restful hello world
首次浏览下go-restful的工程结构,从工程组织上面来看,工程包括两个部分:source文件及example文件,其中source文件组成了工程的主体,包括restful主要功能接口的实现及单元测试文件(以test.go结尾命名的文件),另外example目录中主要包括了接口的使用案例。
第一次阅读go-restful源码,以example目录下的restful-hello-world.go作为入坑样例,来跟踪了解下restful如何组织封装webservice及route的维护。
restful-hello-world.go代码如下:
func main() {
ws := new(restful.WebService)
ws.Route(ws.GET("/hello").To(hello))
restful.Add(ws)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil))
}
func hello(req *restful.Request, resp *restful.Response) {
io.WriteString(resp, "world")
}
restful初始化流程
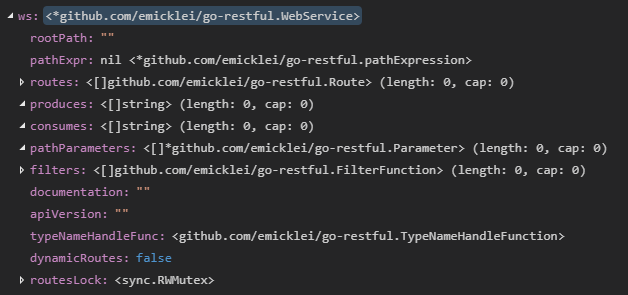
1. ws := new(restful.WebService)
webservice定义在web_service.go中, 通过new分配了webservicef空间, 传递给ws指向新分配零值的指针
// WebService holds a collection of Route values that bind a Http Method + URL Path to a function.
type WebService struct {
rootPath string
pathExpr *pathExpression // cached compilation of rootPath as RegExp
routes []Route
produces []string
consumes []string
pathParameters []*Parameter
filters []FilterFunction
documentation string
apiVersion string
typeNameHandleFunc TypeNameHandleFunction
dynamicRoutes bool
// protects 'routes' if dynamic routes are enabled
routesLock sync.RWMutex
}
2.ws.Route(ws.GET("/hello").To(hello))
2.1 ws.GET("/hello")
第一步执行的函数,GET方法绑定在WebServices结构体上,调用改函数参数为subPath = /hello, 返回RouteBuilder指针
func (w *WebService) GET(subPath string) *RouteBuilder {
return new(RouteBuilder).typeNameHandler(w.typeNameHandleFunc).servicePath(w.rootPath).Method("GET").Path(subPath)
}
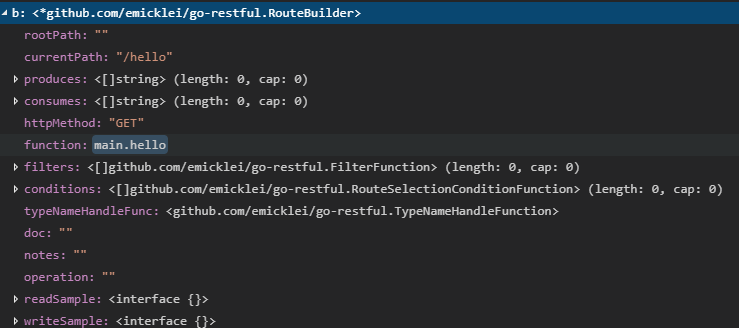
2.1.1 new(RouteBuilder)
在Get函数中,首先执行new(RouteBuilder), 返回routebuilder指针,在webservice的初始化后期可以发现,RouteBuilder的作用是通过用户定义的参数,初始化route结构,route结构最终由websocket中的routes结构进行存储维护
// RouteBuilder is a helper to construct Routes.
type RouteBuilder struct {
rootPath string
currentPath string
produces []string
consumes []string
httpMethod string // required
function RouteFunction // required
filters []FilterFunction
conditions []RouteSelectionConditionFunction
typeNameHandleFunc TypeNameHandleFunction // required
// documentation
doc string
notes string
operation string
readSample, writeSample interface{}
parameters []*Parameter
errorMap map[int]ResponseError
metadata map[string]interface{}
deprecated bool
}
2.1.2 typeNameHandler(w.typeNameHandleFunc)
typeNameHandler方法绑定在RouteBuilder上, 该函数为赋值函数,将webservice中定义的typeNameHandleFunc TypeNameHandleFunction // required传递给routebuilder, 该变量定义了一类环函数的通用化模板,在初始化前RouteBuilder结构体中已经初始化定义了typeNameHandleFunc TypeNameHandleFunction。
// TypeNameHandleFunction declares functions that can handle translating the name of a sample object
// into the restful documentation for the service.
