MapReduce编程模型和原理
MapReduce编程模型和原理
- 推荐书籍:《Hadoop权威指南》第四版
1. MapReduce编程模型
- MapReduce是采用一种分而治之的思想设计出来的分布式计算框架
- 如一项复杂的计算任务,单台服务器无法胜任时,可将此大任务切分成一个个小的任务,分别交给不同的服务器上并行执行,最终再汇总每个小任务的结果
- MapReduce由两个阶段组成:Map阶段(切分成一个个小的任务),Reduce阶段(汇总小任务的结果)
1.1 Map阶段
map task的map()函数以key-value对作为输入,产生一系列kv对作为中间输出写入本地磁盘。
详细过程:
- 首先读取HDFS中的文件,每个文件都以一个个block形式存在,block中的一行数据解析成一个key-value对,并且每一个kv对会调用一次map task中的map函数
- map函数对第一步接收到的kv对进行处理,转换输出为新的kv对。
- 然后对输出的kv对进行分区和排序分组(shuffle处理这个中间结果),存放到本地磁盘中,供后续reduce作为输入参数调用。
1.2 Reduce阶段
reduce()函数通过网络将map的输出(kv对)作为输入,产生另一系列kv对作为最终输出写入到hdfs,这时的key-value对是计算结果。
- reduce函数将多个map任务的输出,按照不同的分区,通过网络复制到不同的reduce task节点上进行合并,排序,这个过程也叫shuffle(洗牌),就像洗零散的扑克牌一样。
- reduce函数对输入的kv对处理,转换成新的kv对
- 最后把reduce的输出保存到hdfs文件中。
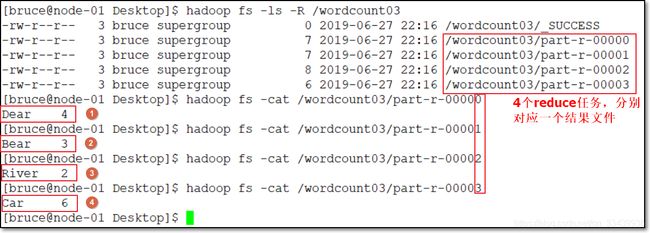
2. MapReduce编程示例
- 以词频统计为例(略)
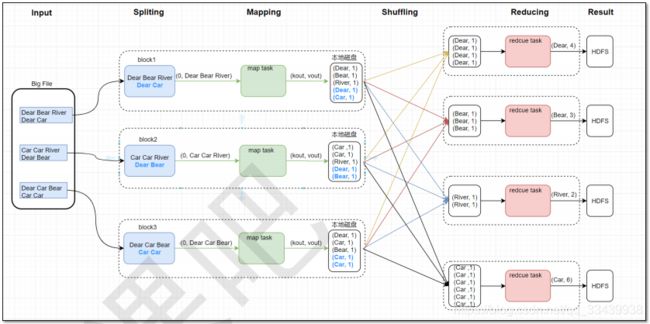
2.1 MapReduce原理图
-
参考以上map和reduce阶段的合并,本文最后会做总结。
-
block对应一个分配split,一个split对应一个map task
2.2 MR参考代码
- hadoop的api类链接:https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r3.1.2/api/index.html
2.2.1 Mapper代码
这里主要用到hadoop自带的一个mapper类,原本在传输过程中需要做一个序列化和反序列化,而hadoop直接将这两个步骤给写到了mapper这个类里面,(LongWrite,Text,Text,IntWritable)
package com.kaikeba.hadoop.wordcount;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
public class WordCountMap extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
public void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//dear bear river
String[] words = value.toString().split("\t");
for (String word : words) {
// 每个单词出现1次,作为中间结果输出
context.write(new Text(word), new IntWritable(1));
}
}
}
2.2.2 Reducer代码
这里Reducer也是hadoop自带的类,它接受的输入参数类型和mapper的输出参数类型是一致的。
public class WordCountReduce extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
/*
(hello, 1)
(hello, 1)
(hello, 1)
...
