matplotlib绘图:散点图、折线图、柱状图、水平条形图、饼图和直方图
目录
- 数据可视化
- Matplotlib
- 安装和导入库
-
- 安装Matplotlib库
- 导入Matplotlib库中的`pyplot`子库
- 一、Matplotlib基础知识
-
- 1. Figure对象
-
- 1.1 定义
- 1.2 划分子图
- 1.3 设置中文字体
- 1.4 添加标题
- 1.5 调整子图
- 二、散点图
-
- 引入
- scatter()函数
- 二、折线图
-
- plot()函数
- 三、柱状图
-
- 1. 普通柱形图
- 2. 并列柱形图
- 3. 堆叠条形图
- 4. 柱线混合图
- 四、水平条形图
- 五、饼图
- 五、直方图
)
数据可视化
- 数据分析阶段:理解和洞察数据之间的关系
- 算法调试阶段:发现问题,优化算法
- 项目总结阶段:展示项目成果
Matplotlib
Matplotlib 是Python中类似 MATLAB 的绘图工具,可以快速方便地生成高质量的图标
安装和导入库
安装Matplotlib库
- Anaconda:安装了anaconda之后,Matplotlib就已经安装好了
- pip
pip install matplotlib
导入Matplotlib库中的pyplot子库
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
matplotlib.pyplot是一个有命令风格的函数集合,它看起来和MATLAB很相似。每一个pyplot函数都使一副图像做出些许改变,例如创建一幅图,在图中创建一个绘图区域,在绘图区域中添加一条线等等。在matplotlib.pyplot中,各种状态通过函数调用保存起来,以便于可以随时跟踪像当前图像和绘图区域这样的东西。绘图函数是直接作用于当前axes(matplotlib中的专有名词,图形中组成部分,不是数学中的坐标系。)
一、Matplotlib基础知识
Matplotlib中的基本图表包括的元素
-
x轴和y轴 axis
水平和垂直的轴线 -
x轴和y轴刻度 tick
刻度标示坐标轴的分隔,包括最小刻度和最大刻度 -
x轴和y轴刻度标签 tick label
表示特定坐标轴的值 -
绘图区域(坐标系) axes
-
坐标系标题 title
-
轴标签 xlabel ylabel
1. Figure对象
1.1 定义
在任何绘图之前,我们需要一个Figure对象,可以理解成我们需要一张画板才能开始绘图。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig = plt.figure(num, figsize, dpi, facecolor, edgecolor, frameon)
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| num | 图形编号或名称,取值为数字/字符串 |
| figsize | 绘图对象的宽和高,单位是英寸 |
| dpi | 绘图对象的分辨率,缺省值为80 |
| facecolor | 背景颜色 |
| edgecolor | 边框颜色 |
| frameon | 表示是否显示边框 |
| FigureClass | Optionally use a custom Figure instance. |
| clear | 如果是True,并且图形已经存在,则清楚该图形 |
例子:
plt.figure(figsize=(3, 2), facecolor="green")
plt.plot()
plt.show()
| 颜色 | 缩略字符 | 颜色 | 缩略字符 |
|---|---|---|---|
| blue | b | black | k |
| green | g | white | w |
| ren | r | cyan | c |
| yellow | y | megenta | m |
1.2 划分子图
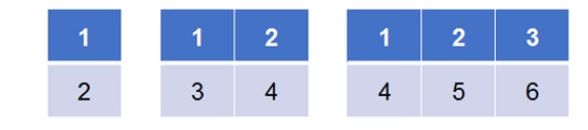
plt.subplot(nrows, ncols, index)
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| nrows | 行数 |
| ncols | 列数 |
| index | 子图序号 |
fig = plt.figure()
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
plt.show()
每个subplot函数只创建一个子图,前两个参数只是说明将画布划分为2*2的区域,可以创建四个子图,但是并没有同时创建四个子图。要创建四个子图就需要执行四条语句,分别创建每个子图。
当subplot函数中的行数,列数和子图序号都小于10时,可以省略各个参数间的逗号,用一个三位数来代替,如下。
plt.subplot(221)
plt.subplot(222)
plt.subplot(223)
plt.subplot(224)
1.3 设置中文字体
- 设置中文字体
