C++演化是从c++98(1.0)到c++03到c++11(2.0)到c++14,当然后面不断更新。从1.0到2.0的变化比较重要。
一 2.0的新增头文件
比如2.0新增的头文件有:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
这些头文件的命名空间都是std
二. 不同版本对应的__cplusplus宏
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << __cplusplus < 首先通过默认的g++编译
aitian@aitian-CW65S:~/at/cpp_project/c11/day1$ g++ main.cpp -o main
aitian@aitian-CW65S:~/at/cpp_project/c11/day1$ ./main
199711
然后指定c++11
aitian@aitian-CW65S:~/at/cpp_project/c11/day1$ g++ main.cpp -std=c++11 -o main
aitian@aitian-CW65S:~/at/cpp_project/c11/day1$ ./main
201103
当然也可以指定c++14
aitian@aitian-CW65S:~/at/cpp_project/c11/day1$ g++ main.cpp -std=c++14 -o main
aitian@aitian-CW65S:~/at/cpp_project/c11/day1$ ./main
201402
二. 可变参数模板
variadic templates用与数量不定的模板参数,用三个点...来表示,...其实就是一个包(pack)。
当...用在模板参数,就叫模板参数包;
当...用在函数参数类型,叫做函数参数类型包;
当...用在函数参数,叫做函数参数包。
例如:
#include
#include //for use bitset template
using namespace std;
void print()
{
}
template
void print(const T& firstArgs, const Types&... args)
{
cout <<"len of aegs is "<(377), 42);
return 0;
}
运行:
aitian@aitian-CW65S:~/at/cpp_project/c11/day1$ g++ variadicTemplate.cpp -std=c++11
aitian@aitian-CW65S:~/at/cpp_project/c11/day1$ ./a.out
len of aegs is 3
7.5
len of aegs is 2
hello
len of aegs is 1
0000000101111001
len of aegs is 0
42
再看下面的程序,两个模板函数竟然可以共存没有报错
#include
#include //for use bitset template
using namespace std;
void print()
{
}
template
void print(const T& firstArgs, const Types&... args)
{
cout <<"len of aegs is "<
void print(const Types&... args)
{
}
int main()
{
print(7.5, "hello", bitset<16>(377), 42);
return 0;
}
运行后和上面的结果完全相同。实际上两种都符合,但是第一种比较特化,第二种比较泛话,所以选择特化的。
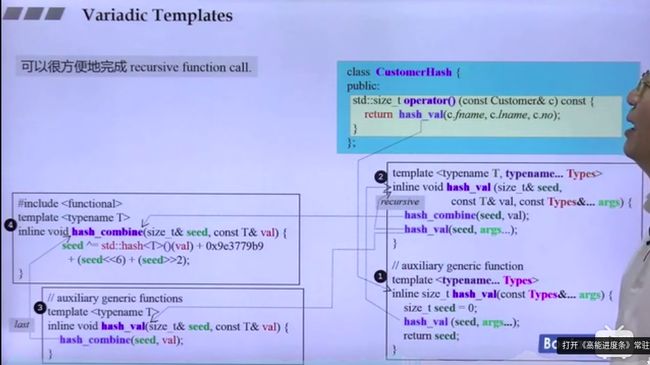
实际上这种变长模板非常适合用于递归函数调用。
再举个例子,看下图:
观察这个图的调用顺序,从类中的hash_val怎么开始调用的。
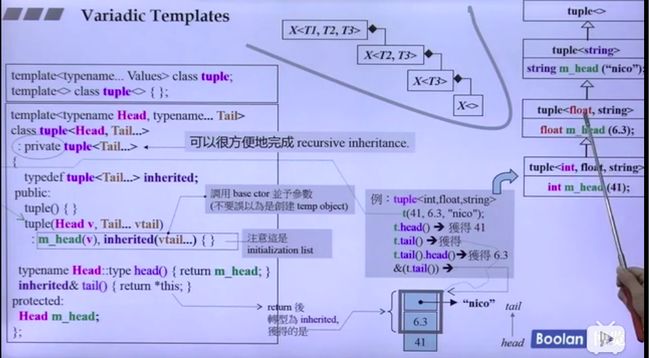
除了完成递归函数调用外,变长模板还可以完成递归继承,比如看看
观察这个图,看是怎么实现变长模板集成。
三. 模板套模板不用空格了
两个模板嵌套使用的时候不用加空格了,以前需要价格空格。
四. nullptr
c++11推荐使用nullptr代表一个空指针,在之前我们都是用NULL表示空指针,但是NULL实际上就是0,所以有歧义,这里用nullptr专门表示空指针,编译器看到nullptr就知道你想传递的是空指针而不是0。
举例:
#include
using namespace std;
void f(int)
{
cout <<"int function called" << endl;
}
void f(void*)
{
cout <<"void* function called" << endl;
}
int main()
{
f(0);//call f(int)
//f(NULL);// call f(int) if NULL is 0,ambiguous otherwise