type TypeNameHandleFunction func(sample interface{}) string
// typeNameHandler sets the function that will convert types to strings in the parameter
// and model definitions.
func (b *RouteBuilder) typeNameHandler(handler TypeNameHandleFunction) *RouteBuilder {
b.typeNameHandleFunc = handler
return b
}
2.1.3 servicePath(w.rootPath)
w.rootPath 初始值为"",在该函数中, 将webservice中定义的rootpath初始值传递给RouteBuilder,在RouteBuilder中默认的rootPath初始值也为""
func (b *RouteBuilder) servicePath(path string) *RouteBuilder {
b.rootPath = path
return b
}
2.1.4 Method("GET")
设置http方法, 在该例子中,传递了GET方法
// Method specifies what HTTP method to match. Required.
func (b *RouteBuilder) Method(method string) *RouteBuilder {
b.httpMethod = method
return b
}
2.1.5 Path(subPath)
设置RouteBuilder的currentPath设置为subPath
// Path specifies the relative (w.r.t WebService root path) URL path to match. Default is "/".
func (b *RouteBuilder) Path(subPath string) *RouteBuilder {
b.currentPath = subPath
return b
}
2.2 To(hello)
改函数绑定用户自定义的的处理函数handler,当用户发起的http访问, 命中method=GET path = subPath后,执行相关逻辑的function handler
func hello(req *restful.Request, resp *restful.Response) {
io.WriteString(resp, "world")
}
实际上在执行webservice GET()函数,直接生成了RouteBuilder并返回对象, 因此function的绑定,直接在RouteBuilder中进行
// RouteFunction declares the signature of a function that can be bound to a Route.
type RouteFunction func(*Request, *Response)
// To bind the route to a function.
// If this route is matched with the incoming Http Request then call this function with the *Request,*Response pair. Required.
func (b *RouteBuilder) To(function RouteFunction) *RouteBuilder {
b.function = function
return b
}
从代码中可以看出自定义的函数类型包括两部分, 分别是*Request, *Response在restful中, 定义的request和response都是结构体, 该结构体中定义了http包数据各个模块的存储及获取格式
type Request struct {
Request *http.Request
pathParameters map[string]string
attributes map[string]interface{} // for storing request-scoped values
selectedRoutePath string // root path + route path that matched the request, e.g. /meetings/{id}/attendees
}
type Response struct {
http.ResponseWriter
requestAccept string // mime-type what the Http Request says it wants to receive
routeProduces []string // mime-types what the Route says it can produce
statusCode int // HTTP status code that has been written explicitly (if zero then net/http has written 200)
contentLength int // number of bytes written for the response body
prettyPrint bool // controls the indentation feature of XML and JSON serialization. It is initialized using var PrettyPrintResponses.
err error // err property is kept when WriteError is called
hijacker http.Hijacker // if underlying ResponseWriter supports it
}
2.3 ws.Route(RouteBuilder))]
该函数主要创建新的路由关系,并将产生的routebuilder添加到路由表中
// Route creates a new Route using the RouteBuilder and add to the ordered list of Routes.
func (w *WebService) Route(builder *RouteBuilder) *WebService {
w.routesLock.Lock()
defer w.routesLock.Unlock()
builder.copyDefaults(w.produces, w.consumes)
w.routes = append(w.routes, builder.Build())
return w
}
2.3.1 w.routesLock.Lock()
在webservice初始化中,routesLock初始化为routesLock sync.RWMutex,该变量主要作用是在动态路由使用后,保护路由表,防止被多线程同时读写
2.3.2 defer w.routesLock.Unlock()
采用defer方式golang特性, 函数执行完成后,stack执行,释放掉持有的锁
2.3.3 builder.copyDefaults(w.produces, w.consumes)
将produces和consumes赋值给RouteBuilder
2.3.4 RouteBuilder.build()
// Build creates a new Route using the specification details collected by the RouteBuilder
func (b *RouteBuilder) Build() Route {
pathExpr, err := newPathExpression(b.currentPath)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("Invalid path:%s because:%v", b.currentPath, err)
os.Exit(1)
}
if b.function == nil {
log.Printf("No function specified for route:" + b.currentPath)
os.Exit(1)
}
operationName := b.operation
if len(operationName) == 0 && b.function != nil {
// extract from definition
operationName = nameOfFunction(b.function)
}
route := Route{
Method: b.httpMethod,
Path: concatPath(b.rootPath, b.currentPath),
Produces: b.produces,
Consumes: b.consumes,
Function: b.function,
Filters: b.filters,
If: b.conditions,
relativePath: b.currentPath,
pathExpr: pathExpr,
Doc: b.doc,
Notes: b.notes,
Operation: operationName,
ParameterDocs: b.parameters,
ResponseErrors: b.errorMap,
ReadSample: b.readSample,
WriteSample: b.writeSample,
Metadata: b.metadata,
Deprecated: b.deprecated}
route.postBuild()
return route
}
build的过程主要是初始化参数的检查及route初始化过程, 在route的初始化中除了使用routebuiler之前初始化的部分参数,还针对path处理了pathexpr,newPathExpression(b.currentPath)
2.3.5 w.routes = append(w.routes, builder.Build())
将创建的route添加到routes slice中。
- 可以看出来结构上 route是由routebuilder进行创建
- 实际上产生作用的是webservice中的route列表
3.restful.Add(ws)
// Add registers a new WebService add it to the DefaultContainer.