由于Matplotlib的默认字体是英文,因此在向图表中添加中文的时候,常常无法显示,这时只要将默认字体改为中文就可以了。
语法
plt.rcParams["font.sans-serif"] = "SimHei"
| 中文字体 | 英文描述 | 中文字体 | 英文描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 宋体 | SimSun | 楷体 | KaiTi |
| 黑体 | SimHei | 仿宋 | FangSong |
| 微软雅黑 | MicrosoftYaHei | 隶书 | LiSu |
| 微软正黑体 | MicrosoftJhengHei | 幼圆 | YouYuan |
- 恢复标准默认配置
rc参数被修改后还可以恢复标准默认配置
plt.rcdefaults()
1.4 添加标题
- 添加全局标题
subtitle("global_title")
- 添加子标题
title("title")
| 参数 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| x | 标题位置的x坐标 | 0.5 |
| y | 标题位置的y坐标 | 0.98 |
| color | 标题颜色 | 黑色 |
| background | 标题背景颜色 | |
| fontsize | 标题的字体大小 | 12 |
| fontweight | 字体粗细 | normal / light / medium / semibold / bold / heavy / black |
| fontstyle | 设置字体类型 | xx-small / x-small / small / medium / large / x-large / xx-large |
| horizontalalignment | 标题水平对齐方式 | center / left / right |
| verticalalignment | 标题的垂直对齐方式 | top / center / bottom / baseline |
title()函数的主要参数:
| 参数 | 说明 | 取值 |
|---|---|---|
| loc | 标题位置 | left / right |
| rotation | 标题文字旋转角度 | |
| color | 标题颜色 | 黑色 |
| fontsize | 标题的字体大小 | 12 |
| fontweight | 字体粗细 | normal / light / medium / semibold / bold / heavy / black |
| fontstyle | 设置字体类型 | xx-small / x-small / small / medium / large / x-large / xx-large |
| horizontalalignment | 标题水平对齐方式 | center / left / right |
| verticalalignment | 标题的垂直对齐方式 | top / center / bottom / baseline |
| fontdict | 设置参数字典 |
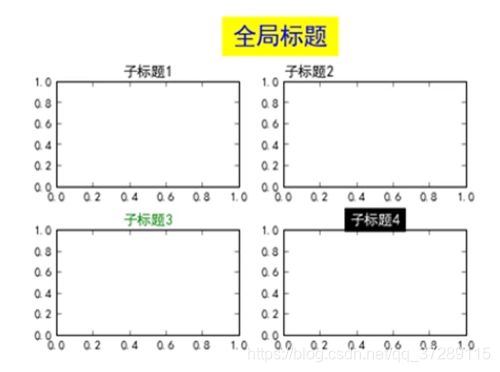
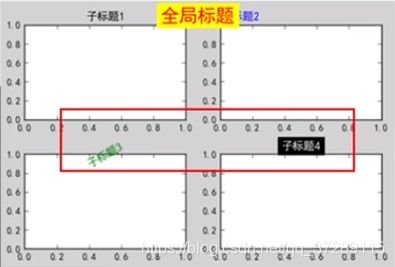
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#%%
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = "SimHei"
fig = plt.figure(facecolor="lightgrey")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
plt.title("子标题1")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
plt.title("子标题2", loc="left", color="b")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
myfontdict = {"fontsize": 12, "color": "g", "rotation": 30}
plt.title("子标题3", fontdict=myfontdict)
plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
plt.title("子标题4", color="w", backgroundcolor="black")
plt.suptitle("全局标题", fontsize=20, color="red", backgroundcolor="yellow")
plt.show()
小技巧:
代码分段运行
- 代码分段
使用 #%% 将代码分段(应该自2018版pycharm就可以这样了)
注意:仅在科学模式Scientific Mode下有效 - 分段运行
法一:Ctrl + Enter 逐端运行