(spark, 1)
key: hello
value: List(1, 1, 1)
*/
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,
Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable count : values) {
sum += count.get();
}
context.write(key, new IntWritable(sum));// 输出最终结果
};
}
2.2.3 Main程序入口
public class WordCountMain { //若在IDEA中本地执行MR程序,需要将mapred-site.xml中的mapreduce.framework.name值修改成local public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException { if (args.length != 2 || args == null) { System.out.println("please input Path!"); System.exit(0); } Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); //configuration.set("mapreduce.job.jar","/home/bruce/project/kkbhdp01/target/com.kaikeba.hadoop-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar"); //调用getInstance方法,生成job实例 Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration, WordCountMain.class.getSimpleName()); // 打jar包 job.setJarByClass(WordCountMain.class); // 通过job设置输入/输出格式 // MR的默认输入格式是TextInputFormat,所以下两行可以注释掉 // job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class); // job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class); // 设置输入/输出路径 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); // 设置处理Map/Reduce阶段的类 job.setMapperClass(WordCountMap.class); //map combine减少网路传出量 job.setCombinerClass(WordCountReduce.class); job.setReducerClass(WordCountReduce.class); //如果map、reduce的输出的kv对类型一致,直接设置reduce的输出的kv对就行;如果不一样,需要分别设置map, reduce的输出的kv类型 //job.setMapOutputKeyClass(.class) // job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); // job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); // 设置reduce task最终输出key/value的类型 job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); // 提交作业 job.waitForCompletion(true); } }
2.3 本地运行
本地运行前,要把idea项目下的mapred-site.xml的mapreduce.framework.name对应的value改成“local”
2.4 集群方式
2.4.1 方式一_java代码
2.4.2 方式二
- 用maven将项目打包(jar包)
- 用命令行运行程序
[hadoop@node1 ~]# hadoop jar jar包的路径 jar包中类的完整类名 hdfs上需统计的文件路径 输出hdfs路径
[hadoop@node1 ~] hadoop jar com.kaikeba.hadoop-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar com.kaikeba.hadoop.wordcount.WordCountMain /NOTICE.txt /wordcount01
#假如输入路径有加端口号,那么输出路径也需要加端口号
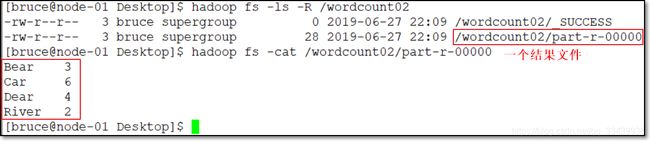
3. Web UI查看结果
3.1 yarn
3.2 HDFS结果
4. Combiner
正常情况下,Hadoop框架使用Mapper将数据处理成一个key-value键值对,在网络节点间对其整理(shuffle洗牌),然后再使用Reduce处理数据并进行最终输出。
但是在中间网络节点整理的这个shuffle过程中,如果数据量很大(假设100亿),而需求只是求一个最大值,那么单个Reduce需要承载的kv对数量也将是庞大的,会降低程序的性能。
于是出现Combiner,就是为了避免map task和reduce task之间的数据传输压力而设置的,它允许用户针对map task的输出指定一个合并函数,减少传输到reduce的数据量,从而减少网络带宽和reduce的负载。
