【数据挖掘】基于Python对Keras版本的卷积神经网络(CNN)可视化
keras实现卷积神经网络(CNN)可视化的Python环境要求如下:
pip install keras==2.3.1
pip install tensorflow==1.8.0
pip install opencv-pythonPython实现卷积神经网络(CNN)可视化,其中卷积神经网络实现模块为keras。卷积神经网络可视化包括以下四方面:
1. 卷积核输出的可视化,即可视化卷积操作后的结果,帮助理解卷积核的作用。
2. 卷积核的可视化,对卷积核本身进行可视化,对卷积核学习到的行为进行解释。
3. 类激活图可视化,通过热度图,了解图像分类问题中图像哪些部分起到了关键作用,同时可以定位图像中物体的位置。
4. 特征可视化,与第一种方法类似,但是输出的不再是卷积层的激活值,而是使用反卷积与反池化来可视化输入图像的激活特征。
不同的卷积神经网络模型的实现程序model.py如下:
import keras.applications as app
def get_model(name='vgg16'):
if name == 'vgg16':
model = app.vgg16.VGG16(weights='imagenet')
preprocess_input = app.vgg16.preprocess_input
if name == 'vgg19':
model = app.vgg19.VGG19(weights='imagenet')
preprocess_input = app.vgg19.preprocess_input
if name == 'resnet50':
model = app.resnet50.ResNet50(weights='imagenet')
preprocess_input = app.resnet50.preprocess_input
if name == 'inception_v3':
model = app.inception_v3.InceptionV3(weights='imagenet')
preprocess_input = app.inception_v3.preprocess_input
if name == 'xception':
model = app.xception.Xception(weights='imagenet')
preprocess_input = app.xception.preprocess_input
if name == 'mobilenet':
model = app.mobilenet.MobileNet(weights='imagenet')
preprocess_input = app.mobilenet.preprocess_input
if name == 'densenet':
model = app.densenet.DenseNet121(weights='imagenet')
preprocess_input = app.densenet.preprocess_input
return model, preprocess_input获得keras模型各层的特征矩阵实现程序vis.py
import numpy as np
from keras.models import Model
from keras import backend as K
import utils
from model import get_model
def conv_output(model, layer_name, img):
"""Get the output of conv layer.
Args:
model: keras model.
layer_name: name of layer in the model.
img: processed input image.
Returns:
intermediate_output: feature map.
"""
# this is the placeholder for the input images
input_img = model.input
try:
# this is the placeholder for the conv output
out_conv = model.get_layer(layer_name).output
except:
raise Exception('Not layer named {}!'.format(layer_name))
# get the intermediate layer model
intermediate_layer_model = Model(inputs=input_img, outputs=out_conv)
# get the output of intermediate layer model
intermediate_output = intermediate_layer_model.predict(img)
return intermediate_output[0]
def conv_filter(model, layer_name, img):
"""Get the filter of conv layer.
Args:
model: keras model.
layer_name: name of layer in the model.
img: processed input image.
Returns:
filters.
"""
# this is the placeholder for the input images
input_img = model.input
# get the symbolic outputs of each "key" layer (we gave them unique names).
layer_dict = dict([(layer.name, layer) for layer in model.layers[1:]])
try:
layer_output = layer_dict[layer_name].output
except:
raise Exception('Not layer named {}!'.format(layer_name))
kept_filters = []
for i in range(layer_output.shape[-1]):
loss = K.mean(layer_output[:, :, :, i])
# compute the gradient of the input picture with this loss
grads = K.gradients(loss, input_img)[0]
# normalization trick: we normalize the gradient
grads = utils.normalize(grads)
# this function returns the loss and grads given the input picture
iterate = K.function([input_img], [loss, grads])
# step size for gradient ascent
step = 1.
# run gradient ascent for 20 steps
fimg = img.copy()
for j in range(40):
loss_value, grads_value = iterate([fimg])
fimg += grads_value * step
# decode the resulting input image
fimg = utils.deprocess_image(fimg[0])
kept_filters.append((fimg, loss_value))
# sort filter result
kept_filters.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
return np.array([f[0] for f in kept_filters])
def output_heatmap(model, last_conv_layer, img):
"""Get the heatmap for image.
Args:
model: keras model.
last_conv_layer: name of last conv layer in the model.
img: processed input image.
Returns:
heatmap: heatmap.
"""
# predict the image class
preds = model.predict(img)
# find the class index
index = np.argmax(preds[0])
# This is the entry in the prediction vector
target_output = model.output[:, index]
# get the last conv layer
last_conv_layer = model.get_layer(last_conv_layer)
# compute the gradient of the output feature map with this target class
grads = K.gradients(target_output, last_conv_layer.output)[0]
# mean the gradient over a specific feature map channel
pooled_grads = K.mean(grads, axis=(0, 1, 2))
# this function returns the output of last_conv_layer and grads
# given the input picture
iterate = K.function([model.input], [pooled_grads, last_conv_layer.output[0]])
pooled_grads_value, conv_layer_output_value = iterate([img])
# We multiply each channel in the feature map array
# by "how important this channel is" with regard to the target class
for i in range(conv_layer_output_value.shape[-1]):
conv_layer_output_value[:, :, i] *= pooled_grads_value[i]
# The channel-wise mean of the resulting feature map
# is our heatmap of class activation
heatmap = np.mean(conv_layer_output_value, axis=-1)
heatmap = np.maximum(heatmap, 0)
heatmap /= np.max(heatmap)
return heatmap可视化工具utils.py实现程序如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from keras import backend as K
def read_img(img_path, preprocess_input, size):
"""util function to read and preprocess the test image.
