自然语言处理向量模型-Word2Vec
自然语言处理向量模型-Word2Vec
自然语言处理与深度学习
- 拼写检查、关键词检索…
- 文本挖掘(产品价格、日期、时间、地点、人名、公司名)
- 文本分类
- 机器翻译
- 客服系统 英语
- 复杂对话系统
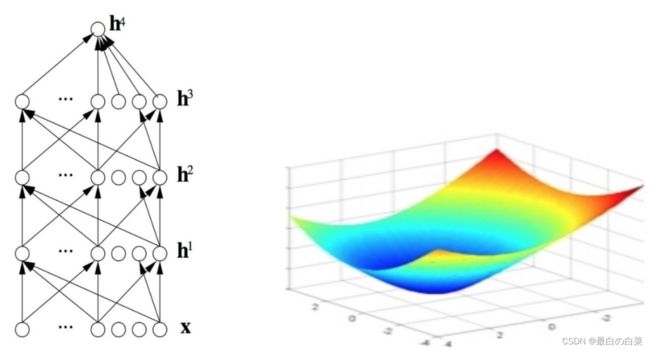
深度学习的基础模型是神经网络,指定学习目标,就可以朝着学习的优化目标前进
为什么需要深度学习?
- 手工特征耗时耗力, 还不易拓展
- 自动特征学习快, 方便拓展
- 深度学习提供了一种通用的学习框架, 可用来表示世界、视觉和语言学信息
- 深度学习既可以无监督学习, 也可以监督学习
语言模型实例:机器翻译;拼写纠错 ;智能问答
我 今天 下午 打 篮球
p(S)=p(w1,w2,w3,w4,w5,…,wn)
=p(w1)p(w2|w1)p(w3|w1,w2)…p(wn|w1,w2,…,wn-1)
p(S)被称为语言模型,即用来计算一个句子概率的模型
语言模型存在哪些问题呢?1.数据过于稀疏2.参数空间太大 p(wi|w1,w2,…,wi-1) = p(w1,w2,…,wi-1,wi) / p(w1,w2,…,wi-1)
解决方法:
假设下一个词的出现依赖它前面的一个词:
p(S)=p(w1)p(w2|w1)p(w3|w1,w2)…p(wn|w1,w2,…,wn-1)
=p(w1)p(w2|w1)p(w3|w2)…p(wn|wn-1)
假设下一个词的出现依赖它前面的两个词:
p(S)=p(w1)p(w2|w1)p(w3|w1,w2)…p(wn|w1,w2,…,wn-1)
=p(w1)p(w2|w1)p(w3|w1,w2)…p(wn|wn-1,wn-2)
假设词典的大小是N则模型参数的量级是 ( O ( N n ) ) \left(O\left(N^{n}\right)\right) (O(Nn))
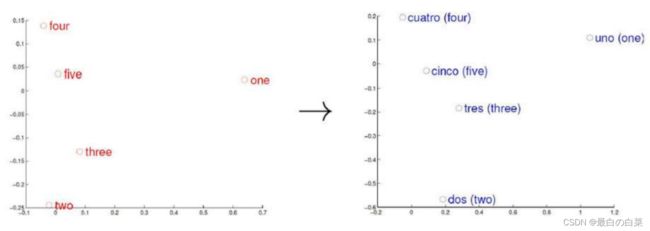
词向量
词是最基本的单位,把词转换为计算机认识的形式。要将词转换为向量。语言空间上词与词之间是有距离的,相似的词离得比较近
不同的语言构造的向量模型是相近的。
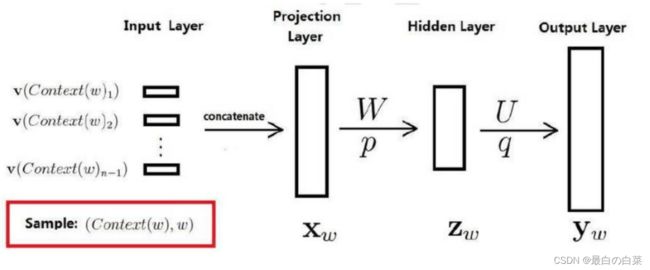
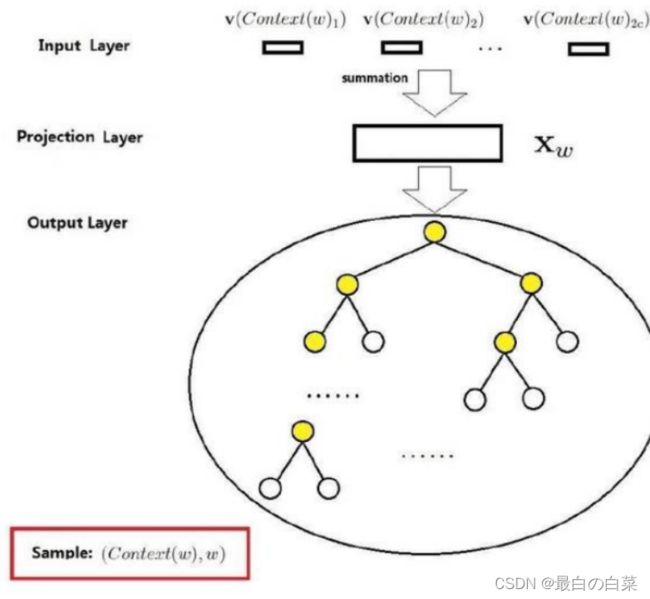
神经网络模型
第一层是输入层,第二层是投影层,将输入的前三个词拼接在一起
训练样本: (Context ( w ) , w ) \text { (Context }(w), w) (Context (w),w) 包括前n-1个词分别的向量,假定每个词向量大小m
投影层:(n-1)*m 首尾拼接起来的大向量
输出: y w = ( y w , 1 , y w , 2 , ⋯ , y w , N ) ⊤ \mathbf{y}_{w}=\left(y_{w, 1}, y_{w, 2}, \cdots, y_{w, N}\right)^{\top} yw=(yw,1,yw,2,⋯,yw,N)⊤
表示上下文为 Context ( w ) \text { Context }(w) Context (w) 时,下一个词恰好为词典中第i个词的概率
归一化: p ( w ∣ Context ( w ) ) = e y w , i w ∑ i = 1 N e y w , i p(w \mid \text { Context }(w))=\frac{e^{y_{w, i_{w}}}}{\sum_{i=1}^{N} e^{y_{w, i}}} p(w∣ Context (w))=∑i=1Neyw,ieyw,iw
