本人需要阅读代码,如果觉得阅读困难可以一步到CSDN
代码中涉及到的通过先序遍历和中序遍历生成一条二叉树的算法,在本人的另一篇博客通过树的中序和先序遍历生成二叉树中进行了详细讲解。
广度优先搜索算法(Breadth First Search),又叫宽度优先搜索,或横向优先搜索。
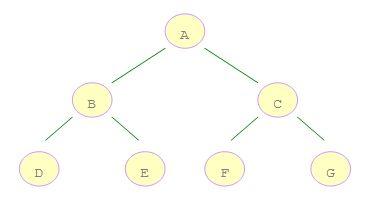
搜索是从根节点开始,沿着树的宽度遍历树的节点。如果所有节点均被访问,则算法中止。如右图所示的二叉树,A 是第一个访问的,然后顺序是 B、C,然后再是 D、E、F、G。
那么,怎样才能来保证这个访问的顺序呢?
借助队列数据结构,由于队列是先进先出的顺序,因此可以先将左子树入队,然后再将右子树入队。
这样一来,左子树结点就存在队头,可以先被访问到。
程序代码如下
import java.util.LinkedList;
/**
* 二叉树的广度优先搜索:我们在二叉树T中搜索节点N是否存在?
* @author
* 针对这样一个问题,我们要考虑一下如何解决以下几个问题:
* 1.使用什么样的数据结构表示 树
* 我们可创建一个类TreeNode,该类包含的属性应该有:节点名,左孩子,右孩子, 父节点 使用二叉链表
*
* 2.如何规范输入格式,能够方便我们进行树的初始化?
* 通过树的中序遍历和先序遍历来进行对数的初始化
*
*/
public class Tree {
private TreeNode rootNode;
/**
*
* @param bef 先序遍历字符串
* @param mid 中序遍历字符串
* @return 树的根节点
*/
public TreeNode creatTree(String bef,String mid) {
String root=bef.substring(0, 1);
int rootindex=mid.indexOf(root);
// System.out.println(rootindex);
String leftBef=bef.substring(1, rootindex+1);
String leftMid=mid.substring(0, rootindex);
// System.out.println("left child:"+leftBef+" "+leftMid);
TreeNode lchild=initTree(leftBef,leftMid);
int len=mid.length();
String rightBef=bef.substring(rootindex+1,len);
String rightMid=mid.substring(rootindex+1,len);
// System.out.println("right child:"+rightBef+" "+rightMid);
TreeNode rchild=initTree(rightBef,rightMid);
rootNode=new TreeNode(root, lchild, rchild);
return rootNode;
}
/**
* 递归
* @param bef
* @param mid
* @return
*/
public TreeNode initTree(String bef,String mid) {
if(bef.length()==1&&mid.length()==1) {
return new TreeNode(bef, null, null);
}
// if(bef.length()==2&&mid.length()==2) { //左子树为空或者右子树为空时
// if(bef.charAt(0)==mid.charAt(0)) {
// return new TreeNode(bef.substring(0,1), null, new TreeNode(bef.substring(1,2), null, null));
// }else {
// return new TreeNode(bef.substring(0,1), new TreeNode(mid.substring(0,1), null, null), null);
// }
// }
String root=bef.substring(0, 1);
int rootindex=mid.indexOf(root);
String leftBef=bef.substring(1, rootindex+1);
String leftMid=mid.substring(0, rootindex);
TreeNode lchild=null;
if(leftBef.length()==leftMid.length()&&leftBef.length()!=0) { //不为空时
lchild=initTree(leftBef,leftMid);
}
int len=mid.length();
String rightBef=bef.substring(rootindex+1,len);
String rightMid=mid.substring(rootindex+1,len);
TreeNode rchild=null;
if(rightMid.length()==rightBef.length()&&rightBef.length()!=0) {
rchild=initTree(rightBef,rightMid);
}
TreeNode rootNode=new TreeNode(root, lchild, rchild);
return rootNode;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tree tree=new Tree();
// System.out.println(tree.rootIndex("ASDFG", "S2"));
// System.out.println("ASF".substring(0, 1));
TreeNode tree2 = tree.creatTree("ABDECFGHI", "DBEAGFHIC");
tree.treeBFS("L");
}
//通过BFS搜索 节点N是否存在
public void treeBFS(String N) {
LinkedList
queue.add(rootNode); //将根节点加入队列中
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(node.lchild!=null) {
queue.add(node.lchild);
}
if(node.rchild!=null) {
queue.add(node.rchild);
}
System.out.print(node.nodeName+" ");
if(node.nodeName.equals(N)) {
System.out.println("节点存在二叉树中");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("\n节点不存在");
}
}
/**
* 内部节点类
* @author 曾鹏
*
*/
class TreeNode{
public String nodeName;
public TreeNode lchild;
public TreeNode rchild;
// public TreeNode parent;
public TreeNode(String nodeName,TreeNode lchild,TreeNode rchild) {
this.nodeName=nodeName;
this.lchild=lchild;
this.rchild=rchild;
// this.parent=parent;
}
}