什么是数据结构
数据的存储与组织方式
数据结构的分类
逻辑结构与物理结构
逻辑结构分为线性结构与非线性结构。线性结构包括 :顺序表、栈、队列;非线性表包括:树、图
物理结构分为顺序存储结构与链式存储结构。线性存储结构:数组;链式存储结构:链表
什么是算法
指解题方案的准确而完整的描述,是一系列解决问题的清晰指令,算法代表着用系统的方法描述解决问题的策略机制
评价算法的好坏
时间复杂度 + 空间复杂度 + 应用场景(重要因素)
时间复杂度
关键代码的执行次数
推导出时间复杂度,有如下几个原则:
- 如果运行时间是常数数量级,则用常数1表示。
- 只保留时间函数中的最高阶项
- 如果最高阶项存在,则省去最高阶项前面的系数
O(n)
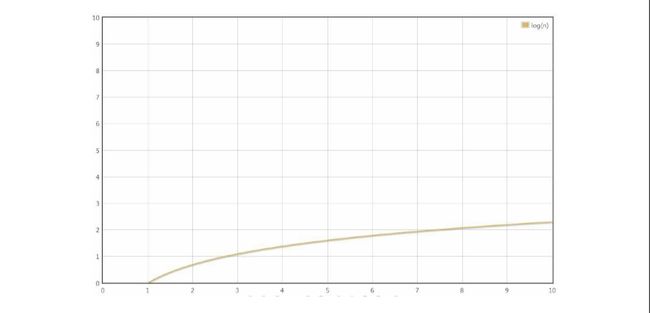
O(logn)
O(1)
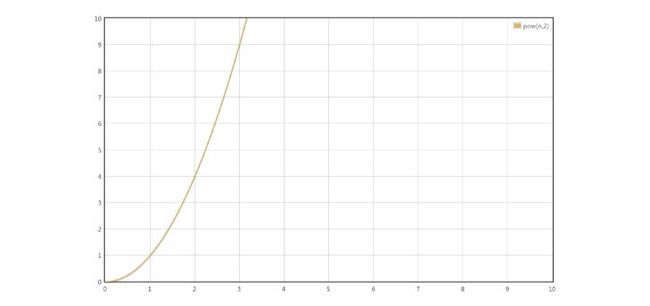
O (n²)
空间复杂度
在运行过程中临时占用存储空间大小的量度。一般只考虑时间复杂度
应用场景
为什么要考虑应用场景
public class SwapData {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
swap1();
swap2();
swap3();
}
/**
* 方法一:借用第三方变量实现数据交换,可读性最好
*/
public static void swap1(){
int a = 5;
int b = 6;
int temp = a;// temp = 5
a = b;//a = 6
b = temp;//b =5
System.out.println("a = "+a);
System.out.println("b = "+b);
}
/**
* 方法二:不借用第三方变量实现数据交换
*/
public static void swap2(){
int a = 5;
int b = 6;
a = a + b;//a=11
b = a - b;//b=5
a = a - b;//a =6
System.out.println("a = "+a);
System.out.println("b = "+b);
}
/**
* 方法三:性能最优,位运算,一般用在嵌入式设备中
*/
public static void swap3(){
int a = 5;
int b = 6;
a = a^b;
b = a^b;
a = a^b;
System.out.println("a = "+a);
System.out.println("b = "+b);
}
}
虽然另外两种性能更好,但是 可读性差,所以在实际应用中,算法的应用场景也是十分重要的
线性表
顺序存储结构(数组)
数组是有限个相同类型的变量组成的有序集合。在内存中是顺序存储的。常用的操作是CRUD,即增删改查。
public class Array {
private int[] mArray;
private int mCapacity;
private int mArraySize;//实际大小
public Array(int capacity){
if (capacity <= 0) {
this.mCapacity = 1;
}
this.mCapacity = capacity;
mArray = new int[mCapacity];
this.mArraySize = 0;
}
/**
* 增(时间复杂度O(n))
* @param index
* @param value
* @return
*/
public int add(int index,int value){
if (index < 0 || index > this.mArraySize) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
if (this.mArraySize >= this.mArray.length) {//扩容
resize();
}
for (int x = this.mArraySize - 1 ; x >= index;x--){
mArray[x + 1] = mArray[x];// 后移
}
mArray[index] = value;
mArraySize++;
return index;
}
private void resize() {
int[] newArray = new int[this.mCapacity * 2];
System.arraycopy(this.mArray,0,newArray,0,this.mArray.length);
this.mArray = newArray;
}
/**
* 删(时间复杂度O(n))
* @param index
* @return
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
*/
public int delete(int index) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {
if (index < 0 || index > this.mArraySize) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
int deleteValue = mArray[index];
for (int x = index;x < this.mArraySize - 1;x++){
mArray[x] = mArray[x+1];// 往前
System.out.println("x = "+x);
}
mArraySize--;
return deleteValue;
}
/**
* 改(时间复杂度O(1))
* @param index
* @param value
* @return
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
*/
public int update(int index,int value) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException{
if (index < 0 || index > this.mArraySize) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
this.mArray[index] = value;
return index;
}
/**
* 查(时间复杂度O(1))
* @param index
* @return
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
*/
public int read(int index) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException{
if (index < 0 || index > this.mArraySize) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
return this.mArray[index];
}
public void printArray(){
for (int i = 0;i < this.mArraySize;i++){
System.out.print(mArray[i]+" , ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
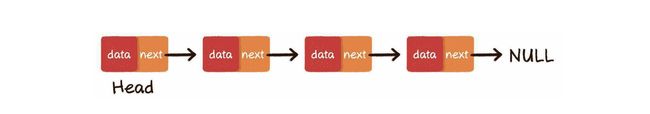
链式存储结构