法二:点击代码段左边的绿色三角形

如果得到下列结果,则需要对画布进行调整

这里主标题挡住了子标题,上下两个子图的间距也过小了
1.5 调整子图
tight_layout()函数
检查坐标轴标签、刻度标签和子图标题,自动调整子图,使之填充整个绘图区域,并消除子图之间的重叠。
在上述代码中增加
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#%%
# 设置默认字体为中文
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = "SimHei"
# 创建一个绘图对象,并将它的前景色绘制为浅灰色
fig = plt.figure(facecolor="lightgrey")
# 创建了四个子图
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
# 创建默认子标题
plt.title("子标题1")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
# 子标题 左对齐,字体颜色是蓝色
plt.title("子标题2", loc="left", color="b")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
# 将参数放在字典中,所有关键字都是字符串
myfontdict = {"fontsize": 12, "color": "g", "rotation": 30}
plt.title("子标题3", fontdict=myfontdict)
plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
# 标题字体为白色,背景色为黑色
plt.title("子标题4", color="w", backgroundcolor="black")
plt.suptitle("全局标题", fontsize=20, color="red", backgroundcolor="yellow")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
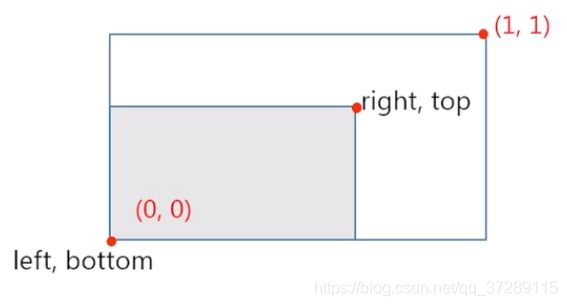
可以看到,子图之间的间距已经被自动调整了。标题和坐标轴之间不再重叠。但是,全局标题和子图区域还是有重叠。这是因为tight_layout()函数使子图区域充满了整个画布。我们现在希望能在画布上面留出一点位置来放置全局标题。这时候,只需要修改tight_layout()函数中的rect参数就可以了。
tight_layout(rect=(left, bottom, right, top))
这是子图区域的左下角坐标和右上角坐标,坐标必须为标准化图形坐标, 默认是(0,0,1,1)
# 设置默认字体为中文
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = "SimHei"
# 创建一个绘图对象,并将它的前景色绘制为浅灰色
fig = plt.figure(facecolor="lightgrey")
# 创建了四个子图
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
# 创建默认子标题
plt.title("子标题1")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
# 子标题 左对齐,字体颜色是蓝色
plt.title("子标题2", loc="left", color="b")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
# 将参数放在字典中,所有关键字都是字符串
myfontdict = {"fontsize": 12, "color": "g", "rotation": 30}
plt.title("子标题3", fontdict=myfontdict)
plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
# 标题字体为白色,背景色为黑色
plt.title("子标题4", color="w", backgroundcolor="black")
plt.suptitle("全局标题", fontsize=20, color="red", backgroundcolor="yellow")
plt.tight_layout(rect=(0, 0, 1, 1))
plt.show()
二、散点图
引入
散点图(Scatter):是数据点在直角坐标系中的分布图
scatter()函数
scatter(x, y, scale, color, marker, label)
参数说明如下
| 参数 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| x | 标题位置的x坐标 | 不可忽略 |
| y | 标题位置的y坐标 | 不可忽略 |