func Add(service *WebService) {
DefaultContainer.Add(service)
}
在ws外面在加了一层container, 改container在init中进行了初始化
func init() {
DefaultContainer = NewContainer()
DefaultContainer.ServeMux = http.DefaultServeMux
}
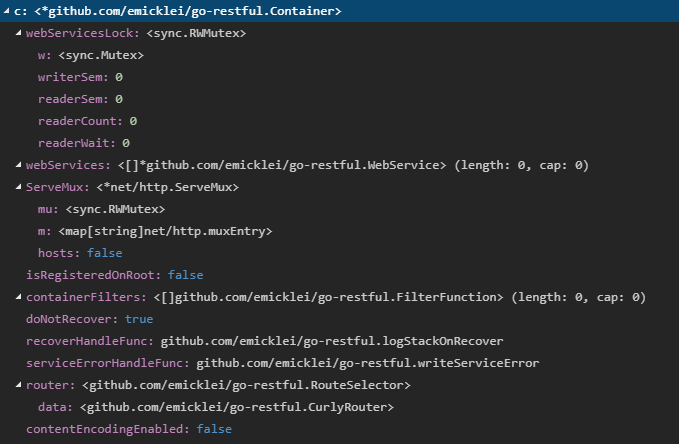
3.1 DefaultContainer = NewContainer()
创建container对象,并进行初始化, 因此可以看出ws可以有很多个,统一由container进行维护,默认的route路径/就是在这里进行的赋值
// NewContainer creates a new Container using a new ServeMux and default router (CurlyRouter)
func NewContainer() *Container {
return &Container{
webServices: []*WebService{},
ServeMux: http.NewServeMux(),
isRegisteredOnRoot: false,
containerFilters: []FilterFunction{},
doNotRecover: true,
recoverHandleFunc: logStackOnRecover,
serviceErrorHandleFunc: writeServiceError,
router: CurlyRouter{},
contentEncodingEnabled: false}
}
3.2 DefaultContainer.Add(service)
从代码中可以看出来webservice的区分是通过rootPath进行区分的, webservices要保证rootpath的唯一性
// Add a WebService to the Container. It will detect duplicate root paths and exit in that case.
func (c *Container) Add(service *WebService) *Container {
c.webServicesLock.Lock()
defer c.webServicesLock.Unlock()
// if rootPath was not set then lazy initialize it
if len(service.rootPath) == 0 {
service.Path("/")
}
// cannot have duplicate root paths
for _, each := range c.webServices {
if each.RootPath() == service.RootPath() {
log.Printf("WebService with duplicate root path detected:['%v']", each)
os.Exit(1)
}
}
// If not registered on root then add specific mapping
if !c.isRegisteredOnRoot {
c.isRegisteredOnRoot = c.addHandler(service, c.ServeMux)
}
c.webServices = append(c.webServices, service)
return c
}
其中有一点仍然需要注意,在container的绑定中,只将根目录注册到了ServeMux中, 绑定的对应的函数为container.dispatch(),这样做的原因是在http请求中,通过golang中net包中的ServeMux进行路由转发,将所有命中根目录的uri流量分发到ws中。
// addHandler may set a new HandleFunc for the serveMux
// this function must run inside the critical region protected by the webServicesLock.
