)
对于大堆和小堆的创建我们需要重写Comparator方法来进行操作。
我们使用匿名内部类进行编写详细方法如下:
小堆:
PriorityQueue queue=new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1-o2;
}
}); 大堆:
PriorityQueue queue=new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2-o1;
}
}); 我们也可以简写为:(在做题中我们可以使用)
小堆:
PrioritQueue pq=new PriorityQueue<>((x,y) -> (x-y)); 大堆:
PriorityQueue pq=new PriorityQueue<>((x,y) -> (y-x)); 四、堆排序(大堆)
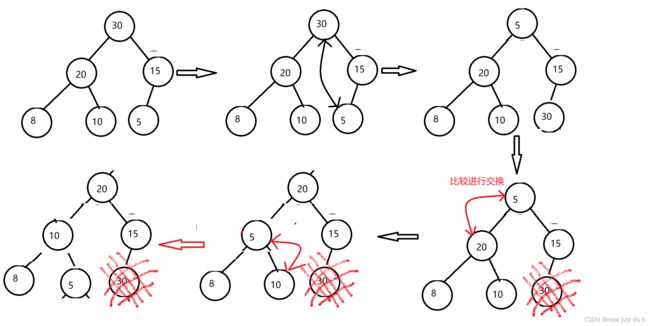
我们先将数组变成大堆,然后将第一个数和最后一个数进行交换,这时将最大的一个数就确定下来了,固定这个数,将第一个数进行排序,重复上述过程。
代码实现:
//堆排序
public void heapSory(){
int end=this.usedSize-1;
while (end>0){
int temp=this.elem[0];
this.elem[0]=this.elem[end];
this.elem[end]=temp;
shiftDown01(0,end);
end--;
}
}
public void shiftDown01(int parent,int k){
int child=parent*2+1;
while (childthis.elem[child]){
child++;
}
if(this.elem[child]>this.elem[parent]){
int temp=this.elem[child];
this.elem[child]=this.elem[parent];
this.elem[parent]=temp;
parent=child;
child=child*2+1;
}else{
break;
}
}
} 五、查找和最小的K对数字
力扣链接:题目链接。
5.1利用小堆来实现
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class Data{
public int val01;
public int val02;
public Data(int val01,int val02){
this.val01=val01;
this.val02=val02;
}
public int get01(){
return this.val01;
}
public int get02(){
return this.val02;
}
}
public class Test01 {
public List> kSmallestPairs(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int k) {
List> list=new ArrayList<>();
PriorityQueue pq=new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Data o1, Data o2) { //小堆
return (o1.get01()+o1.get02())-(o2.get01()+o2.get02());
}
});
for(int i=0;i list1=new ArrayList<>();
Data temp=pq.poll();
list1.add(temp.get01());
list1.add(temp.get02());
list.add(list1);
}
return list;
}
} 5.2利用大堆来实现
public class Test03 {
public List> kSmallestPairs(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int k) {
PriorityQueue> pq=new PriorityQueue<>
(new Comparator>() {
@Override
public int compare(List o1, List o2) {
return (o2.get(0)+o2.get(1))-(o1.get(0)+o1.get(1));//大堆
}
});
for(int i=0;i list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(nums1[i]);
list.add(nums2[j]);
pq.offer(list);
}else{
int temp=pq.peek().get(0)+pq.peek().get(1);
if(temp>nums1[i]+nums2[j]){
pq.poll();
List list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(nums1[i]);
list.add(nums2[j]);
pq.offer(list);
}
}
}
}
List> lists=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i 注意:要判断一些临界条件,一定要注意。