优势:
S1 = ‘’我 今天 去 网咖’’ 出现了1000次
S2 = ‘’我 今天 去 网吧’’ 出现了10次
对于N-gram模型:P(S1) >> P(S2)
而神经网络模型计算的P(S1) ≈ P(S2)
只要语料库中出现其中一个,其他句子的概率也会相应的增大
Hierarchical Softmax
分层的Softmax
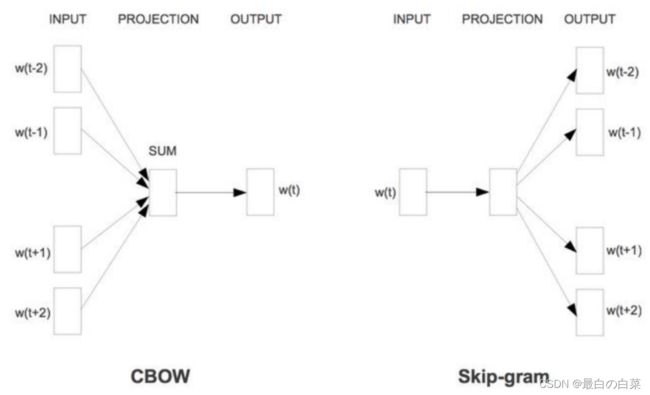
CBOW 是 Continuous Bag-of-Words Model 的缩写,是一种根据上下文的词语预测当前词语的出现概率的模型
L = ∑ w ∈ C log p ( w ∣ Context ( w ) ) \mathcal{L}=\sum_{w \in \mathcal{C}} \log p(w \mid \text { Context }(w)) L=∑w∈Clogp(w∣ Context (w))
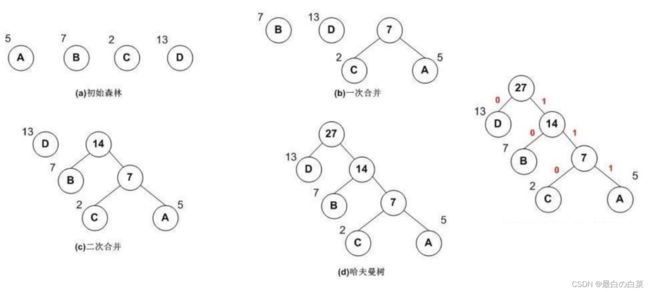
哈夫曼树介绍
走左子树还是右子树,是二分类通常用逻辑回归
CBOW的输入层是上下文的词语的词向量,在训练CBOW模型,词向量只是个副产品,确切来说,是CBOW模型的一个参数。训练开始的时候,词向量是个随机值,随着训练的进行不断被更新)。
投影层对其求和,所谓求和,就是简单的向量加法。
输出层输出最可能的w。由于语料库中词汇量是固定的|C|个,所以上述过程其实可以看做一个多分类问题。给定特征,从|C|个分类中挑一个。
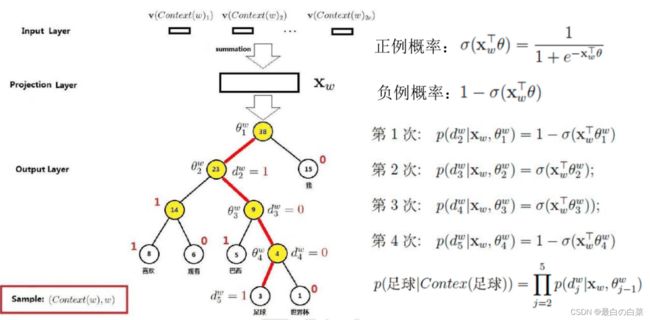
- p w p^{w} pw 从根结点出发到达 $\mathrm{W} $ 对应叶子结点的路径.
- $l^{w} $ 路径中包含结点的个数
- $p_{1}^{w}, p_{2}^{w}, \cdots, p_{l{w}}{w} $ 路径 p w p^{w} pw 中的各个节点
p ( d j w ∣ x w , θ j − 1 w ) = [ σ ( x w ⊤ θ j − 1 w ) ] 1 − d j w ⋅ [ 1 − σ ( x w ⊤ θ j − 1 w ) ] d j w L = ∑ w ∈ C log p ( w ∣ Context ( w ) ) L = ∑ w ∈ C log ∏ j = 2 l w { [ σ ( x w ⊤ θ j − 1 w ) ] 1 − d j w ⋅ [ 1 − σ ( x w ⊤ θ j − 1 w ) ] d j w } = ∑ w ∈ C ∑ j = 2 l w { ( 1 − d j w ) ⋅ log [ σ ( x w ⊤ θ j − 1 w ) ] + d j w ⋅ log [ 1 − σ ( x w ⊤ θ j − 1 w ) ] } \begin{array}{l} p\left(d_{j}^{w} \mid \mathbf{x}_{w}, \theta_{j-1}^{w}\right)=\left[\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta_{j-1}^{w}\right)\right]^{1-d_{j}^{w}} \cdot\left[1-\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta_{j-1}^{w}\right)\right]^{d_{j}^{w}} \\ \mathcal{L}=\sum_{w \in \mathcal{C}} \log