题目:给定一棵二叉树和其中的一个节点,如何找出中序遍历序列的下一个节点?树中的节点除了有两个分别指向左、右子节点的指针,还有一个指向父节点的指针。
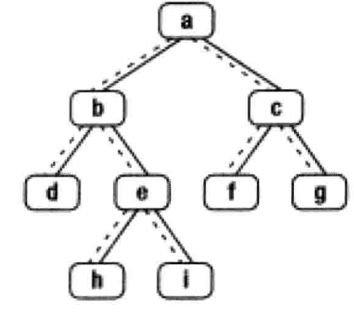
如下图中的二叉树的中序遍历序列是{d,b,h,e,i,a,f,c,g}。我们将以这棵树为例来分析如何找出二叉树的下一个节点
分析
如果一个节点有右子树,那么它的下一个节点就是它的右子树。也就是说,从右子节点出发沿着指向左子节点的指针,我们就能找到它的下一个节点。如上图节点b的下一个节点就是h,节点a的下一个节点是f
如果节点没有右子树,当节点是它父节点的左子节点,那么它的下一个节点就是它的父节点。如图节点d的下一个节点b,节点f的下一个节点是c
如果一个节点既没有右子树,并且它还是它父节点的右子树,那么这种情况就有点复杂。我们可以沿着指向父节点的指针一直向上遍历,直到找到一个是它父节点的左子节点的节点。如果这样的节点存在,那么这个节点的父节点就是我们要找的下一个节点
比如找图中节点i的下一个节点,我们沿着指向父节点的指针向上遍历,先到达节点e。由于节点e是它父节点b的右节点,我们继续向上遍历到节点b。节点b是它父节点a的左子节点,因此节点b的父节点a就是节点i的下一个节点
找出节点g的下一个节点的步骤类似,我们先沿着父节点的指针到达节点c。由于节点c是它父节点a的右子节点,因此我们继续向上遍历到节点a。由于节点a是树的根节点,它没有父节点,因此节点g没有下一个节点
总结
- 如果一个节点有右子树,那么它的下一个节点就是它的右子树中的最左节点
- 如果一个节点没有右子树:
- 如果节点是它父节点的左孩子,那么它的下一个节点就是它的父节点
- 如果节点是它父节点的右孩子,那么它的下一个节点是,沿着父节点向上遍历,父节点A是它本身父节点B的左孩子,B是下一个节点
- 如果没有就是尾节点,返回NULL
算法实现
二叉树
struct BinaryTreeNode {
int m_nValue;
BinaryTreeNode *m_pLeft;
BinaryTreeNode *m_pRight;
BinaryTreeNode *m_pParent;
};
获取下一个节点
BinaryTreeNode* GetNext(BinaryTreeNode *pNode)
{
if (pNode == nullptr)
return nullptr;
BinaryTreeNode *pNext = nullptr; // 用于记录下一个节点
if (pNode->m_pRight != nullptr) // 右子树存在
{
BinaryTreeNode *pRight = pNode->m_pRight; // 获得当前右子节点
while (pRight->m_pLeft != nullptr) // 左子节点不为空,那么循环遍历找到叶子节点
pRight = pRight->m_pLeft;
pNext = pRight; // 找到下一个节点
}
else if (pNode->m_pParent != nullptr) // 当前节点的父节点存在
{
BinaryTreeNode *pCurrent = pNode; // 当前节点
BinaryTreeNode *pPrarent = pNode->m_pParent; // 父节点
// 父节点不为空,并且当前节点是父节点的右子节点,循环向上遍历
while (pPrarent != nullptr && pCurrent == pPrarent->m_pRight) {
pCurrent = pPrarent;
pPrarent = pPrarent->m_pParent;
}
pNext = pPrarent;
}
return pNext;
}
辅助函数
// 创建二叉树
BinaryTreeNode* CreateBinaryTreeNode(int value)
{
BinaryTreeNode* pNode = new BinaryTreeNode();
pNode->m_nValue = value;
pNode->m_pLeft = nullptr;
pNode->m_pRight = nullptr;
pNode->m_pParent = nullptr;
return pNode;
}
// 连接二叉树
void ConnectTreeNodes(BinaryTreeNode* pParent, BinaryTreeNode* pLeft, BinaryTreeNode* pRight)
{
if(pParent != nullptr)
{
pParent->m_pLeft = pLeft;
pParent->m_pRight = pRight;
if(pLeft != nullptr)
pLeft->m_pParent = pParent;
if(pRight != nullptr)
pRight->m_pParent = pParent;
}
}
// 打印节点
void PrintTreeNode(BinaryTreeNode* pNode)
{
if(pNode != nullptr)
{
printf("value of this node is: %d\n", pNode->m_nValue);
if(pNode->m_pLeft != nullptr)
printf("value of its left child is: %d.\n", pNode->m_pLeft->m_nValue);
else
printf("left child is null.\n");
if(pNode->m_pRight != nullptr)
printf("value of its right child is: %d.\n", pNode->m_pRight->m_nValue);
else
printf("right child is null.\n");
}
else
{
printf("this node is null.\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
// 打印树
void PrintTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot)
{
PrintTreeNode(pRoot);
if(pRoot != nullptr)
{
if(pRoot->m_pLeft != nullptr)
PrintTree(pRoot->m_pLeft);
if(pRoot->m_pRight != nullptr)
PrintTree(pRoot->m_pRight);
}
}
// 销毁树
void DestroyTree(BinaryTreeNode* pRoot)
{
if(pRoot != nullptr)
{
BinaryTreeNode* pLeft = pRoot->m_pLeft;
BinaryTreeNode* pRight = pRoot->m_pRight;
delete pRoot;
pRoot = nullptr;
DestroyTree(pLeft);
DestroyTree(pRight);
}
}
// 测试
void Test(char* testName, BinaryTreeNode* pNode, BinaryTreeNode* expected)
{
if(testName != nullptr)
printf("%s begins: ", testName);
BinaryTreeNode* pNext = GetNext(pNode);
if(pNext == expected)
printf("Passed.\n");
else
printf("FAILED.\n");
}
简单使用
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
BinaryTreeNode* pNode8 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(8);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode6 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(6);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode10 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(10);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode5 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(5);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode7 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(7);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode9 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(9);
BinaryTreeNode* pNode11 = CreateBinaryTreeNode(11);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode8, pNode6, pNode10);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode6, pNode5, pNode7);
ConnectTreeNodes(pNode10, pNode9, pNode11);
Test("Test1", pNode8, pNode9);
Test("Test2", pNode6, pNode7);
Test("Test3", pNode10, pNode11);
Test("Test4", pNode5, pNode6);
Test("Test5", pNode7, pNode8);
Test("Test6", pNode9, pNode10);
Test("Test7", pNode11, nullptr);
DestroyTree(pNode8);
return 0;
}