// returns true if the function was registered on root ("/")
func (c *Container) addHandler(service *WebService, serveMux *http.ServeMux) bool {
pattern := fixedPrefixPath(service.RootPath())
// check if root path registration is needed
if "/" == pattern || "" == pattern {
serveMux.HandleFunc("/", c.dispatch)
return true
}
// detect if registration already exists
alreadyMapped := false
for _, each := range c.webServices {
if each.RootPath() == service.RootPath() {
alreadyMapped = true
break
}
}
if !alreadyMapped {
serveMux.HandleFunc(pattern, c.dispatch)
if !strings.HasSuffix(pattern, "/") {
serveMux.HandleFunc(pattern+"/", c.dispatch)
}
}
return false
}
4. log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil))
创建端口监听,将用户的http请求route到对应的函数中, ListenAndServe 在net package中, http routes相关由ServMux进行维护, 由于在上文hello worlde的样子中,container将根目录及c.dispatch初始化到ServeMux中。因此,当发送get请求后,会跳转到container.dispatch中进行二次http route。
// ListenAndServe always returns a non-nil error.
func ListenAndServe(addr string, handler Handler) error {
server := &Server{Addr: addr, Handler: handler}
return server.ListenAndServe()
}
restful响应流程
1. 路由
上文中通过container、webservice、route的初始化流程,在helloworld的样例中,外部通过http get访问时,http package中的servMux进行了第一次路由找到了对应的container,后调用container.dispatch进行二次路由查找
//闭包
func() {
c.webServicesLock.RLock()
defer c.webServicesLock.RUnlock()
webService, route, err = c.router.SelectRoute(
c.webServices,
httpRequest)
}()
2 c.router.SelectRoute
func (c CurlyRouter) SelectRoute(
webServices []*WebService,
httpRequest *http.Request) (selectedService *WebService, selected *Route, err error) {
requestTokens := tokenizePath(httpRequest.URL.Path)
detectedService := c.detectWebService(requestTokens, webServices)
if detectedService == nil {
if trace {
traceLogger.Printf("no WebService was found to match URL path:%s\n", httpRequest.URL.Path)
}
return nil, nil, NewError(http.StatusNotFound, "404: Page Not Found")
}
candidateRoutes := c.selectRoutes(detectedService, requestTokens)
if len(candidateRoutes) == 0 {
if trace {
traceLogger.Printf("no Route in WebService with path %s was found to match URL path:%s\n", detectedService.rootPath, httpRequest.URL.Path)
}
return detectedService, nil, NewError(http.StatusNotFound, "404: Page Not Found")
}
selectedRoute, err := c.detectRoute(candidateRoutes, httpRequest)
if selectedRoute == nil {
return detectedService, nil, err
}
return detectedService, selectedRoute, nil
}
在路由转换的逻辑中, 主要包含了3次路由转换
2.1 路由查找webservice
//从url中split路径为token列表
requestTokens := tokenizePath(httpRequest.URL.Path)
/*
将获取到的tokens与webServices中的pathExpr.tokens进行计算最大分值(计算分值的方式是token比对
直到出现不同对于{分数自增1跳转到下一步),并返回分值最高的匹配
*/
c.detectWebService(requestTokens, webServices)
func (c CurlyRouter) detectWebService(requestTokens []string, webServices []*WebService) *WebService {
var best *WebService
score := -1
for _, each := range webServices {
//在该例子中each.pathExpr.tokens为空,如果为空,默认范围列表中第一个ws
matches, eachScore := c.computeWebserviceScore(requestTokens, each.pathExpr.tokens)
if matches && (eachScore > score) {
best = each
score = eachScore
}
}
return best
}
2.2 路由查找Route
func (c CurlyRouter) selectRoutes(ws *WebService, requestTokens []string) sortableCurlyRoutes {
candidates := sortableCurlyRoutes{}
for _, each := range ws.routes {
//遍历路由查找,将routes中的tokens进行遍历查找, 找到能够匹配到当前路径的route
matches, paramCount, staticCount := c.matchesRouteByPathTokens(each.pathParts, requestTokens)
if matches {
candidates.add(curlyRoute{each, paramCount, staticCount}) // TODO make sure Routes() return pointers?