p(w \mid \operatorname{Context}(w)) \\ \mathcal{L}=\sum_{w \in \mathcal{C}} \log \prod_{j=2}^{l^{w}}\left\{\left[\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta_{j-1}^{w}\right)\right]^{1-d_{j}^{w}} \cdot\left[1-\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta_{j-1}^{w}\right)\right]^{d_{j}^{w}}\right\} \\ \quad=\sum_{w \in \mathcal{C}} \sum_{j=2}^{l^{w}}\left\{\left(1-d_{j}^{w}\right) \cdot \log \left[\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta_{j-1}^{w}\right)\right]+d_{j}^{w} \cdot \log \left[1-\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta_{j-1}^{w}\right)\right]\right\} \end{array} p(djw∣xw,θj−1w)=[σ(xw⊤θj−1w)]1−djw⋅[1−σ(xw⊤θj−1w)]djwL=∑w∈Clogp(w∣Context(w))L=∑w∈Clog∏j=2lw{[σ(xw⊤θj−1w)]1−djw⋅[1−σ(xw⊤θj−1w)]djw}=∑w∈C∑j=2lw{(1−djw)⋅log[σ(xw⊤θj−1w)]+djw⋅log[1−σ(xw⊤θj−1w)]}
梯度上升求解
∂ L ( w , j ) ∂ θ j − 1 w = ∂ ∂ θ j − 1 w { ( 1 − d j w ) ⋅ log [ σ ( x w ⊤ θ j − 1 w ) ] + d j w ⋅ log [ 1 − σ ( x w ⊤ θ j − 1 w ) ] } \frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(w, j)}{\partial \theta_{j-1}^{w}}=\frac{\partial}{\partial \theta_{j-1}^{w}}\left\{\left(1-d_{j}^{w}\right) \cdot \log \left[\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta_{j-1}^{w}\right)\right]+d_{j}^{w} \cdot \log \left[1-\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta_{j-1}^{w}\right)\right]\right\} ∂θj−1w∂L(w,j)=∂θj−1w∂{(1−djw)⋅log[σ(xw⊤θj−1w)]+djw⋅log[1−σ(xw⊤θj−1w)]}
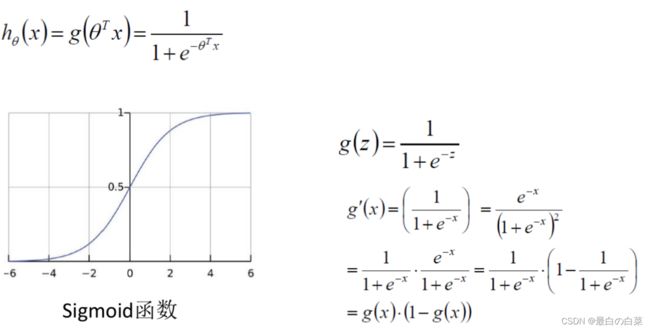
sigmoid函数的导数: σ ′ ( x ) = σ ( x ) [ 1 − σ ( x ) ] . \sigma^{\prime}(x)=\sigma(x)[1-\sigma(x)] . σ′(x)=σ(x)[1−σ(x)].
