iOS 底层探索 文章汇总
目录
- 一、KVC基本使用
- 二、KVC设值、取值底层分析
- 三、简单自定义KVC设值、取值
- 四、KVC 使用场景
相关面试题:谈谈你对KVC的理解
KVC的全称是Key-Value Coding,翻译成中文是键值编码,键值编码是由NSKeyValueCoding非正式协议启用的一种机制,对象采用该协议来间接访问其属性。即可以通过一个字符串key来访问某个属性。这种间接访问机制补充了实例变量及其相关的访问器所提供的直接访问。
一、KVC基本使用
// 1:基本类型使用
NAPerson *person = [NAPerson new];
[person setValue:@"differ" forKey:@"name"];
CJLog(@"%@",person.name);
// 2:集合类型使用
person.array = @[@"1",@"2",@"3"];
//person.array[0] = @"100"; 不能直接修改数组中的元素
// 方式一:创建一个新的数组
NSArray *array = @[@"100",@"2",@"3"];
[person setValue:array forKey:@"array"];
CJLog(@"%@",[person valueForKey:@"array"]);
// 方式二:构建可变数组
NSMutableArray *mArray = [person mutableArrayValueForKey:@"array"];
mArray[0] = @"200";
CJLog(@"%@",[person valueForKey:@"array"]);
// 3:集合操作符使用
// 遍历
NSEnumerator *enumerator = [array objectEnumerator];
NSString *str = nil;
while (str = [enumerator nextObject]) {
CJLog(@"%@", str);
}
// 字典操作
NSDictionary *dict = @{@"name":@"differ",@"subject":@"iOS",};
NAStudent *p = [[NAStudent alloc] init];
// 字典转模型
[p setValuesForKeysWithDictionary:dict];
// 键数组转模型到字典
NSArray *keyArray = @[@"name",@"subject"];
NSDictionary *dic = [p dictionaryWithValuesForKeys:keyArray];
// 聚合操作符 @avg、@count、@max、@min、@sum
// 数组操作符 @distinctUnionOfObjects @unionOfObjects
// 嵌套集合(array&set)操作 @distinctUnionOfArrays @unionOfArrays @distinctUnionOfSets
// 4:访问非对象属性 - 面试可能问到
// 结构体-官方文档示例
ThreeFloats floats = {1.,2.,3.};
NSValue *value = [NSValue valueWithBytes:&floats objCType:@encode(ThreeFloats)];
[person setValue:value forKey:@"threeFloats"];
NSValue *value1 = [person valueForKey:@"threeFloats"];
CJLog(@"%@",value1);
ThreeFloats th;
[value1 getValue:&th];
CJLog(@"%f-%f-%f",th.x,th.y,th.z);
// 5:KVC - 层层访问 - keyPath
NAStudent *student = [NAStudent alloc];
student.subject = @"differ";
person.student = student;
[person setValue:@"Swift" forKeyPath:@"student.subject"];
CJLog(@"%@",[person valueForKeyPath:@"student.subject"]);
typedef struct {
float x, y, z;
} ThreeFloats;
进入setValue:forKey:方法我们可以看到该方法在NSObject的NSKeyValueCoding分类中,因此所有继承于NSObject的类均有KVC功能。
官方文档地址:Key-Value Coding Programming Guide
二、KVC设值、取值底层分析
在官方文档Search Pattern for the Basic Setter描述中可以看到KVC的设值过程。
Search Pattern for the Basic Setter
The default implementation of setValue:forKey:, given key and value parameters as input, attempts to set a property named key to value (or, for non-object properties, the unwrapped version of value, as described in Representing Non-Object Values) inside the object receiving the call, using the following procedure:
Look for the first accessor named
setor: _set, in that order. If found, invoke it with the input value (or unwrapped value, as needed) and finish.If no simple accessor is found, and if the class method
accessInstanceVariablesDirectlyreturnsYES, look for an instance variable with a name like_,_is,is, in that order. If found, set the variable directly with the input value (or unwrapped value) and finish.Upon finding no accessor or instance variable, invoke
setValue:forUndefinedKey:. This raises an exception by default, but a subclass ofNSObjectmay provide key-specific behavior.