| scale | 数据点的大小 | 36 |
| color | 数据点的颜色 | |
| marker | 数据点的样式 | ‘o’(远点) |
| label | 图例文字 |
这是其他数据点样式
| 取值 | 中文描述 | 取值 | 中文描述 | 取值 | 中文描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | 实线 | 1 | 朝下的三角 | v | 朝下的三角 |
| – | 虚线 | 2 | 朝上的三角 | ^ | 朝上的三角 |
| -. | 点线 | 3 | 朝左的三角 | < | 朝左的三角 |
| : | 点虚线 | 4 | 朝右的三角 | > | 朝右的三角 |
| . | 点 | s | 正方形 | D | 钻石形 |
| , | 像素 | p | 五角形 | d | 小版钻石形 |
| o | 圆形 | * | 星型 | | |
垂直线形 |
| + | +号标记 | h | 1号六角形 | _ | 水平线形 |
| x | x号标记 | H | 2号六角形 |
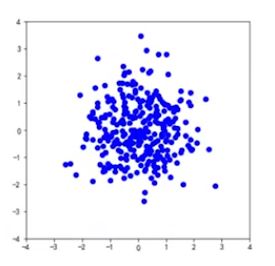
# 设置默认字体为中文
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = "SimSun"
# 标准正态分布
n = 1024
x = np.random.normal(0, 1, n)
y = np.random.normal(0, 1, n)
# 绘制散点图
plt.scatter(x, y, color="blue", marker="*")
# 设置标题
plt.title("标准正态分布", fontsize=20)
plt.show()
text(x, y, s, fontsize, color)
| 参数 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| x | 标题位置的x坐标 | 不可忽略 |
| y | 标题位置的y坐标 | 不可忽略 |
| s | 显示的文字 | 不可忽略 |
| fontsize | 文字的大小 | |
| color | 文字的颜色 | 黑色 |
这里我们看到由于设置了中文字体,负号不能正常显示,因此我们需要设置坐标轴
plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"] = False
绘图时,pyplot会根据数据的分布区间,自动加上坐标轴。如果要改变x轴,y轴的坐标范围,设置坐标轴的刻度样式或者给坐标轴加上标签,那么可以使用这几个函数
| 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| xlabel(x, y, fontsize, color) | 设置x轴标签 |
| ylabel(x, y, fontsize, color) | 设置y轴标签 |
| xlim(xmin, xmax) | 设置x轴坐标的范围 |
| ylim(ymin, ymax) | 设置y轴坐标的范围 |
| tick_params(labelsize) | 设置刻度文字的字号 |
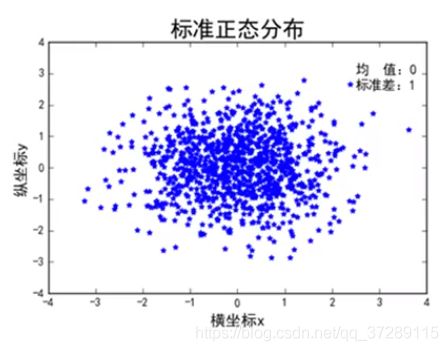
# 设置默认字体为中文
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = "SimHei"
# 标准正态分布
n = 1024
x = np.random.normal(0, 1, n)
y = np.random.normal(0, 1, n)
# 绘制散点图
plt.scatter(x, y, color="blue", marker="*")
# 设置标题
plt.title("标准正态分布", fontsize=20)
# 解决负号显示不出来的问题
plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"] = False
# 设置文本
plt.text(2.5, 2.5, "均值:0\n标准差:1")
# 设置坐标轴范围
plt.xlim(-4, 4)
plt.ylim(-4, 4)
# 设置轴标签文本
plt.xlabel('横坐标x', fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('纵坐标y', fontsize=14)
plt.show()
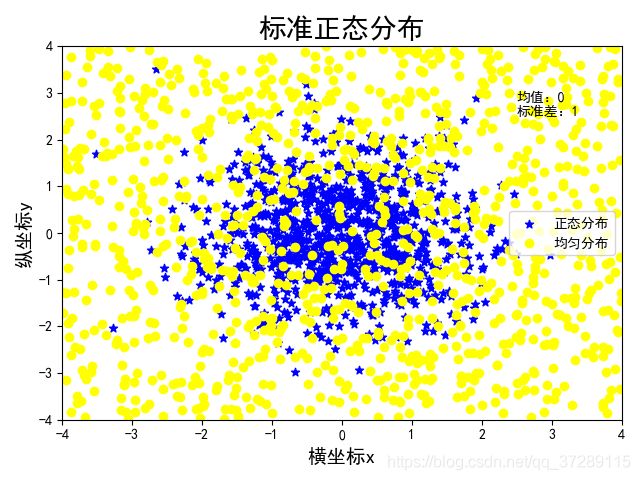
# 设置默认字体为中文
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = "SimHei"
# 标准正态分布
n = 1024
x1 = np.random.normal(0, 1, n)
y1 = np.random.normal(0, 1, n)
# 均匀分布
x2 = np.random.uniform(-4, 4, (1, n))
y2 = np.random.uniform(-4, 4, (1, n))
