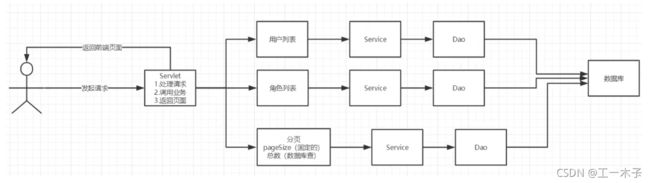
javaweb-35:smbms用户管理底层实现
用户管理实现
思路:
1.导入分页的工具类
package com.gongyi.util;
public class PageSupport {
//当前页码-来自于用户输入
private int currentPageNo = 1;
//总数量(表)
private int totalCount = 0;
//页面容量
private int pageSize = 0;
//总页数-totalCount/pageSize(+1)
private int totalPageCount = 1;
public int getCurrentPageNo() {
return currentPageNo;
}
public void setCurrentPageNo(int currentPageNo) {
if (currentPageNo > 0) {
this.currentPageNo = currentPageNo;
}
}
public int getTotalCount() {
return totalCount;
}
//OOP三大特性:封装(属性私有,set/get,在set中限定一些不安全的情况),继承,多态
public void setTotalCount(int totalCount) {
if (totalCount > 0) {
this.totalCount = totalCount;
//设置总页数
this.setTotalPageCountByRs();
}
}
public void setTotalPageCountByRs() {
if (this.totalCount % this.pageSize == 0) {
this.totalPageCount = this.totalCount / this.pageSize;
} else if (this.totalCount % this.pageSize == 0) {
this.totalPageCount = this.totalCount / this.pageSize + 1;
} else {
this.totalPageCount = 0;
}
}
public int getPageSize() {
return pageSize;
}
public void setPageSize(int pageSize) {
if (pageSize > 0) {
this.pageSize = pageSize;
}
}
public int getTotalPageCount() {
return totalPageCount;
}
public void setTotalPageCount(int totalPageCount) {
this.totalPageCount = totalPageCount;
}
}
2.用户列表页面导入
userlist.jsp
1、获取用户数量
1.UserDao
//根据用户名或者角色查询用户总数
int getUserCount(Connection connection, String username, int userRole) throws SQLException;
2.UserDaoImpl
//根据用户名或者角色查询用户总数【最难理解的sql】
@Override
public int getUserCount(Connection connection, String username, int userRole) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
int count = 0;
if (connection != null) {
StringBuffer sql = new StringBuffer();
sql.append("select count(1) as count from smbms_user u,smbms_role r where u.userRole=r.id");
ArrayList<Object> list = new ArrayList<>();//存放我们的参数
if (!StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(username)) {
sql.append(" and u.userName like ?");
list.add("%" + username + "%");//index:0
}
if (userRole > 0) {
sql.append(" and u.userRole = ?");
list.add(userRole);//index:1
}
//怎么把list转化为数组
Object[] params = list.toArray();
System.out.println("UserDaoImpl->getUserCount:" + sql.toString());//输出最后完整的SQL语句
rs = BaseDao.execute(connection, pstm, rs, sql.toString(), params);
if (rs.next()) {
count = rs.getInt("count");//从结果集中获取最终的数量
}
BaseDao.closeResource(null, pstm, rs);
}
return count;
}
3.UserService
//查询记录数
int getUserCount(String username,int userRole);
4.UserServiceImpl
//查询记录数
@Override
public int getUserCount(String username, int userRole) {
Connection connection = null;
int count = 0;
try {
connection = BaseDao.getConnection();
count = userDao.getUserCount(connection, username, userRole);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
BaseDao.closeResource(connection, null, null);
}
return count;
}
@Test
public void testUserCount() {
UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl();
int userCount = userService.getUserCount(null, 2);
System.out.println(userCount);
}
2、获取用户列表
1.UserDao
//通过条件查询-userList
List<User> getUserList(Connection connection, String userName, int userRole, int currentPageNo, int pageSize) throws SQLException;
2.UserDaoImpl
@Override
public List<User> getUserList(Connection connection, String userName, int userRole, int currentPageNo, int pageSize) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement pstm = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<User>();
if (connection != null) {
StringBuffer sql = new StringBuffer();
sql.append("select u.*,r.roleName as userRoleName from smbms_user u,smbms_role r where u.userRole=r.id ");
List<Object> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (!StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(userName)) {
sql.append(" and u.userName like ?");
list.add("%" + userName + "%");
}
if (userRole > 0) {
sql.append(" and u.userRole = ?");
list.add(userRole);
}
//在数据库中,分页使用 limit startIndex,pageSize;总数
//当前页(当前页-1)*页面大小
//0,5 1 0 01234
//5,5 2 5 56789
//10,5 3 10
sql.append(" order by creationDate DESC limit ?,?");
currentPageNo = (currentPageNo - 1) * pageSize;
list.add(currentPageNo);
list.add(pageSize);
Object[] params = list.toArray();
System.out.println("sql--->" + sql.toString());
rs = BaseDao.execute(connection, pstm, rs, sql.toString(), params);
while (rs.next()) {
User _user = new User();
_user.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
_user.setUserCode(rs.getString("userCode"));
_user.setUserName(rs.getString("userName"));
_user.setGender(rs.getInt("gender"));
_user.setBirthday(rs.getDate("birthday"));
_user.setPhone(rs.getString("phone"));
_user.setUserRole(rs.getInt("userRole"));
_user.setUserRoleName(rs.getString("userRoleName"));
userList.add(_user);
}
BaseDao.closeResource(null, pstm, rs);
}
return userList;
}
3.UserService
//根据条件查询用户列表
List<User> getUserList(String queryUserName, int queryUserRole, int currentPageNo, int pageSize);
4.UserServiceImpl
@Override
public List<User> getUserList(String queryUserName, int queryUserRole, int currentPageNo, int pageSize) {
Connection connection = null;
List<User> userList = null;
System.out.println("queryUserName --- >" + queryUserName);
System.out.println("queryUserRole --- >" + queryUserRole);
System.out.println("currentPageNo --- >" + currentPageNo);
System.out.println("pageSize --- >" + pageSize);
try {
connection = BaseDao.getConnection();
userList = userDao.getUserList(connection, queryUserName, queryUserRole, currentPageNo, pageSize);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
BaseDao.closeResource(connection, null, null);
}
return userList;
}
@Test
public void testUserList() {
UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl();
List<User> userList = userService.getUserList("系统管理员", 1, 1, 10);
System.out.println(userList.size());
}
彩蛋
1.学习时开启两个tomcat,一个学习用,一个方便调试用(成品)
2.流程图软件与架构师
process.cn
3.实体类的set方法是可以做一些判断的,防止非法输入【OOP之封装完美体现】
4.select count(1)与count(*) 区别?
因为使用count(*)的时候会对所有的列进行扫描,相比而言count(1)不用扫描所有列,所以count(1)要快一些
5.默认idea实现接口方法时,无@Override,是因为idea默认jdk compile level是1.5,而注解是1.5之后引入的
6.原始dao拼接sql的弊端
繁琐,容易写错,反人类
7.Integer使用与int使用
慎用Integer,因为可能空指针