Args:
img_path: path of image.
preprocess_input: preprocess_input function.
size: resize.
Returns:
img: original image.
pimg: processed image.
"""
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
pimg = cv2.resize(img, size)
pimg = np.expand_dims(pimg, axis=0)
pimg = preprocess_input(pimg)
return img, pimg
def deprocess_image(x):
"""util function to convert a tensor into a valid image.
Args:
x: tensor of filter.
Returns:
x: deprocessed tensor.
"""
# normalize tensor: center on 0., ensure std is 0.1
x -= x.mean()
x /= (x.std() + 1e-5)
x *= 0.1
# clip to [0, 1]
x += 0.5
x = np.clip(x, 0, 1)
# convert to RGB array
x *= 255
if K.image_data_format() == 'channels_first':
x = x.transpose((1, 2, 0))
x = np.clip(x, 0, 255).astype('uint8')
return x
def normalize(x):
"""utility function to normalize a tensor by its L2 norm
Args:
x: gradient.
Returns:
x: gradient.
"""
return x / (K.sqrt(K.mean(K.square(x))) + K.epsilon())
def vis_conv(images, n, name, t):
"""visualize conv output and conv filter.
Args:
img: original image.
n: number of col and row.
t: vis type.
name: save name.
"""
size = 64
margin = 5
if t == 'filter':
results = np.zeros((n * size + 7 * margin, n * size + 7 * margin, 3))
if t == 'conv':
results = np.zeros((n * size + 7 * margin, n * size + 7 * margin))
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if t == 'filter':
filter_img = images[i + (j * n)]
if t == 'conv':
filter_img = images[..., i + (j * n)]
filter_img = cv2.resize(filter_img, (size, size))
# Put the result in the square `(i, j)` of the results grid
horizontal_start = i * size + i * margin
horizontal_end = horizontal_start + size
vertical_start = j * size + j * margin
vertical_end = vertical_start + size
if t == 'filter':
results[horizontal_start: horizontal_end, vertical_start: vertical_end, :] = filter_img
if t == 'conv':
results[horizontal_start: horizontal_end, vertical_start: vertical_end] = filter_img
# Display the results grid
plt.imshow(results)
plt.savefig('images\{}_{}.jpg'.format(t, name), dpi=600)
plt.show()
def vis_heatmap(img, heatmap):
"""visualize heatmap.
Args:
img: original image.
heatmap:heatmap.
"""
img = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(221)
plt.imshow(cv2.resize(img, (224, 224)))
plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(222)
plt.imshow(heatmap)
plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(212)
heatmap = cv2.resize(heatmap, (img.shape[1], img.shape[0]))
heatmap = np.uint8(255 * heatmap)
# We apply the heatmap to the original image
heatmap = cv2.applyColorMap(heatmap, cv2.COLORMAP_JET)
superimposed_img = heatmap * 0.4 + img
plt.imshow(superimposed_img)
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('images\heatmap.jpg', dpi=600)
plt.show()
实现可视化案例程序如下:
img_path = 'images\cat.jpg'
layer_name = 'block4_conv3'
last_conv_layer = 'block5_conv3'
model, preprocess_input = get_model('vgg16')
img, pimg = utils.read_img(img_path, preprocess_input, (224, 224))
cout = conv_output(model, layer_name, pimg)
utils.vis_conv(cout, 8, layer_name, 'conv')
pimg = np.random.random((1, 224, 224, 3)) * 20 + 128.
fout = conv_filter(model, layer_name, pimg)
utils.vis_conv(fout, 8, layer_name, 'filter')
heatmap = output_heatmap(model, last_conv_layer, pimg)
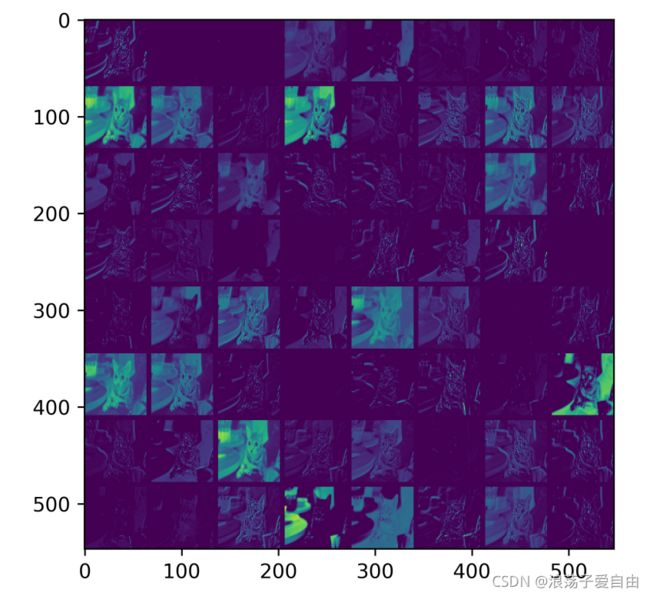
utils.vis_heatmap(img, heatmap)结果展示:
- 原图:
特征可视化结果:
【参考资料】
[1]Keras实现卷积神经网络(CNN)可视化
[2]利用Python实现卷积神经网络的可视化