代入上上式得到: ( 1 − d j w ) [ 1 − σ ( x w ⊤ θ j − 1 w ) ] x w − d j w σ ( x w ⊤ θ j − 1 w ) x w \left(1-d_{j}^{w}\right)\left[1-\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta_{j-1}^{w}\right)\right] \mathbf{x}_{w}-d_{j}^{w} \sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta_{j-1}^{w}\right) \mathbf{x}_{w} (1−djw)[1−σ(xw⊤θj−1w)]xw−djwσ(xw⊤θj−1w)xw
合并同类项得到: [ 1 − d j w − σ ( x w ⊤ θ j − 1 w ) ] x w \left[1-d_{j}^{w}-\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta_{j-1}^{w}\right)\right] \mathbf{x}_{w} [1−djw−σ(xw⊤θj−1w)]xw
∂ L ( w , j ) ∂ x w = [ 1 − d j w − σ ( x w ⊤ θ j − 1 w ) ] θ j − 1 w \frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(w, j)}{\partial \mathbf{x}_{w}}=\left[1-d_{j}^{w}-\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta_{j-1}^{w}\right)\right] \theta_{j-1}^{w} ∂xw∂L(w,j)=[1−djw−σ(xw⊤θj−1w)]θj−1w
v ( w ~ ) : = v ( w ~ ) + η ∑ j = 2 l w ∂ L ( w , j ) ∂ x w , w ~ ∈ Context ( w ) \mathbf{v}(\widetilde{w}):=\mathbf{v}(\widetilde{w})+\eta \sum_{j=2}^{l^{w}} \frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(w, j)}{\partial \mathbf{x}_{w}}, \quad \widetilde{w} \in \operatorname{Context}(w) v(w ):=v(w )+η∑j=2lw∂xw∂L(w,j),w ∈Context(w)
负采样模型(Negative Sampling)
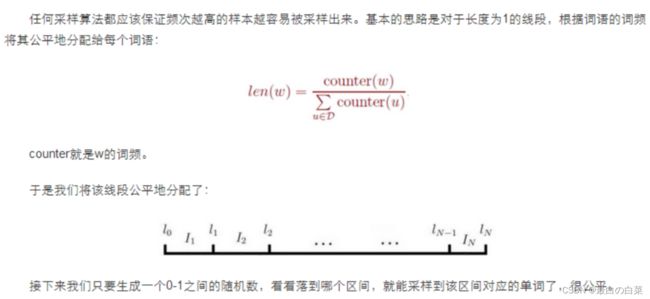
L w ( w ~ ) = { 1 , w ~ = w : 0 , w ~ ≠ w . 负样本那么多, 该如何选取呢? L^{w}(\widetilde{w})=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} 1, & \widetilde{w}=w: \\ 0, & \widetilde{w} \neq w . \end{array}\right. \text { 负样本那么多, 该如何选取呢? } Lw(w )={1,0,w =w:w =w. 负样本那么多, 该如何选取呢?