f(nullptr); // call f(void*)
cout << NULL << endl;
return 0;
}
运行后:
aitian@aitian-CW65S:~/at/cpp_project/c11/day1$ g++ nullptr.cpp -std=c++11
nullptr.cpp: In function ‘int main()’:
nullptr.cpp:18:13: warning: passing NULL to non-pointer argument 1 of ‘std::basic_ostream<_CharT, _Traits>::__ostream_type& std::basic_ostream<_CharT, _Traits>::operator<<(long int) [with _CharT = char; _Traits = std::char_traits; std::basic_ostream<_CharT, _Traits>::__ostream_type = std::basic_ostream]’ [-Wconversion-null]
cout << NULL << endl;
^
aitian@aitian-CW65S:~/at/cpp_project/c11/day1$ ./a.out
int function called
void* function called
0
调用f(NULL)的时候会报错,因为不知道调用哪个函数。f(0)知道0是一个int,f(nullptr)知道了你想传递一个空指针。
nullptr能自动转成任意类型的空指针,nullptr的类型是std::nullptr_t,在头文件
四. auto关键字
auto自动推导类型,在lambda表达式中使用非常方便。但是也要注意,不要太偷懒写auto,除非类型很长(比如一些迭代器),尽量还是自己写。
举例使用auto
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// auto for iterator
string str="hello world";
for (auto item:str) {
cout << item<bool {
if (x>100) {
return true;
}
return false;
};
bool result = fun(0);
cout <<"result=" << result< 运行结果为:
aitian@aitian-CW65S:~/at/cpp_project/c11/day1$ g++ auto.cpp -std=c++11
aitian@aitian-CW65S:~/at/cpp_project/c11/day1$ ./a.out
h
e
l
l
o
w
o
r
l
d
result=0
五. 统一用大括号初始化
在c++11之前,初始化的方法各种各样,比如有用小括号初始化的,用大括号和等于号初始化的,为了能够统一,c++11之后可以直接在变量名后面用中括号进程初始化,比如
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
struct Rect {
int a;
int b;
int c;
int d;
Rect(int a_,int b_,int c_,int d_){
a = a_;
b = b_;
c = c_;
d = d_;
}
};
int main()
{
//before c++ 11
//braces and assignment operations
int array[6] = {27,210,12,47,109,83};
//parentheses
Rect r1(3, 7, 20, 25);
Rect r2 = {2, 4, 6, 8};
// after c++11
int value[] {1,2,3};
vector v {2,3,5,6,11,13,17};
vector cities {"Berlin", "New York", "London"};
Rect r3 {1, 4, 6, 8};
complex c{4.0, 3.0};
return 0;
}
可以看出,在变量后面加一个大括号就是进行初始化的动作,甚至针对自己定义的类型(Rect)也可以这么用,对c++自带的那些类型,更加可以了。
实现用大括号的原理实际上用到了initializer_list和array,这两个东西也都是c++11提供的。当编译器看到了{t1,t2,t3,...,tn}的时候,会构造一个initializer_list
比如上面的:
vector cities {"Berlin", "New York", "London"};
编译器会先形成一个initlizer_list
再比如上面的:
complex c{4.0, 3.0};
编译器会先形成一个initlizer_list
六 总结
本节讲解:
宏,变长模板,去空格,nullptr,auto,大括号初始化