# 绘制散点图
plt.scatter(x1, y1, color="blue", marker="*")
plt.scatter(x2, y2, color="yellow", marker="o")
# 设置标题
plt.title("标准正态分布", fontsize=20)
# 解决负号显示不出来的问题
plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"] = False
# 设置文本
plt.text(2.5, 2.5, "均值:0\n标准差:1")
# 设置坐标轴范围
plt.xlim(-4, 4)
plt.ylim(-4, 4)
# 设置轴标签文本
plt.xlabel('横坐标x', fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('纵坐标y', fontsize=14)
plt.show()
scatter(x, y, scale, color, marker, label) # label是图例参数
legend(loc, fontsize)
loc参数的取值
| 取值 | 图例位置 | 取值 | 图例位置 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | best | 6 | center left |
| 1 | upper right | 7 | center right |
| 2 | upper left | 8 | lower center |
| 3 | lower left | 9 | upper center |
| 4 | lower right | 10 | center |
| 5 | right |
# 设置默认字体为中文
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = "SimHei"
# 标准正态分布
n = 1024
x1 = np.random.normal(0, 1, n)
y1 = np.random.normal(0, 1, n)
# 均匀分布
x2 = np.random.uniform(-4, 4, (1, n))
y2 = np.random.uniform(-4, 4, (1, n))
# 绘制散点图
plt.scatter(x1, y1, color="blue", marker="*", label="正态分布")
plt.scatter(x2, y2, color="yellow", marker="o", label="均匀分布")
# 默认位置, 使用默认字体
plt.legend()
# 设置标题
plt.title("标准正态分布", fontsize=20)
# 解决负号显示不出来的问题
plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"] = False
# 设置文本
plt.text(2.5, 2.5, "均值:0\n标准差:1")
# 设置坐标轴范围
plt.xlim(-4, 4)
plt.ylim(-4, 4)
# 设置轴标签文本
plt.xlabel('横坐标x', fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('纵坐标y', fontsize=14)
plt.show()
二、折线图
折线图:散点图的基础上,将相邻的点用线段想连接
plot()函数
plot(x, y, cplor, marker,label, linewidth, markersize)
参数说明如下:
| 参数 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| x | 标题位置的x坐标 | 0,1,2,… |
| y | 标题位置的y坐标 | 不可忽略 |
| color | 数据点的颜色 | |
| marker | 数据点的样式 | ‘o’(圆点) |
| label | 图例文字 | |
| linewidth | 折线的宽度 | |
| markersize | 数据点的大小 |
例子:
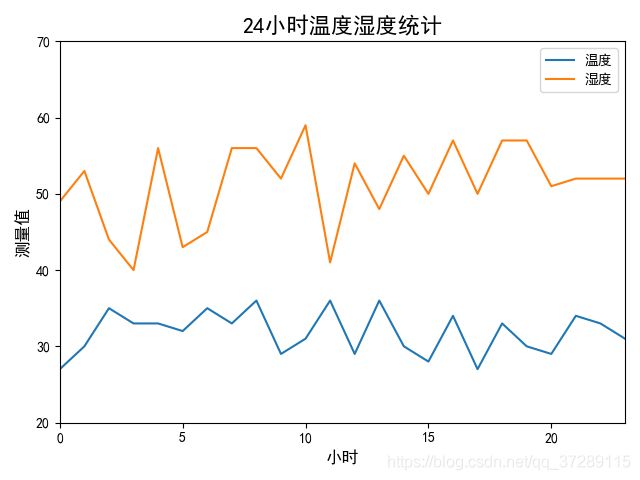
绘制这样一个折线图,这是一个房间24小时的温度和湿度的监测记录

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 设置默认字体为中文
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = "SimHei"
# 生成随机数列
n = 24
y1 = np.random.randint(27, 37, n)
y2 = np.random.randint(40, 60, n)
# 绘制折线图
plt.plot(y1, label="温度")
plt.plot(y2, label="湿度")
plt.xlim(0, 23)
# 多留一点空间好放置图例
plt.ylim(20, 70)