}
}
sort.Sort(sort.Reverse(candidates))
return candidates
}
func (c CurlyRouter) matchesRouteByPathTokens(routeTokens, requestTokens []string) (matches bool, paramCount int, staticCount int) {
if len(routeTokens) < len(requestTokens) {
// proceed in matching only if last routeToken is wildcard
count := len(routeTokens)
if count == 0 || !strings.HasSuffix(routeTokens[count-1], "*}") {
return false, 0, 0
}
// proceed
}
for i, routeToken := range routeTokens {
if i == len(requestTokens) {
// reached end of request path
return false, 0, 0
}
requestToken := requestTokens[i]
if strings.HasPrefix(routeToken, "{") {
paramCount++
if colon := strings.Index(routeToken, ":"); colon != -1 {
// match by regex
matchesToken, matchesRemainder := c.regularMatchesPathToken(routeToken, colon, requestToken)
if !matchesToken {
return false, 0, 0
}
if matchesRemainder {
break
}
}
} else { // no { prefix
if requestToken != routeToken {
return false, 0, 0
}
staticCount++
}
}
return true, paramCount, staticCount
}
在routes中查找到的对应的route,统计放在sortableCurlyRoute中进行处理,sortableCurlyRoute是一个封装的按照一定规则进行排序的curlyRoute数组
type curlyRoute struct {
route Route
paramCount int //正则命中
staticCount int //完全匹配命中
}
2.3. route属性相关匹配
在上面中通过path的比对拿到了一个route列表, 列表中记录了route的优先级,在列表中的route都保证了对path的命中, 在function的匹配过程中需要依次检查:
- http method
// http method methodOk := []Route{} for _, each := range ifOk { if httpRequest.Method == each.Method { methodOk = append(methodOk, each) } } if len(methodOk) == 0 { if trace { traceLogger.Printf("no Route found (in %d routes) that matches HTTP method %s\n", len(routes), httpRequest.Method) } return nil, NewError(http.StatusMethodNotAllowed, "405: Method Not Allowed") } inputMediaOk := methodOk - content-type
contentType := httpRequest.Header.Get(HEADER_ContentType) inputMediaOk = []Route{} for _, each := range methodOk { if each.matchesContentType(contentType) { inputMediaOk = append(inputMediaOk, each) } } - accept
outputMediaOk := []Route{} accept := httpRequest.Header.Get(HEADER_Accept) if len(accept) == 0 { accept = "*/*" } for _, each := range inputMediaOk { if each.matchesAccept(accept) { outputMediaOk = append(outputMediaOk, each) } } if len(outputMediaOk) == 0 { if trace { traceLogger.Printf("no Route found (from %d) that matches HTTP Accept: %s\n", len(inputMediaOk), accept) } return nil, NewError(http.StatusNotAcceptable, "406: Not Acceptable") }pathProcessor, routerProcessesPath := c.router.(PathProcessor) if !routerProcessesPath { pathProcessor = defaultPathProcessor{} }
在go-restful中支持fliter的定义, 在执行对应function之前,需要对fliter检查是否命中
pathProcessor, routerProcessesPath := c.router.(PathProcessor)
if !routerProcessesPath {
pathProcessor = defaultPathProcessor{}
}
pathParams := pathProcessor.ExtractParameters(route, webService, httpRequest.URL.Path)
wrappedRequest, wrappedResponse := route.wrapRequestResponse(writer, httpRequest, pathParams)
// pass through filters (if any)
if len(c.containerFilters)+len(webService.filters)+len(route.Filters) > 0 {
// compose filter chain
allFilters := []FilterFunction{}
allFilters = append(allFilters, c.containerFilters...)
allFilters = append(allFilters, webService.filters...)
allFilters = append(allFilters, route.Filters...)
chain := FilterChain{Filters: allFilters, Target: func(req *Request, resp *Response) {
// handle request by route after passing all filters
route.Function(wrappedRequest, wrappedResponse)
}}
chain.ProcessFilter(wrappedRequest, wrappedResponse)
} else {
// no filters, handle request by route
route.Function(wrappedRequest, wrappedResponse)
}
在hello world例子中没有fliter相关功能, 因此可以直接跳转到route.Function(wrappedRequest, wrappedResponse),执行hello world对应的function, function中调用io.WriteString(resp, "world")将resp写回到net/server缓冲区中,io loop并写回到socket fd中完成通信。
func hello(req *restful.Request, resp *restful.Response) {
fmt.Println("hello world")
io.WriteString(resp, "world")
}
层级关系
Route
路由包含两种,一种是标准JSR311接口规范的实现RouterJSR311,一种是快速路由CurlyRouter。
CurlyRouter支持正则表达式和动态参数,相比RouterJSR11更加轻量级,apiserver中使用的就是这种路由。
一种Route的设定包含:请求方法(http Method),请求路径(URL Path),输入输出类型(JSON/YAML)以及对应的回掉函数restful.RouteFunction,响应内容类型(Accept)等。
WebService
webservice中维护了route的集合,功能上主要维护了一组route的rootpath、method、fliter等属性
Container
Container逻辑上是WebService的集合,功能上可以实现多终端的效果,不同的container可以绑定到不同的ip或者port上面