- combiner会压缩key-value中具有同一key值的键值对。
- map端本地合并,不论运行多少次combiner操作,都不会影响最终结果。combiner只是作为可选的操作。
- 并非所有的mr都适合combine操作,比如求平均值就不适合。
下面是combiner部分的代码:
- WordCountMap和WordCountReduce代码不变
- WordCountMain中增加job.setConbinerClass(WordCountReduce.class)
package com.kaikeba.hadoop.wordcount;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
public class WordCountMain {
//若在IDEA中本地执行MR程序,需要将mapred-site.xml中的mapreduce.framework.name值修改成local
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException,
ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
if (args.length != 2 || args == null) {
System.out.println("please input Path!");
System.exit(0);
}
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
//configuration.set("mapreduce.job.jar","/home/bruce/project/kkbhdp01/target/com.kaikeba.hadoop-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar"); 集群调用的方式
//调用getInstance方法,生成job实例
Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration, WordCountMain.class.getSimpleName());
// 打jar包
job.setJarByClass(WordCountMain.class);
// 通过job设置输入/输出格式
// MR的默认输入格式是TextInputFormat,所以下两行可以注释掉
// job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
// job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
// 设置输入/输出路径
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
// 设置处理Map/Reduce阶段的类
job.setMapperClass(WordCountMap.class);
//map combine减少网路传出量
job.setCombinerClass(WordCountReduce.class);
job.setReducerClass(WordCountReduce.class);
//如果map、reduce的输出的kv对类型一致,直接设置reduce的输出的kv对就行;如果不一样,需要分别设置map, reduce的输出的kv类型
//job.setMapOutputKeyClass(.class)
// job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
// job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 设置reduce task最终输出key/value的类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
// 提交作业
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
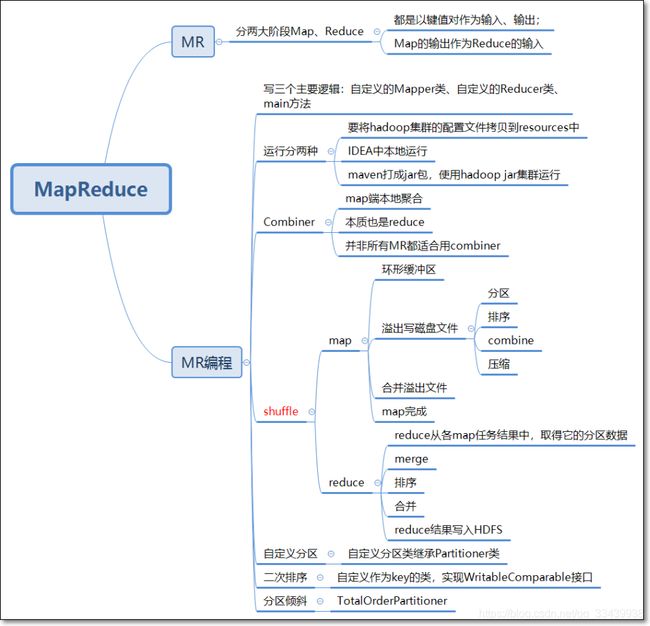
5. Shuffle
hadoop的shuffle过程实际上包含在map阶段和Reduce阶段,即分为Map Shuffle和Reduce Shuffle。
5.1 Map Shuffle
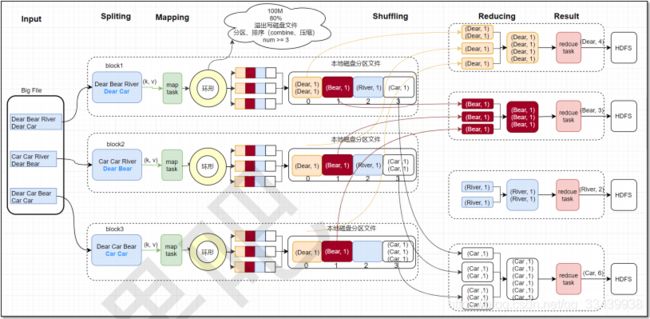
在Map端的shuffle过程是对Map的结果进行分区、排序、分割,然后将属于同一划分(分区)的输出合并在一起并写在磁盘上,最终得到一个分区有序的文件。分区有序的含义是map输出的键值对按分区进行排列,具有相同partition值的键值对存储在一起,每个分区里面的键值对又按key值进行升序排列(默认)。
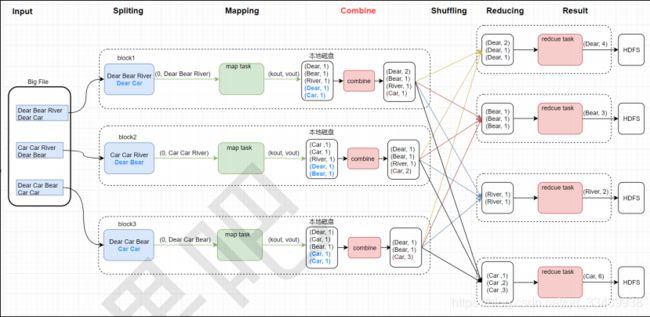
结合第二张图片,map的shuffle大致流程如下:
- 从map task输出的kv对数据会先存入到环形缓冲区中,环形缓冲区大小为100m,当数据在环形缓冲区存储满80%时,就会溢出写入磁盘文件。
- 在写入磁盘文件过程中,会对kv对数据进行HashPartition分区和对key排序,之后会判断是否需要combine压缩具有同一键的键值对数据。
- 最后作为map输出传输出去。
5.2 Reduce Shuffle
在Reduce端,shuffle主要通过网络向磁盘获取reduce需要的数据,一般是把key相同的键值对数据放到一起,然后排序合并,最终输出一个整体有序的数据块。