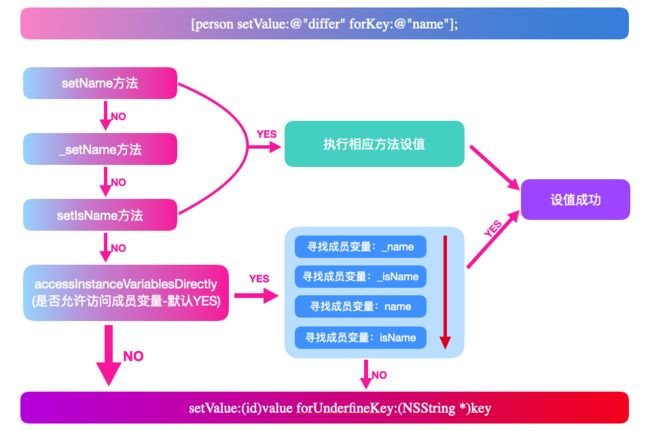
根据官方文档可以绘制如下设值流程图:
- 设值方法的顺序为:
setName->_setName->setIsName - 寻找变量的顺序为:
_name->_isName->name->isName(没有定义前面的成员变量才会向后寻找)
取值方法:[person valueForKey@"name"];
- 取值方法的顺序为:
getName->name->isName->_name - 寻找变量的顺序为:
_name->_isName->name->isName
三、简单自定义KVC设值、取值
这里通过简单自定义KVC设值、取值加深对KVC底层机制的理解
自定义KVC设置流程,主要分为以下几个步骤:
- 判断
key非空 - 查找
setter方法,顺序是:setKey、_setKey、 setIsKey - 判断
accessInstanceVariablesDirectly方法的返回值,即是否允许间接访问成员变量
3.1 返回YES,继续下一步设值,
3.2 返回NO,抛出异常 - 间接访问变量赋值(只会走一次),顺序是:
_key、_isKey、key、isKey
4.1 定义一个收集实例变量的数组
4.2 通过class_getInstanceVariable方法,获取相应的ivar
4.3 通过object_setIvar方法,对相应的ivar设置值 - 如果找不到相关实例变量,则抛出异常
//设值
- (void)lcj_setValue:(nullable id)value forKey:(NSString *)key{
// 1、判断key 是否存在
if (key == nil || key.length == 0) return;
// 2、找setter方法,顺序是:setKey、_setKey、 setIsKey
// key 要大写
NSString *Key = key.capitalizedString;
// key 要大写
NSString *setKey = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"set%@:", Key];
NSString *_setKey = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"_set%@:", Key];
NSString *setIsKey = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"setIs%@:", Key];
if ([self lcj_performSelectorWithMethodName:setKey value:value]) {
NSLog(@"*************%@*************", setKey);
return;
} else if([self lcj_performSelectorWithMethodName:_setKey value:value]) {
NSLog(@"*************%@*************", _setKey);
return;
} else if([self lcj_performSelectorWithMethodName:setIsKey value:value]) {
NSLog(@"*************%@*************", setIsKey);
return;
}
// 3、判断accessInstanceVariablesDirectly方法的返回值,即是否允许间接访问成员变量,返回YES,继续下一步设值,如果是NO,则抛出异常
if (![self.class accessInstanceVariablesDirectly]) {
@throw [NSException exceptionWithName:@"CJLUnKnownKeyException" reason:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"****[%@ valueForUndefinedKey:]: this class is not key value coding-compliant for the key name.****",self] userInfo:nil];
}
// 4、间接访问变量赋值,顺序为:_key、_isKey、key、isKey
// 4.1 定义一个收集实例变量的数组
NSMutableArray *mArray = [self getIvarListName];
// _ _is is
NSString *_key = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"_%@", key];
NSString *_isKey = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"_is%@", key];
NSString *isKey = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"is%@", key];
if ([mArray containsObject:_key]) {
// 4.2 获取相应的 ivar
Ivar ivar = class_getInstanceVariable([self class], _key.UTF8String);
// 4.3 对相应的 ivar 设置值
object_setIvar(self, ivar, value);
return;
} else if ([mArray containsObject:_isKey]) {
Ivar ivar = class_getInstanceVariable([self class], _isKey.UTF8String);
object_setIvar(self, ivar, value);
return;
} else if ([mArray containsObject:key]) {
Ivar ivar = class_getInstanceVariable([self class], key.UTF8String);
object_setIvar(self, ivar, value);
return;
} else if ([mArray containsObject:isKey]) {
Ivar ivar = class_getInstanceVariable([self class], isKey.UTF8String);
object_setIvar(self, ivar, value);
return;
}
// 5、如果找不到则抛出异常
@throw [NSException exceptionWithName:@"LCJUnknownKeyException" reason:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"****[%@ %@]: this class is not key value coding-compliant for the key name.****",self,NSStringFromSelector(_cmd)] userInfo:nil];
}
自定义KVC取置流程,主要分为以下几个步骤:
- 判断
key非空 - 查找相应方法,顺序是:
get(、 、is 、 _ NSArray还会寻找countOf)and objectIn AtIndex - 判断
accessInstanceVariablesDirectly方法的返回值,即是否允许间接访问成员变量
3.1 返回YES,继续下一步设值,
3.2 返回NO,抛出异常 - 间接访问实例变量,顺序依然是:
_、 _is 、 、 is