plt.xlabel("小时", fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel("测量值", fontsize=12)
plt.title("24小时温度湿度统计", fontsize=16)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
三、柱状图
1. 普通柱形图
bar(x, left, height, width, facecolor, edgecolor, label)
参数说明如下:
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| x | x轴的位置序列,一般采用arange函数产生一个序列 |
| height | y轴的数值序列,也就是柱形图的高度,一般就是我们需要展示的数据 |
| alpha | 透明度 |
| width | 为柱形图的宽度,默认0.8 |
| color或facecolor | 柱形图填充的颜色 |
| edgecolor | 图形边缘颜色 |
| label | 图例文字 |
| linewidth or linewidths or lw | 边缘or线的宽度 |
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 设置默认字体为中文
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = "SimHei"
# 解决负号问题
plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"] = False
# 条纹高度
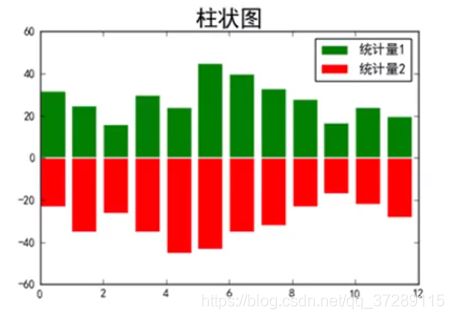
y1 = [32, 25, 16, 30, 24, 45, 40, 33, 28, 17, 24, 20]
y2 = [-23, -35, -26, -35, -45, -43, -35, -32, -23, -17, -22, -28]
# 条纹left坐标
plt.bar(range(len(y1)), y1, width=0.8, facecolor="green", edgecolor="white", label="统计量1")
plt.bar(range(len(y2)), y2, width=0.8, facecolor="red", edgecolor="white", label="统计量2")
plt.title("柱状图", fontsize=20)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
2. 并列柱形图
# 设置中文字体和负号正常显示
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
label_list = ['2014', '2015', '2016', '2017'] # 横坐标刻度显示值
num_list1 = [20, 30, 15, 35] # 纵坐标值1
num_list2 = [15, 30, 40, 20] # 纵坐标值2
x = range(len(num_list1))
rects1 = plt.bar(x=x, height=num_list1, width=0.4, alpha=0.8, color='red', label="一部门")
rects2 = plt.bar(x=[i + 0.4 for i in x], height=num_list2, width=0.4, color='green', label="二部门")
plt.ylim(0, 50) # y轴取值范围
plt.ylabel("数量")
# 设置x轴刻度显示值 参数一:中点坐标 参数二:显示值
plt.xticks([index + 0.2 for index in x], label_list)
plt.xlabel("年份")
plt.title("某某公司")
plt.legend() # 设置题注
# 编辑文本
for rect in rects1:
height = rect.get_height()
plt.text(rect.get_x() + rect.get_width() / 2, height+1, str(height), ha="center", va="bottom")
for rect in rects2:
height = rect.get_height()
plt.text(rect.get_x() + rect.get_width() / 2, height+1, str(height), ha="center", va="bottom")
plt.show()
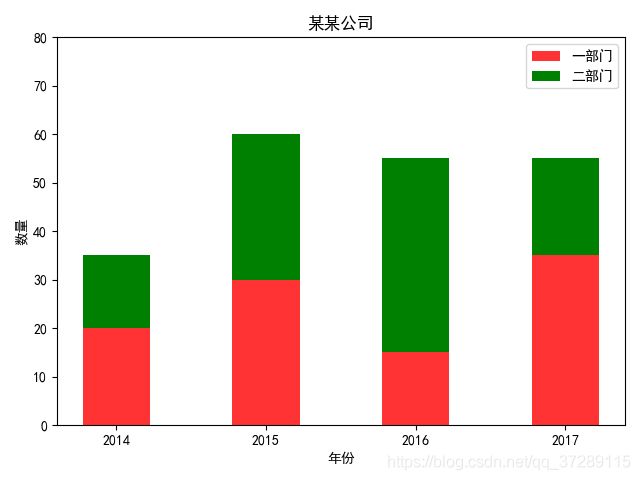
3. 堆叠条形图
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
label_list = ['2014', '2015', '2016', '2017']
num_list1 = [20, 30, 15, 35]