还是参考第二张图片
但是这里要注意的是,虽然叫做Reduce shuffle,但实际是不包含调用reduce方法的。完整的shuffle是从map输出kv对到内存,再到调用reduce方法之前的这个过程。
6. 自定义分区Partition
- Map自带的分区器是HashPartitioner,如下图所示。
- 对于从map输出的key-value键值对,先根据key求hash值,然后模上reduce task个数,得出分区号,根据分区号决定输出kv对。
6.1 默认分区
默认按字典字母升序排序。
-
读取文件customPartition.txt,内容如下:
Dear River Dear River Bear Car Car Dear Car Bear Car Dear Car Bear Car
结果如下:
6.2 自定义分区
- 主要继承Partitioner,将getPartition方法根据key返回固定值。可以看到dist这里的kv对其实是写死了的。
package com.kaikeba.hadoop.partitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
import java.util.HashMap;
//传如的是
public class CustomPartitioner extends Partitioner<Text, IntWritable> {
public static HashMap<String, Integer> dict = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
static{
dict.put("Dear", 0);
dict.put("Bear", 1);
dict.put("River", 2);
dict.put("Car", 3);
}
public int getPartition(Text text, IntWritable intWritable, int i) {
//这里做了一个自定义逻辑,它是直接判断dist上写的value是多少来做分区的
int partitionIndex = dict.get(text.toString());
return partitionIndex;
}
}
- 运行结果
7. 二次排序
MapReduce中,根据key进行分区,排序,分组。MapReduce会按照基本类型对应的key进行排序,比如int类型intwritable,默认升序排序,取反则降序排序。
但如果这时有需求要对工资排序,若工资相同,则继续对年龄排序,则需要自定义key类型,并自定义key的排序规则。
-
现有需求,需要自定义key类型,并自定义key的排序规则,如按照人的salary降序排序,若相同,则再按age升序排序;若salary、age相同,则放入同一组
-
详见工程代码
-
Person.java
//Comparable比较,Writable序列化
public class Person implements WritableComparable<Person> {
private String name;
private int age;
private int salary;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, int age, int salary) {
//super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(int salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
//设置输出的格式
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.salary + " " + this.age + " " + this.name;
}
//先比较salary,高的排序在前;若相同,age小的在前
//int类型默认升序排序,取反就降序排序
public int compareTo(Person o) {
int compareResult1= this.salary - o.salary;
if(compareResult1 != 0) {
return -compareResult1;
} else {
return this.age - o.age;
}
}
//序列化,将NewKey转化成使用流传送的二进制
public void write(DataOutput dataOutput) throws IOException {
dataOutput.writeUTF(name);
dataOutput.writeInt(age);
dataOutput.writeInt(salary);
}
//反序列化,使用in读字段的顺序,要与write方法中写的顺序保持一致
public void readFields(DataInput dataInput) throws IOException {
//read string
this.name = dataInput.readUTF();
this.age = dataInput.readInt();
this.salary = dataInput.readInt();
}
}
- SecondarySort.java
public class SecondarySort {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.set("mapreduce.job.jar","/home/bruce/project/kkbhdp01/target/com.kaikeba.hadoop-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar");
Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration, SecondarySort.class.getSimpleName());
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(URI.create(args[1]), configuration);
if (fileSystem.exists(new Path(args[1]))) {
fileSystem.delete(new Path(args[1]), true);
}
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
job.setMapperClass(MyMap.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Person.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
//设置reduce的个数
job.setNumReduceTasks(1);
job.setReducerClass(MyReduce.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Person.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
public static class MyMap extends
Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Person, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value,
Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] fields = value.toString().split("\t");
String name = fields[0];
int age = Integer.parseInt(fields[1]);
int salary = Integer.parseInt(fields[2]);
//在自定义类中进行比较
Person person = new Person(name, age, salary);
context.write(person, NullWritable.get());
}
}
public static class MyReduce extends
Reducer<Person, NullWritable, Person, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Person key, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write(key, NullWritable.get());
}
}
}
8. MapReduce分区倾斜
-
什么是数据倾斜?
简单书数据倾斜就是数据的key值 分化严重不均,造成一部分数据很多,一部分数据很少,出现离群值。就拿广东一年四季的气温成正态分布来说,一年的气温集中在25°到35°之间,而其他温度比较少,这个集中值在数据中就容易出现数据倾斜。
-
数据倾斜会显著的拖慢MR的执行,因为如果有些数据量分布少,就能提前执行完,但它要继续等待数据量多的mr任务。
-
常见的数据倾斜有以下两类:
- 数据频率倾斜——某一个区域的数据量要远远大于其他区域。比如某一个key对应的键值对数量远远大于其他键的键值对数量。
- 数据大小倾斜——部分数据记录的大小远远大于平均值。
阿里的ADS库中也有防止数据倾斜的办法,通常是修改表结构,增加聚集列等。
-
在map端和reduce端都有可能发生数据倾斜。在reduce端的数据倾斜常常来源于MapReduce的默认分区器。
数据倾斜会导致map和reduce的任务执行时间大为延长,也会让缓存数据操作消耗更多的内存资源。
8.1 如何诊断发现是否有数据倾斜的存在?
- 在reduce方法中添加变量追踪每个键的最大值,为了减少追踪量,可以设置数据量阈值,只追踪哪些大于阈值(yu)的键,然后输出到日志信息。
- 另一种是关注map的输出数据中是否有数据频率倾斜问题,通常可以在业务层面判断自定义分区键是否合理。
下面是第一种方法的类似代码,新增maxValueThreshold变量判断。
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import java.io.IOException;
public class WordCountReduce extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
private int maxValueThreshold;
//日志类
private static final Logger LOGGER = Logger.getLogger(WordCountReduce.class);
@Override
protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//一个键达到多少后,会做数据倾斜记录
maxValueThreshold = 10000;
}
/*
(hello, 1)
(hello, 1)
(hello, 1)
...