对于一个给定的正样本 ( Context ( w ) , w ) (\operatorname{Context}(w), w) (Context(w),w) , 我们希望最大化
p ( u ∣ Context ( w ) ) = { σ ( x w ⊤ θ u ) , 1 − σ ( x w ⊤ θ u ) g ( w ) = ∏ u ∈ { w } ∪ N E G ( w ) p ( u ∣ Context ( w ) ) \begin{array}{l} p(u \mid \text { Context }(w))=\left\{\begin{array}{l} \sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta^{u}\right), \\ 1-\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta^{u}\right) \end{array}\right. \\ g(w)=\prod_{u \in\{w\} \cup N E G(w)} p(u \mid \text { Context }(w)) \end{array} p(u∣ Context (w))={σ(xw⊤θu),1−σ(xw⊤θu)g(w)=∏u∈{w}∪NEG(w)p(u∣ Context (w))
g ( w ) = σ ( x w ⊤ θ w ) ∏ u ∈ N E G ( w ) [ 1 − σ ( x w ⊤ θ u ) ] g(w)=\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta^{w}\right) \prod_{u \in N E G(w)}\left[1-\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta^{u}\right)\right] g(w)=σ(xw⊤θw)∏u∈NEG(w)[1−σ(xw⊤θu)]
σ ( x w ⊤ θ w ) 表示当上下文为 Context ( w ) 时, 预测中心词为 w 的概率: \sigma\left(\mathrm{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta^{w}\right) \text { 表示当上下文为 Context }(w) \text { 时, 预测中心词为 } w \text { 的概率: } σ(xw⊤θw) 表示当上下文为 Context (w) 时, 预测中心词为 w 的概率:
σ ( x w ⊤ θ u ) , u ∈ N E G ( w ) 则表示当上下文为 Context ( w ) 时, 预测中心词为 u 的概率 \sigma\left(\mathrm{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta^{u}\right), u \in N E G(w) \text { 则表示当上下文为 } \operatorname{Context}(w) \text { 时, 预测中心词为 } u \text { 的概率 } σ(xw⊤θu),u∈NEG(w) 则表示当上下文为 Context(w) 时, 预测中心词为 u 的概率
对于一个给定的语料库 C . \mathcal{C} . C.
G = ∏ w ∈ C g ( w ) G=\prod_{w \in \mathcal{C}} g(w) G=∏w∈Cg(w)
L = log G = log ∏ w ∈ C g ( w ) = ∑ w ∈ C log g ( w ) = ∑ w ∈ C log ∏ u ∈ { w } ∪ N E G ( w ) { [ σ ( x w ⊤ θ u ) ] L w ( u ) ⋅ [ 1 − σ ( x w ⊤ θ u ) ] 1 − L w ( u ) } = ∑ w ∈ C ∑ u ∈ { w } ∪ N E G ( w ) { L w ( u ) ⋅ log [ σ ( x w ⊤ θ u ) ] + [ 1 − L w ( u ) ] ⋅ log [ 1 − σ ( x w ⊤ θ u ) ] } \begin{aligned} \mathcal{L} &=\log G=\log \prod_{w \in \mathcal{C}} g(w)=\sum_{w \in \mathcal{C}} \log g(w) \\ &=\sum_{w \in \mathcal{C}} \log \prod_{u \in\{w\} \cup N E G(w)}\left\{\left[\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta^{u}\right)\right]^{L^{w}(u)} \cdot\left[1-\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta^{u}\right)\right]^{1-L^{w}(u)}\right\} \\ &=\sum_{w \in \mathcal{C}} \sum_{u \in\{w\} \cup N E G(w)}\left\{L^{w}(u) \cdot \log \left[\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta^{u}\right)\right]+\left[1-L^{w}(u)\right] \cdot \log \left[1-\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta^{u}\right)\right]\right\} \end{aligned} L=logG=logw∈C∏g(w)=w∈C∑logg(w)=w∈C∑logu∈{w}∪NEG(w)∏{[σ(xw⊤θu)]Lw(u)⋅[1−σ(xw⊤θu)]1−Lw(u)}=w∈C∑u∈{w}∪NEG(w)∑{Lw(u)⋅log[σ(xw⊤θu)]+[1−Lw(u)]⋅log[1−σ(xw⊤θu)]}
