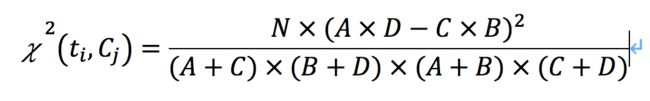收集好了训练样本集,需要对文本词语进行特征选择。
特征选择的意义有两个:
1.去掉噪音
去噪一个是去掉无意义的词,像只有几个文档出现过的词,或者每一个文档都出现的词。或者在很多类别里面都存在的词,其实都没有太大的意义。因为这些词对分类的结果起不到太大的作用。
2.降低维度
降维的作用主要是减少运算复杂度,加快运算速度。如果是自己的电脑一般也不会配置一个256g内存,从这个方面看,筛选的特征越少越好。
常见的特征选择方法,就如宗成庆的《统计自然语言处理》里面写的,有文档频率DF,互信息MI,信息增益IG,卡方检验CHI等等这几种方法。
DF很好理解的,文档频率。就是计算一个词出现的文章数目,非常简单的统计。
先跑了一遍DF,文本数是25236篇。十个类型,数据量分布不均匀。
跑出来词量是88w+。
贴上计算DF的代码
HashMap DFMap = new HashMap();
//在挑选训练集的基础上,计算文档频率DF
public void getDF(String path) throws IOException {
for (int i = 0; i < fileList.size(); i++) {
HashSet idSet = readid(fileList.get(i));
for (String id : idSet) {
Item item = hbase.getItem(id);
if(item == null) {
LOG.info("is null . id "+id);
continue;
}
List keywords = item.getkeywords();
for (Feature feature : keywords) {
if(DFMap.containsKey(feature.getName().trim())) {
DFMap.put(feature.getName().trim(), DFMap.get(feature.getName().trim())+1);
}
else {
DFMap.put(feature.getName().trim(), 1.0);
}
}
}
}
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(path,true);
for(Entry entry : DFMap.entrySet()) {
fw.write(entry.getKey()+"\t"+entry.getValue()+"\n");
}
fw.flush();
fw.close();
}
然后,观察了一下,去掉了某些无意义的词,然后把DF小于6的都去掉了,一下就清爽了不少。还有把大于7000的都去掉了,这部分没多少。这样剩下9w+的词汇。
接着计算CHI检验。
CHI又叫卡方统计量,或者卡方检验。
先画个表格
| 特征\类别 | Cx | ~Cx |
|---|---|---|
| ti | A | B |
| ~ti | C | D |
然后我来说说这几个变量的意思。
表头C表示某个类别C,某个用Cx来说明
~C自然就表示非某个类别C
t表示预料中的词,ti就表示某个词
有一个全局变量N,表示训练集中全部文档数目。
A表示属于Cj类且包含ti的文档数目
B表示不属于Cj包含ti的文档数目
C表示属于Cj类但不包含ti的文档数目
D表示不属于Cj类也不包含ti的文档数目
是不是很简单~~~
然后 这个卡方统计量的计算方法就是
好像这里不好输入公式我还是粘个图吧
就是这样的,最后,选取在所有类别C中,卡方最大的值作为ti的最后结果。
double n = 0;
//chi检验
class chiword {
public chiword() {
a = 0;
b = 0;
c = 0;
d = 0;
chi = 0;
}
String category;
double a;
double b;
double c;
double d;
double chi;
public double calCHI() {
double result = n * Math.sqrt((a * d - c * b)) / ((a + c) * (b + d) * (a + b) * (c + d));
return result;
}
}
HashSet keywordSet = new HashSet();
private void readDFWord(String path) throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader(path);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
String keyword = line.split("\t")[0].trim();
keywordSet.add(keyword);
}
br.close();
fr.close();
}
private HashSet readid(String path) throws IOException {
HashSet idSet = new HashSet();
FileReader fr = new FileReader(path);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
String line = null;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
idSet.add(line.trim());
}
br.close();
fr.close();
return idSet;
}
List categoryList = new ArrayList();
List fileList = new ArrayList();
public void refreshFileList(String localPath) {
File dir = new File(localPath);
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
if (files == null)
return;
for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {
if (files[i].isDirectory()) {
refreshFileList(files[i].getAbsolutePath());
} else {
fileList.add(files[i].getAbsolutePath());
categoryList.add(files[i].getName());
}
}
LOG.info("get category num is "+categoryList.size());
}
HashMap> termMap = new HashMap>();
HashMap categoryNum = new HashMap();
public void process() throws IOException {
for (int i = 0; i < fileList.size(); i++) {
String category = categoryList.get(i);
HashSet idSet = readid(fileList.get(i));
double cateNum = 0;
for (String id : idSet) {
LOG.info("Begin process id "+id);
travel_item item = hbase.getItem(id);
if(item == null) {
LOG.info("is null . id "+id);
continue;
}
cateNum++;
n++;
LOG.info("n is "+n);
List keywords = item.getkeywords();
for (Feature feature : keywords) {
if(!keywordSet.contains(feature.getName().trim())) {
continue;
}
if (termMap.containsKey(feature.getName().trim())) {
List chilist = termMap.get(feature.getName().trim());
for (int j = 0; j < chilist.size(); j++) {
chiword chiw = chilist.get(j);
if (chiw.category.equals(category)) {
chiw.a = chiw.a + 1;
} else {
chiw.b = chiw.b + 1;
}
chilist.set(j, chiw);
}
termMap.put(feature.getName().trim(), chilist);
} else {
List chilist = new ArrayList();
for (int k = 0; k < categoryList.size(); k++) {
chiword chiw = new chiword();
chiw.category = categoryList.get(k);
LOG.info("chiw category is "+ chiw.category);
if (chiw.category.equals(category)) {
chiw.a = chiw.a + 1;
} else {
chiw.b = chiw.b + 1;
}
chilist.add(chiw);
}
termMap.put(feature.getName().trim(), chilist);
}
}
}
categoryNum.put(category, cateNum);
LOG.info("categoryMap put "+category+"\t"+cateNum);
}
}
HashMap termChiMap = new HashMap();
public void getMax() {
LOG.info("keyword size is "+termMap.size());
for(Entry> entry : termMap.entrySet()) {
String term = entry.getKey();
LOG.info(" get keyword is "+term);
double chivalue = 0;
List chilist = entry.getValue();
for(int i = 0; i< chilist.size(); i++) {
chiword chiw = chilist.get(i);
chiw.c = categoryNum.get(chiw.category) - chiw.a;
chiw.d = n - categoryNum.get(chiw.category) - chiw.b;
chiw.chi = chiw.calCHI();
LOG.info("CHI value is "+chiw.category+"\t"+chiw.a+"\t"+chiw.b+"\t"+chiw.c+"\t"+chiw.d+"\t"+chiw.chi);
if(chiw.chi > chivalue) {
chivalue = chiw.chi;
}
}
termChiMap.put(term, chivalue);
}
}
public void output(String path) throws IOException {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(path);
for(Entry entry: termChiMap.entrySet()) {
fw.write(entry.getKey()+"\t"+entry.getValue()+"\n");
}
fw.flush();
fw.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FeatureSelect ob = new FeatureSelect();
ob.refreshFileList(args[0]);
//计算CHI
ob.readDFWord(args[2]);
ob.process();
ob.getMax();
ob.output(args[1]);
}
通过上述的计算,最后保留了CHI较大的数值,维度为81000个词。
好了 ,结束了。