num_list2 = [15, 30, 40, 20]
x = range(len(num_list1))
rects1 = plt.bar(x=x, height=num_list1, width=0.45, alpha=0.8, color='red', label="一部门")
rects2 = plt.bar(x=x, height=num_list2, width=0.45, color='green', label="二部门", bottom=num_list1)
plt.ylim(0, 80)
plt.ylabel("数量")
plt.xticks(x, label_list)
plt.xlabel("年份")
plt.title("某某公司")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
4. 柱线混合图
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用黑体显示中文
# 构建数据
x = [2, 4, 6, 8]
y = [450, 500, 200, 1000]
# 画柱形图
plt.bar(x=x, height=y, label='书库大全', color='steelblue', alpha=0.8)
# 在柱状图上显示具体数值, ha参数控制水平对齐方式, va控制垂直对齐方式
for x1, yy in zip(x, y):
plt.text(x1, yy + 1, str(yy), ha='center', va='bottom', fontsize=20, rotation=0)
# 设置标题
plt.title("80小说网活跃度")
# 为两条坐标轴设置名称
plt.xlabel("发布日期")
plt.ylabel("小说数量")
# 显示图例
plt.legend()
# 画折线图
plt.plot(x, y, "r", marker='*', ms=10, label="a")
plt.xticks(rotation=45)
plt.legend(loc="upper left")
plt.savefig("a.jpg")
plt.show()
四、水平条形图
语法
barh(y, width, height, left, align='center')
参数说明如下:
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| y | y轴的位置序列,一般采用arange函数产生一个序列 |
| width | 柱形图的宽,默认0.8 |
| height | x轴的数值序列,也就是柱形图的高度,一般就是我们需要展示的数据 |
| alpha | 透明度 |
| align | 柱形图在x坐标的哪侧,可选值 ‘center’ ‘edge’ |
| left | 额外增量 |
| color或facecolor | 柱形图填充的颜色 |
| edgecolor | 图形边缘颜色 |
| label | 图例文字 |
| linewidth or linewidths or lw | 边缘or线的宽度 |
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
price = [39.5, 39.9, 45.4, 38.9, 33.34]
plt.barh(range(5), price, height=0.7, color='steelblue', alpha=0.8) # 从下往上画
plt.yticks(range(5), ['亚马逊', '当当网', '中国图书网', '京东', '天猫'])
plt.xlim(30,47)
plt.xlabel("价格")
plt.title("不同平台图书价格")
for x, y in enumerate(price):
plt.text(y + 0.2, x - 0.1, '%s' % y)
plt.show()
五、饼图
语法
barh(y, width, height, left, align='center')
参数说明如下:
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| x | (每一块)的比例,如果sum(x) > 1会使用sum(x)归一化 |
| explode | 设置各部分间隔值, 每一块离开中心距离 |
| labels | 每一块饼图外侧显示的图例 |
| colors | 每一块的颜色 |
| autopct | 控制饼图内百分比设置,可以使用format字符串或者format function '%1.1f’指小数点前后位数(没有用空格补齐) |
| pctdistance | 类似于labeldistance,指定autopct的位置,默认值为0.6 |
| shadow | 在饼图下面画一个阴影。默认值:False |
| labeldistance | label标记的绘制位置,相对于半径的比例,默认值为1.1, 如<1则绘制在饼图内侧 |