∂ L ( w , u ) ∂ θ u = ∂ ∂ θ u { L w ( u ) ⋅ log [ σ ( x w ⊤ θ u ) ] + [ 1 − L w ( u ) ] ⋅ log [ 1 − σ ( x w ⊤ θ u ) ] } = L w ( u ) [ 1 − σ ( x w ⊤ θ u ) ] x w − [ 1 − L w ( u ) ] σ ( x w ⊤ θ u ) x w = { L w ( u ) [ 1 − σ ( x w ⊤ θ u ) ] − [ 1 − L w ( u ) ] σ ( x w ⊤ θ u ) } x w = [ L w ( u ) − σ ( x w ⊤ θ u ) ] x w \begin{aligned} \frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(w, u)}{\partial \theta^{u}} &=\frac{\partial}{\partial \theta^{u}}\left\{L^{w}(u) \cdot \log \left[\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta^{u}\right)\right]+\left[1-L^{w}(u)\right] \cdot \log \left[1-\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta^{u}\right)\right]\right\} \\ &=L^{w}(u)\left[1-\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta^{u}\right)\right] \mathbf{x}_{w}-\left[1-L^{w}(u)\right] \sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta^{u}\right) \mathbf{x}_{w} \\ &=\left\{L^{w}(u)\left[1-\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta^{u}\right)\right]-\left[1-L^{w}(u)\right] \sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta^{u}\right)\right\} \mathbf{x}_{w} \\ &=\left[L^{w}(u)-\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta^{u}\right)\right] \mathbf{x}_{w} \end{aligned} ∂θu∂L(w,u)=∂θu∂{Lw(u)⋅log[σ(xw⊤θu)]+[1−Lw(u)]⋅log[1−σ(xw⊤θu)]}=Lw(u)[1−σ(xw⊤θu)]xw−[1−Lw(u)]σ(xw⊤θu)xw={Lw(u)[1−σ(xw⊤θu)]−[1−Lw(u)]σ(xw⊤θu)}xw=[Lw(u)−σ(xw⊤θu)]xw
θ u 的更新公式可写为 θ u : = θ u + η [ L w ( u ) − σ ( x w ⊤ θ u ) ] x w \theta^{u} \text { 的更新公式可写为 } \theta^{u}:=\theta^{u}+\eta\left[L^{w}(u)-\sigma\left(\mathrm{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta^{u}\right)\right] \mathrm{x}_{w} θu 的更新公式可写为 θu:=θu+η[Lw(u)−σ(xw⊤θu)]xw
∂ L ( w , u ) ∂ x w = [ L w ( u ) − σ ( x w ⊤ θ u ) ] θ u \frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(w, u)}{\partial \mathbf{x}_{w}}=\left[L^{w}(u)-\sigma\left(\mathbf{x}_{w}^{\top} \theta^{u}\right)\right] \theta^{u} ∂xw∂L(w,u)=[Lw(u)−σ(xw⊤θu)]θu
v ( w ~ ) : = v ( w ~ ) + η ∑ u ∈ { w } ∪ N E G ( w ) ∂ L ( w , u ) ∂ x w , w ~ ∈ Context ( w ) \mathbf{v}(\widetilde{w}):=\mathbf{v}(\widetilde{w})+\eta \sum_{u \in\{w\} \cup N E G(w)} \frac{\partial \mathcal{L}(w, u)}{\partial \mathbf{x}_{w}}, \widetilde{w} \in \operatorname{Context}(w) v(w ):=v(w )+η∑u∈{w}∪NEG(w)∂xw∂L(w,u),w ∈Context(w)