链表是一种在物理上非连续的,非顺序的数据结构。由若干节点组成。分为单向链表和双向链表
单向链表
public class LinkedListDemo {
class Node{
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int data){
this.data = data;
}
}
private Node head;
private Node last;
private int listSize;// 链表大小
public int add(int index,int data) throws Exception {
if (index < 0 || index > this.listSize){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
Node node = new Node(data);
if (listSize == 0){// 如果链表为空
head = node;
last = node;
} else if (index == 0) {// 1. 头部插入
node.next = head;
head = node;
} else if (index == this.listSize ) {// 2. 插入尾部
last.next = node;
last = node;
} else {// 3.中间插入
Node prvNode = get(index - 1);
node.next = prvNode.next;
prvNode.next = node;
}
this.listSize++;
return index;
}
public int delete(int index) throws Exception {
if (index < 0 || index > this.listSize){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
if (this.listSize == 0) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return -1;
}
Node deleteNode = get(index);
if (index == 0) {// 1. 头部
head = head.next;
} else if (index == this.listSize) {// 2. 尾部
Node prvNode = get(index - 1);
last = prvNode;
} else {// 3. 中间
Node prvNode = get(index - 1);
prvNode.next = deleteNode.next;
}
deleteNode = null;
this.listSize--;
return index;
}
public int update(int index,int data) throws Exception {
if (index < 0 || index > this.listSize){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
Node node = get(index);
node.data = data;
return index;
}
public Node get(int index) throws Exception {
if (index < 0 || index > this.listSize){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
Node node = head;
for (int i = 0;i < index;i++){
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}
public void printLinkedList(){
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
Node node = head;
for (int i = 0;i < listSize;i++){
System.out.print(node.data+" , ");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
}
}
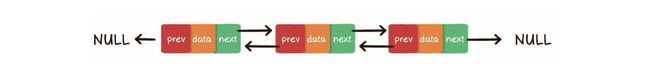
双向链表
双链表比单链表,查询效率更高,因为可以从后往前查找
public class LinkedListDemo {
class Node{
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node prv;
public Node(int data){
this.data = data;
}
}
private Node head;
private Node last;
private int listSize;// 链表大小
public int add(int index,int data) throws Exception {
if (index < 0 || index > this.listSize){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
Node node = new Node(data);
if (listSize == 0){// 如果链表为空
head = node;
last = node;
} else if (index == 0) {// 1. 头部插入
node.next = head;
head.prv = node;
head = node;
} else if (index == this.listSize ) {// 2. 插入尾部
last.next = node;
node.prv = last;
last = node;
} else {// 3.中间插入
Node prvNode = get(index - 1);
node.next = prvNode.next;
prvNode.next.prv = node;
prvNode.next = node;
node.prv = prvNode;
}
this.listSize++;
return index;
}
public int delete(int index) throws Exception {
if (index < 0 || index > this.listSize){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
if (this.listSize == 0) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return -1;
}
Node deleteNode = get(index);
if (index == 0) {// 1. 头部
head = head.next;
} else if (index == this.listSize) {// 2. 尾部
Node prvNode = get(index - 1);
last = prvNode;
} else {// 3. 中间
Node prvNode = get(index - 1);
prvNode.next = deleteNode.next;
deleteNode.next.prv = prvNode;
}
deleteNode = null;
this.listSize--;