(spark, 1)
key: hello
value: List(1, 1, 1)
*/
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,
Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
//用于记录键出现的次数
int i = 0;
for (IntWritable count : values) {
sum += count.get();
i++;
}
//如果当前键超过10000个,则打印日志
if(i > maxValueThreshold) {
LOGGER.info("Received " + i + " values for key " + key);
}
context.write(key, new IntWritable(sum));// 输出最终结果
};
}
8.2 减缓Reduce数据倾斜的重要方法(面试可能考)
-
Reduce数据倾斜一般是指map的输出数据中存在数据频率倾斜的状况,即部分输出键的数据量远远大于其它的输出键
-
如何减小reduce端数据倾斜的性能损失?常用方式有:
- 抽样和范围分区(重要)
Hadoop默认的分区器是HashPartitioner,基于map输出键的哈希值分区。这仅在数据分布比较均匀时比较好。在有数据倾斜时就很有问题。
使用分区器需要首先了解数据的特性。TotalOrderPartitioner中,可以通过对原始数据进行抽样得到的结果集来预设分区边界值。TotalOrderPartitioner中的范围分区器可以通过预设的分区边界值进行分区。因此它也可以很好地用在矫正数据中的部分键的数据倾斜问题。
简单来说,就是TotalOrderPartitioner能采样得知哪些键的数据量大,然后按照采样结果寻找key值的最佳分割点,将key-value对均匀的分布到不同分区中。
- 自定义分区
基于输出键的业务知识进行自定义分区。例如,淘宝一年的销售数据可能集中在双十一活动上,那么就把双十一的销售数据值均分给其他时间段的来分区。
- Combine
使用Combine可以大量地减小数据频率倾斜和数据大小倾斜。
- 限制ReduceReader读取键值对的最大长度(在mapreduce.input.linerecordreader.line.maxlength方法中)
9.MR总结
9.1 整个过程概括
-
MR程序读取HDFS的文件
-
文件分片成block,每一行数据解析成键值对
-
Map阶段
- 键值对调用map()方法
- map输出写入环形缓冲区(100M)
- 溢出写入磁盘文件,其中会错以下操作:
- HashPartitioner做分区
- 排序
- Combine,压缩
- 合并溢出文件
-
Reduce阶段
- 从各个map任务结果中,取得它需要的分区数据
- 合并写入Reduce的JVM内存
- 溢出写入磁盘,期间可选combine
- 磁盘再次合并排序
- 调用reduce()方法
-
reduce方法输出写入到HDFS文件系统。
9.2细节描述过程
(1)MR读取HDFS的文件,将文件分片成一个个block,并且block的每一行解析成key-value键值对。
(2)键值对调用map阶段的map()方法,输出的数据存入一个环形缓冲区,该环形缓冲区为100M大小,当输出数据存满这个缓冲区的80%内存后,就会溢出写入磁盘。
(3)在溢出写入磁盘的过程中,会做以下几个操作:
- 第一个是分区,基于map方法输出键值对的key做Hash计算,并与reduce task的个数做模运算确定分区号,后续将同一分区号的键值对数据交由同一个reduce处理。
- 第二个是排序,对每个分区中的键值进行排序,先按照键排序,对于键相同的再按照值排序。
- 第三个是可选的Combine压缩,不论是否运行combine操作,都不会影响最终结果,而combine操作可以避免map task到reduce task之间的数据传输压力,可以压缩key-value中具有同一key值的键值对。
(4)然后到map阶段的最后一步,在磁盘中将溢出的键值对合并输出。
(5)Reduce task从各个map任务结果中,获取它需要的分区数据,合并写入JVM内存;
(6)同样当内存达到一定阈值后会将数据写入到磁盘,如果指定了combine,运行它会减少写入磁盘的数据量。
(7)随着磁盘文件或者内存文件的增多,还会进行合并排序,将最后一次合并的结果作为输入参数调用reduce()方法。
(8)reduce方法的输出结果写入到HDFS文件系统。
修改记录
| 时间 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| 2020年04月10日 | 第一次发布 |
| 2020年9月13日 | 修改部分图片显示不全问题 |
- 学习参考:《开课吧-大数据开发高级工程师一期》课程
本文为学习课程做的笔记,如有侵权,请联系作者删除。