4.1 定义一个收集实例变量的数组
4.2 通过class_getInstanceVariable方法,获取相应的ivar
4.3 通过object_getIvar方法,返回相应的ivar的值 - 如果找不到相关实例变量,返回空字符串
//取值
- (nullable id)lcj_valueForKey:(NSString *)key {
// 1、判断非空
if (key == nil || key.length == 0) {
return nil;
}
// 2、找到相关方法:get、 、is、 _、countOf 、objectInAtIndex
// key 要大写
NSString *Key = key.capitalizedString;
// 拼接方法
NSString *getKey = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"get%@",Key];
NSString *countOfKey = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"countOf%@",Key];
NSString *objectInKeyAtIndex = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"objectIn%@AtIndex:",Key];
#pragma clang diagnostic push
#pragma clang diagnostic ignored "-Warc-performSelector-leaks"
if ([self respondsToSelector:NSSelectorFromString(getKey)]) {
return [self performSelector:NSSelectorFromString(getKey)];
} else if ([self respondsToSelector:NSSelectorFromString(key)]) {
return [self performSelector:NSSelectorFromString(key)];
} else if (is、 _) {}
//集合类型
else if ([self respondsToSelector:NSSelectorFromString(countOfKey)]) {
if ([self respondsToSelector:NSSelectorFromString(objectInKeyAtIndex)]) {
int num = (int)[self performSelector:NSSelectorFromString(countOfKey)];
NSMutableArray *mArray = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:1];
for (int i = 0; i、 _is、 、 is
// 4.1 定义一个收集实例变量的数组
NSMutableArray *mArray = [self getIvarListName];
// 例如:_name -> _isName -> name -> isName
NSString *_key = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"_%@",key];
NSString *_isKey = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"_is%@",Key];
NSString *isKey = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"is%@",Key];
if ([mArray containsObject:_key]) {
Ivar ivar = class_getInstanceVariable([self class], _key.UTF8String);
return object_getIvar(self, ivar);
} else if ([mArray containsObject:_isKey]) {
Ivar ivar = class_getInstanceVariable([self class], _isKey.UTF8String);
return object_getIvar(self, ivar);
} else if ([mArray containsObject:key]) {
Ivar ivar = class_getInstanceVariable([self class], key.UTF8String);
return object_getIvar(self, ivar);
} else if ([mArray containsObject:isKey]) {
Ivar ivar = class_getInstanceVariable([self class], isKey.UTF8String);
return object_getIvar(self, ivar);
}
return @"";
}
四、KVC 使用场景
1、动态设值和取值
- 常用的可以通过
setValue:forKey:和valueForKey: - 也可以通过路由的方式
setValue:forKeyPath:和valueForKeyPath:
2、通过KVC访问和修改私有变量
在日常开发中,对于类的私有属性,在外部定义的对象,是无法直接访问私有属性的,但是对于KVC而言,一个对象没有自己的隐私,所以可以通过KVC修改和访问任何私有属性
3、多值操作(model和字典互转)
model和字典的转换可以通过下面两个KVC的API实现:
//字典转模型
- (void)setValuesForKeysWithDictionary:(NSDictionary *)keyedValues;
//模型转字典
- (NSDictionary *)dictionaryWithValuesForKeys:(NSArray *)keys;
4、修改一些系统空间的内部属性
在日常开发中,我们知道,很多UI控件都是在其内部由多个UI空间组合而成,这些内部控件苹果并没有提供访问的API,但是使用KVC可以解决这个问题,常用的就是自定义tabbar、个性化UITextField中的placeHolderText(iOS13开始逐步不允许通过valueForKey、setValue: forKey获取和设置私有属性,如:_placeholderLabel.textColor)。
5、用KVC实现高阶消息传递
在对容器类使用KVC时,valueForKey:将会被传递给容器中的每一个对象,而不是对容器本身进行操作,结果会被添加到返回的容器中,这样可以很方便的操作集合 来返回 另一个集合
//KVC实现高阶消息传递
- (void)transmitMsg{
NSArray *arrStr = @[@"english", @"franch", @"chinese"];
NSArray *arrCapStr = [arrStr valueForKey:@"capitalizedString"];
for (NSString *str in arrCapStr) {
CJLog(@"%@", str);
}
NSArray *arrCapStrLength = [arrCapStr valueForKeyPath:@"capitalizedString.length"];
for (NSNumber *length in arrCapStrLength) {
CJLog(@"%ld", (long)length.integerValue);
}
}
// 打印结果:
English
Franch
Chinese
7
6
7
参考:
DIS_KVC_KVO自定义实现