Tensorflow2.x 用Lenet神经网络训练 fashion_mnist数据集 并预测。
小白自己的学习笔记,大佬勿喷,多多指教。
目录
1.用Tensorflow2.x 建立神经网络需要导入的库文件
2.用Tensorflow2.x 建立Lenet神经网络:
(1)建立Lenet网络
1.tf.keras.layers.Conv2D
2.keras.layers.Flatten()
3.如何将(28,28)格式转换成 (28,28,1)格式?
4.预处理过程中,通常把图像转成什么数据格式?几维度?多大的?
5.model.evaluate()
(2)整个程序:
(3)运行过程
3.参考文献:
1.用Tensorflow2.x 建立神经网络需要导入的库文件
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
# Helper libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2.用Tensorflow2.x 建立Lenet神经网络:
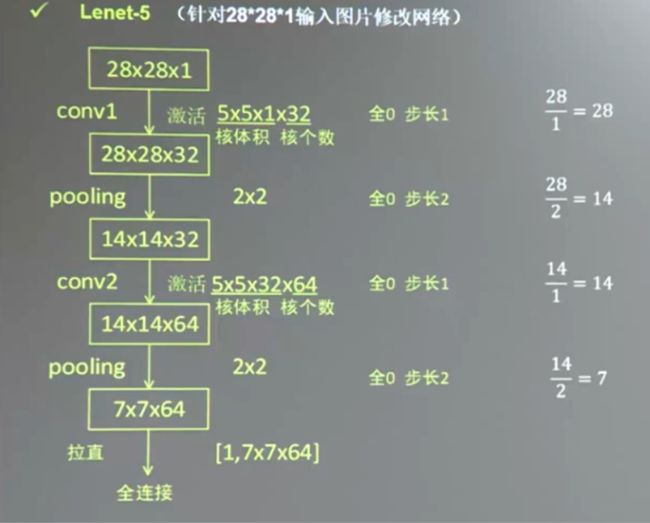
Lenet网络长这样
还有的up是这样描述
上图的lenet网络用Tensorflow 2.x代码写(还没有加入全连接层),如下:
# 搭建LeNet网络
net = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=6,kernel_size=5,activation='sigmoid',input_shape=(28,28,1)),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2,strides=2),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=16,kernel_size=5,activation='sigmoid'),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2,strides=2),
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(120,activation='sigmoid'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(84,activation='sigmoid'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10,activation='sigmoid')
])但是,我在了解了什么是Lenet网络之后,又想在网络后面加上一些全连接层,看看训练的效果。
因此,我用Tensorflow 2.0 代码实现该想法网络:
(1)建立Lenet网络
这是加了四层全连接层后的CNN网络:
#建立网络
model = keras.Sequential([
#增加全连接层,使得准确率增加?
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=6,kernel_size=5,activation='sigmoid',input_shape=(28,28,1)),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2,strides=2),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=16,kernel_size=5,activation='sigmoid'),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2,strides=2),
keras.layers.Flatten(),
keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(120,activation='sigmoid'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(84,activation='sigmoid'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10,activation='sigmoid')
#tf.keras.layers.Softmax()
#tf.keras.layers.Softmax()
])model.summary() 用来输出模型各层的参数状况。
通过动手敲代码以及查阅资料,我学到了在 Tensorflow2.x下,卷积层,池化层,全连接层的api,以及其他api内部的参数含义。
1.tf.keras.layers.Conv2D
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D中,input_shape参数是几维度的?
答:
何出此问?
当 input_shape = (28,28)时候,程序出错。当 input_shape = (28,28,1)时候程序运行成功。
2.keras.layers.Flatten()
keras.layers.Flatten()这个api有何用?几种解释:
①用于将输入层的数据压成一维的数据,一般用再卷积层和全连接层之间(因为全连接层只能接收一维数据,而卷积层可以处理二维数据,就是全连接层处理的是向量,而卷积层处理的是矩阵)
②Flatten层用来将输入“压平”,即把多维的输入一维化,常用在从卷积层到全连接层的过渡。
3.如何将(28,28)格式转换成 (28,28,1)格式?
如何将(28,28)格式转换成 (28,28,1)格式?
train_images = tf.reshape(train_images,(train_images.shape[0],train_images.shape[1],train_images.shape[2],1))
print(train_images.shape)
test_images = tf.reshape(test_images,(test_images.shape[0],test_images.shape[1],test_images.shape[2],1))4.预处理过程中,通常把图像转成什么数据格式?几维度?多大的?
答:
5.model.evaluate()
(2)整个程序:
#建立一个 LeNet 模型
#问:随便一个卷积网络都可以训练个二分类吗?
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
# Helper libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 查看当前tensorflow版本,2.3.0
print("当前tensorflow版本", tf.__version__)
fashion_mnist = keras.datasets.fashion_mnist
(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = fashion_mnist.load_data()
# 每个图像都映射到一个标签
class_names = ['T-shirt/top', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat',
'Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle boot']
#lenet 模型实现十分类
model = keras.Sequential([
#增加全连接层,使得准确率增加?
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=6,kernel_size=5,activation='sigmoid',input_shape=(28,28,1)),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2,strides=2),
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=16,kernel_size=5,activation='sigmoid'),
tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2,strides=2),
keras.layers.Flatten(),
keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(120,activation='sigmoid'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(84,activation='sigmoid'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10,activation='sigmoid')
#tf.keras.layers.Softmax()
#tf.keras.layers.Softmax()
])
#编译模型
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.9,momentum=0.0,nesterov=False)
model.compile(optimizer=optimizer,
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
#这里非常重要,此处的变换好像是更改了图片的维度?
