关于缓存
缓存是实际工作中非常常用的一种提高性能的方法。而在java中,所谓缓存,就是将程序或系统经常要调用的对象存在内存中,再次调用时可以快速从内存中获取对象,不必再去创建新的重复的实例。这样做可以减少系统开销,提高系统效率。
在增删改查中,数据库查询占据了数据库操作的80%以上,而非常频繁的磁盘I/O读取操作,会导致数据库性能极度低下。而数据库的重要性就不言而喻了:
数据库通常是企业应用系统最核心的部分
数据库保存的数据量通常非常庞大
数据库查询操作通常很频繁,有时还很复杂
在系统架构的不同层级之间,为了加快访问速度,都可以存在缓存
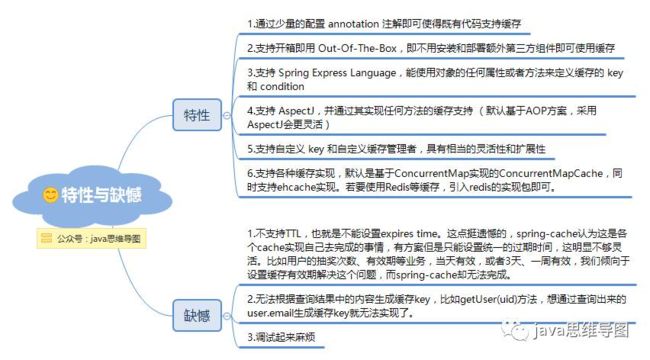
spring cache特性与缺憾
现在市场上主流的缓存框架有ehcache、redis、memcached。spring cache可以通过简单的配置就可以搭配使用起来。其中使用注解方式是最简单的。
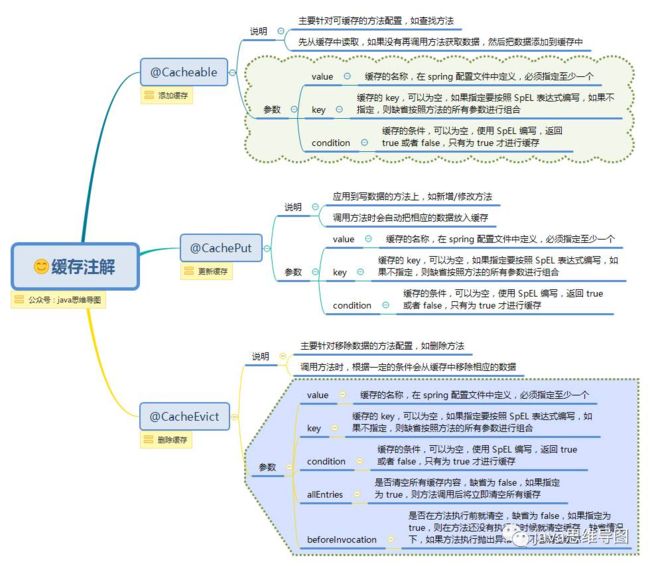
Cache注解
从以上的注解中可以看出,虽然使用注解的确方便,但是缺少灵活的缓存策略,
缓存策略:
TTL(Time To Live )
存活期,即从缓存中创建时间点开始直到它到期的一个时间段(不管在这个时间段内有没有访问都将过期)
TTI(Time To Idle)
空闲期,即一个数据多久没被访问将从缓存中移除的时间
项目中可能有很多缓存的TTL不相同,这时候就需要编码式使用编写缓存。
条件缓存
根据运行流程,如下@Cacheable将在执行方法之前( #result还拿不到返回值)判断condition,如果返回true,则查缓存;
@Cacheable(value = "user", key = "#id", condition = "#id lt 10")
public User conditionFindById(final Long id)
如下@CachePut将在执行完方法后(#result就能拿到返回值了)判断condition,如果返回true,则放入缓存
@CachePut(value = "user", key = "#id", condition = "#result.username ne 'zhang'")
public User conditionSave(final User user)
如下@CachePut将在执行完方法后(#result就能拿到返回值了)判断unless,如果返回false,则放入缓存;(即跟condition相反)
@CachePut(value = "user", key = "#user.id", unless = "#result.username eq 'zhang'")
public User conditionSave2(final User user)
如下@CacheEvict, beforeInvocation=false表示在方法执行之后调用(#result能拿到返回值了);且判断condition,如果返回true,则移除缓存;
@CacheEvict(value = "user", key = "#user.id", beforeInvocation = false, condition = "#result.username ne 'zhang'")
public User conditionDelete(final User user)
小试牛刀,综合运用:
@CachePut(value = "user", key = "#user.id")
public User save(User user) {
users.add(user);
return user;
}
@CachePut(value = "user", key = "#user.id")
public User update(User user) {
users.remove(user);
users.add(user);
return user;
}
@CacheEvict(value = "user", key = "#user.id")
public User delete(User user) {
users.remove(user);
return user;
}
@CacheEvict(value = "user", allEntries = true)
public void deleteAll() {
users.clear();
}
@Cacheable(value = "user", key = "#id")
public User findById(final Long id) {
System.out.println("cache miss, invoke find by id, id:" + id);
for (User user : users) {
if (user.getId().equals(id)) {
return user;
}
}
return null;
}
配置ehcache与redis
可以通过其他配置搭配使用两个缓存机制。比如ecache做一级缓存,redis做二级缓存。
更加详细的使用与配置,可以参考项目中spring-shiro-training中有关spring cache的配置。
https://git.oschina.net/wangzhixuan/spring-shiro-training.git