| startangle | 起始绘制角度,默认图是从x轴正方向逆时针画起,如设定=90则从y轴正方向画起 |
| radius | 控制饼图半径,默认值为1 |
| counterclock | 指定指针方向布尔值,默认为True,即逆时针。将值改为False即可改为顺时针 |
| wedgeprops | 字典类型,默认值:None。参数字典传递给wedge对象用来画一个饼图。例如:wedgeprops={‘linewidth’:3}设置wedge线宽为3。 |
| textprops | 设置标签(labels)和比例文字的格式字典类型,可选参数,默认值为:None。传递给text对象的字典参数。 |
| center | 浮点类型的列表,可选参数,默认值:(0,0)。图标中心位置。 |
| frame | 布尔类型,可选参数,默认值:False。如果是true,绘制带有表的轴框架。 |
| rotatelabels | 布尔类型,可选参数,默认为:False。如果为True,旋转每个label到指定的角度。 |
返回值
- patches:List matplotlib.patches.Wedge object 每块饼对象
- l_text:List 圆内部文本,matplotlib.text.Text object
- p_text:List 圆外部文本,matplotlib.text.Text object
例子:
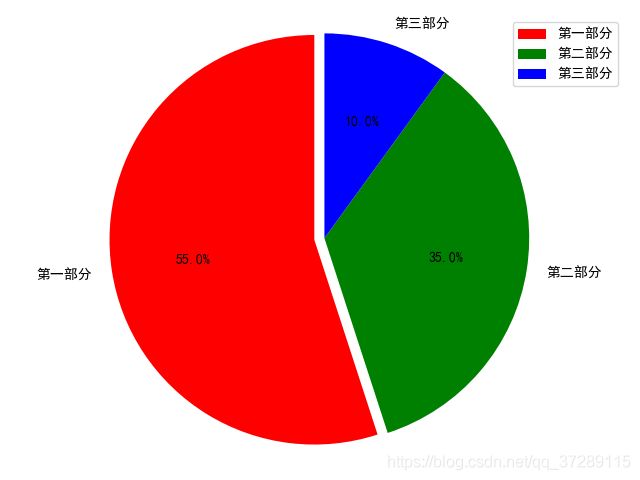
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
label_list = ["第一部分", "第二部分", "第三部分"] # 各部分标签
size = [55, 35, 10] # 各部分大小
color = ["red", "green", "blue"] # 各部分颜色
explode = [0.05, 0, 0] # 各部分突出值
patches, l_text, p_text = plt.pie(size, explode=explode, colors=color, labels=label_list, labeldistance=1.1, autopct="%1.1f%%", shadow=False, startangle=90, pctdistance=0.6)
plt.axis("equal") # 设置横轴和纵轴大小相等,这样饼才是圆的
plt.legend()
plt.show()
五、直方图
hist 用于绘制直方图
语法
hist(y, width, height, left, align='center')
参数说明如下:
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| x | 需要计算直方图的一维数组 |
| bins | 直方图的柱数 |
| ranges | bins的上下范围,如果没有则是(x.min(),x.max()) |
| density | 绘制并返回一个概率密度:每个箱子将显示箱子的原始计数除以总数density = counts / (sum(counts) * np.diff(bins)) |
| weight | 与x相同形状的权重数组。每个值在x只将其相关权重贡献给箱子计数(而不是1).如果density为’ ’ True ',则权重为标准化,所以密度在这个范围内的积分仍然是1。 |
| cumulative | 如果True,则计算直方图中每个容器给出计算那个箱子里的值加上所有小的箱子里的值。 |
| histtype | 直方图类型,‘bar’, ‘barstacked’, ‘step’, ‘stepfilled’ |
| align | 直方图条的水平对齐。{‘left’, ‘mid’, ‘right’}, default: ‘mid’ |
| facecolor | 直方图颜色 |
| edgecolor | 直方图边框颜色 |
| alpha | 透明度 |
| color | 颜色 |
| label | 标签 |
| bottom | |
| orientation | |
| rwidth | |
| log | |
| stacked |
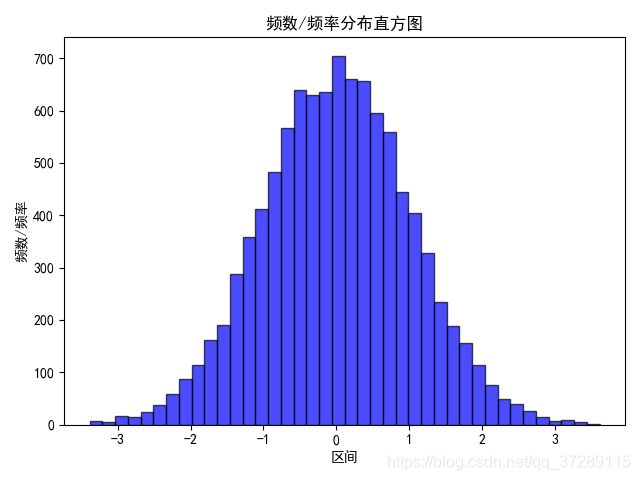
# 设置matplotlib正常显示中文和负号
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] # 用黑体显示中文
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False # 正常显示负号
# 随机生成(10000,)服从正态分布的数据
data = np.random.randn(10000)
plt.hist(data, bins=40, facecolor="blue", edgecolor="black", alpha=0.7)
# 显示横轴标签
plt.xlabel("区间")
# 显示纵轴标签
plt.ylabel("频数/频率")
# 显示图标题
plt.title("频数/频率分布直方图")
plt.show()