return index;
}
public int update(int index,int data) throws Exception {
if (index < 0 || index > this.listSize){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
Node node = get(index);
node.data = data;
return index;
}
public Node get(int index) throws Exception {
if (index < 0 || index > this.listSize){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
Node node = head;
for (int i = 0;i < index;i++){
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}
public void printLinkedList(){
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
Node node = head;
for (int i = 0;i < listSize;i++){
System.out.print(node.data+" , ");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
}
public void printLinkedListReverse(){
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
Node node = last;
for (int i = listSize;i > 0;i--){
System.out.print(node.data+" , ");
node = node.prv;
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
}
}
蛮力法
蛮力法(brute force method,也称为穷举法或者枚举法)
是一种简单直接地解决问题的方法,
常常直接基于问题的描述,
所以,蛮力法也是最容易应用的方法,
但是,用蛮力法设计的算法时间特性往往也是最低的,
典型的指数时间算法一般都是通过蛮力搜索而得到的。
冒泡排序
蛮力法的一种,当 N < 5时,比其他的算法要快。
斗牛棋牌中的排序,就是用的冒泡排序算法。
public class BubbleSort {
public void bubbleSort(int[] arrays){
for (int i = 1;i < arrays.length;i++){
boolean flag = false;//标志位,用于减少算法的执行次数,时间复杂度可降至N
for (int j = 0;j < arrays.length - i;j++){// 一趟
if (arrays[j] > arrays[j+1]) {
// 交换数据
int temp = arrays[j];
arrays[j] = arrays[j+1];
arrays[j+1] = temp;
flag = true;
}
}
if (flag == false) {
break;
}
System.out.println("一趟 "+arrays[i]);
}
}
public void printArray(int[] arrays){
for (int i = 0;i < arrays.length;i++){
System.out.print(arrays[i]+" , ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
选择排序
public class SelectSort {
public void selectSort(int[] arrays){
for (int i = 0;i < arrays.length - 1;i++){
int index = i;
for (int j = i + 1;j < arrays.length;j++){// 一趟
if (arrays[index] < arrays[j]) {
index = j;
}
}
// 交换数据
if (index != i) {
int temp = arrays[i];
arrays[i] = arrays[index];
arrays[index] = temp;
System.out.println("一趟 "+arrays[i]+" index = "+index);
}
}
}
public void printArray(int[] arrays){
for (int i = 0;i < arrays.length;i++){
System.out.print(arrays[i]+" , ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
基数排序
基数排序,适合数据量在二三十个的情况
/**
* Created by 48608 on 2017/12/6.
*/
public class Mahjong {
public int suit;//筒,万,索
public int rank;//点数 一 二 三
public Mahjong(int suit, int rank) {
this.suit = suit;
this.rank = rank;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "("+this.suit+" "+this.rank+")";
}
}
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class RadixSortUtils {
public void radixSort(LinkedList mahjongs){
LinkedList[] rankList = new LinkedList[9];
// 第一步,按点数就行分类
for (int i = 0;i < rankList.length;i++){
rankList[i] = new LinkedList();
}
while(mahjongs.size() > 0){// 用for循环不行,因为大小在不断地变小
Mahjong mahjong = mahjongs.remove();// 一个个的取出来
rankList[mahjong.rank - 1].add(mahjong);
}
// 九个链表合成一个链表
for (int i = 0;i < rankList.length;i++){
mahjongs.addAll(rankList[i]);
}
// 第二步,按花色进行分类
LinkedList[] suitList = new LinkedList[3];
for (int i = 0;i < suitList.length;i++){
suitList[i] = new LinkedList();
}
while (mahjongs.size() > 0){// 用for循环不行
Mahjong mahjong = mahjongs.remove();// 一个个的取出来
suitList[mahjong.suit - 1].add(mahjong);
}
// 三个链表合成一个链表
for (int i = 0;i < suitList.length;i++){
mahjongs.addAll(suitList[i]);
}
}
}