java中实现线程的方式
- 继承
Thread类,重写run()方法,然后通过调用start()开启一个线程,并执行我们的run()方法。 - 实现
Runnable接口的run()方法,然后通过Thread的构造函数传入Runnable接口,balabala...
这两种方式都是基于模板模式,用户不用关心怎么向操作系统申请一个线程,只需要关心开启的线程中执行什么逻辑就可以。但是我们都知道Runnable接口是这样的
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
public abstract void run();
}
是没有返回值的。但是有些场景,我们需要开启线程执行一段逻辑后,拿到返回值,这时候,就需要Callable相关接口。
先举个使用Callable的栗子,为了演示我在使用Callable接口,我这里不使用java8的函数式简化。
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
RunnableFuture runnableFuture = new FutureTask<>(new Callable() {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
return "HelloCallable";
}
});
new Thread(runnableFuture).start();
String s = runnableFuture.get();
System.out.println(s);
}
我们将需要执行的逻辑编写在call方法中,然后使用FutureTask包装该接口,最后,将runnableFuture 提交给Thread,这时候,我们就可以通过runnableFuture.get
获取到返回值。
原理
-
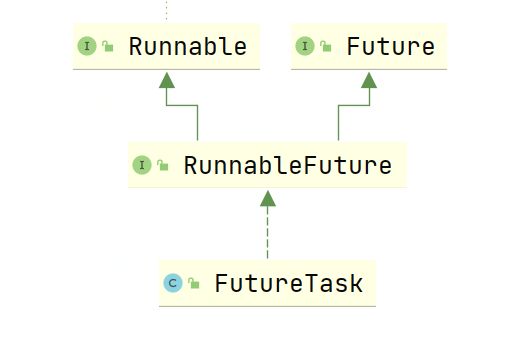
FutureTask的类图如下
- Future接口中包含获取返回值结果的方法
get如果线程没有执行完任务,调用该方法会阻塞当前线程,以及取消执行任务cancel,查看任务是否执行完毕isDone,以及任务是否取消isCancelled。
public interface Future {
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
boolean isCancelled();
boolean isDone();
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
- RunnableFuture接口相当于整合和Future和Runnable接口,没有添加其他功能。
public interface RunnableFuture extends Runnable, Future {
void run();
}
具体的原理是这样的,FutureTask中有两个很关键的属性,一个是callable接口,一个是存放call方法的返回值outcome属性。
public class FutureTask implements RunnableFuture {
private Callable callable;
private Object outcome; // non-volatile, protected by state reads/writes
...
}
FutureTask中run方法最核心的代码如下:
public void run() {
V result;
result = c.call();
set(result);
}
protected void set(V v) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
outcome = v;
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, NORMAL); // final state
finishCompletion();
}
}
run方法执行了Callable的call方法,然后将返回值赋值给了成员变量。
然后,通过get方法获取返回值,get方法具体逻辑如下:
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING)
s = awaitDone(false, 0L);
return report(s);
}
private V report(int s) throws ExecutionException {
Object x = outcome;
if (s == NORMAL)
return (V)x;
if (s >= CANCELLED)
throw new CancellationException();
throw new ExecutionException((Throwable)x);
}
get方法会判断此时callable任务的状态,如果没有完成,那么阻塞当前线程,等待完成,如果处于已经取消状态直接抛出异常,如果已经执行完毕,将结果返回。
FutureTask接口实现的比较复杂,阅读源码理解起来相对困难,但是本质上,FutureTask接口是一个生产者消费者模式,如果生产者没有生产完,那么会阻塞消费者,将消费者放到一个阻塞队列中,生产者生产完后,会唤醒阻塞的消费者去消费结果,大概原理就是这样,下面是一个简易版的实现。
class MyRunnableFuture implements RunnableFuture {
private Callable callable;
private Object returnObj;
private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition getCondition = lock.newCondition();
public MyRunnableFuture(Callable callable) {
this.callable = callable;
}
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
this.returnObj = this.callable.call();
try {
lock.lock();
this.getCondition.signalAll();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
@Override
public boolean isCancelled() {
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
@Override
public boolean isDone() {
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
@Override
public T get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
if (returnObj == null) {
try {
lock.lock();
this.getCondition.await();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
return (T) returnObj;
}
@Override
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}