#如果没有这一步骤,那么,lenet网络无法完成,也就是卷积层无法加入。
#如果没有这部,只能使用全连接网络进行模型训练,不能使用CNN
train_images = tf.reshape(train_images,(train_images.shape[0],train_images.shape[1],train_images.shape[2],1))
print(train_images.shape)
test_images = tf.reshape(test_images,(test_images.shape[0],test_images.shape[1],test_images.shape[2],1))
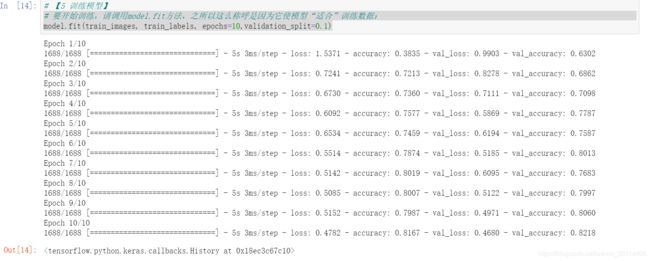
# 要开始训练,请调用model.fit方法,之所以这么称呼是因为它使模型“适合”训练数据:
model.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=10,validation_split=0.1)
#
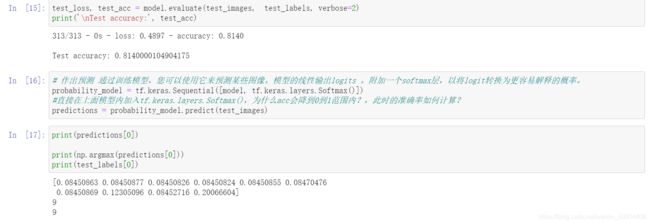
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels, verbose=2)
print('\nTest accuracy:', test_acc)
# 作出预测 通过训练模型,您可以使用它来预测某些图像。模型的线性输出logits 。附加一个softmax层,以将logit转换为更容易解释的概率。
probability_model = tf.keras.Sequential([model, tf.keras.layers.Softmax()])
#直接在上面模型内加入tf.keras.layers.Softmax(),为什么acc会降到0到1范围内?,此时的准确率如何计算?
predictions = probability_model.predict(test_images)
print(predictions[1])
print(np.argmax(predictions[1]))
print(test_labels[1])
# 以图形方式查看完整的10个类预测。
def plot_image(i, predictions_array, true_label, img):
true_label, img = true_label[i], img[i]
plt.grid(False)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.imshow(img, cmap=plt.cm.binary)
predicted_label = np.argmax(predictions_array)
if predicted_label == true_label:
color = 'blue'
else:
color = 'red'
plt.xlabel("{} {:2.0f}% ({})".format(class_names[predicted_label],
100*np.max(predictions_array),
class_names[true_label]),
color=color)
def plot_value_array(i, predictions_array, true_label):
true_label = true_label[i]
plt.grid(False)
plt.xticks(range(10))
plt.yticks([])
thisplot = plt.bar(range(10), predictions_array, color="#777777")
plt.ylim([0, 1])
predicted_label = np.argmax(predictions_array)
thisplot[predicted_label].set_color('red')
thisplot[true_label].set_color('blue')
i = 2
plt.figure(figsize=(6,3))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plot_image(i, predictions[i], test_labels, test_images)
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plot_value_array(i, predictions[i], test_labels)
plt.show()
num_rows = 5
num_cols = 3
num_images = num_rows*num_cols
plt.figure(figsize=(2*2*num_cols, 2*num_rows))
for i in range(num_images):
plt.subplot(num_rows, 2*num_cols, 2*i+1)
plot_image(i, predictions[i], test_labels, test_images)
plt.subplot(num_rows, 2*num_cols, 2*i+2)
plot_value_array(i, predictions[i], test_labels)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
img = test_images[6]
# 将图像添加到唯一的批处理
img = (np.expand_dims(img,0))
# 为该图像预测正确的标签:
predictions_single = probability_model.predict(img)
print("输出每一个标签的把握:", predictions_single) # 一共10个标签,索引从0,1,2到9
plot_value_array(1, predictions_single[0], test_labels)
_ = plt.xticks(range(10), class_names, rotation=45)
# keras.Model.predict返回一个列表列表-数据批次中每个图像的一个列表。批量获取我们(仅)图像的预测
print("模型预测的结果:", np.argmax(predictions_single[0]))
(3)运行过程
效果不是太好:
运行
num_rows = 5
num_cols = 3
num_images = num_rows*num_cols
plt.figure(figsize=(2*2*num_cols, 2*num_rows))
for i in range(num_images):
plt.subplot(num_rows, 2*num_cols, 2*i+1)
plot_image(i, predictions[i], test_labels, test_images)
plt.subplot(num_rows, 2*num_cols, 2*i+2)
plot_value_array(i, predictions[i], test_labels)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
3.参考文献:
https://www.cnblogs.com/CuteyThyme/p/12741241.html
https://www.numpy.org.cn/reference/arrays/ndarray.html#%E6%9E%84%E9%80%A0%E6%95%B0%E7%BB%84