ThreadLocal
定义
ThreadLocal很容易让人望文生义,想当然地认为是一个“本地线程”。
其实,ThreadLocal并不是一个Thread,而是Thread的局部变量,也许把它命名为ThreadLocalVariable更容易让人理解一些。
各个线程的ThreadLocal关联的实例互不干扰。特征:
- ThreadLocal表示线程的"局部变量",它确保每个线程的ThreadLocal变量都是各自独立的
- ThreadLocal适合在一个线程的处理流程中保持上下文(避免了同一参数在所有方法中传递)
- 使用ThreadLocal要用try ... finally结构,并在finally中清除
常用方法
- set:为当前线程设置变量,当前ThreadLocal作为索引
- get:获取当前线程变量,当前ThreadLocal作为索引
- initialValue:(需要子类实现,默认mull)执行get时,发现线程本地变量为null,就会执行initialValue的内容
- remove:清空当前线程的ThreadLocal索引与映射的元素
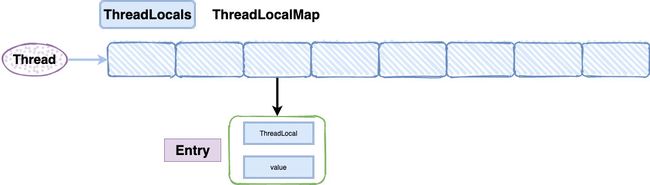
底层结构及逻辑
Thread对象的属性
public class Thread implements Runnable {
// .....
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
// .....
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null;
}
ThreadLocalMap对象
public class ThreadLocal {
// .....
static class ThreadLocalMap {
static class Entry extends WeakReference> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
/**
* The initial capacity -- MUST be a power of two.
*/
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
/**
* The table, resized as necessary.
* table.length MUST always be a power of two.
*/
private Entry[] table;
/**
* The number of entries in the table.
*/
private int size = 0;
/**
* The next size value at which to resize.
*/
private int threshold; // Default to 0
/**
* Set the resize threshold to maintain at worst a 2/3 load factor.
*/
private void setThreshold(int len) {
threshold = len * 2 / 3;
}
/**
* Increment i modulo len.
*/
private static int nextIndex(int i, int len) {
return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0);
}
/**
* Decrement i modulo len.
*/
private static int prevIndex(int i, int len) {
return ((i - 1 >= 0) ? i - 1 : len - 1);
}
}
}
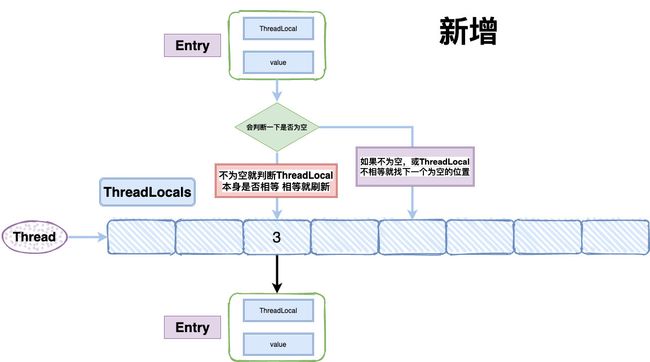
set值流程
源码摘要:
// java.lang.ThreadLocal#set
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// map惰性创建
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
重点来关注下 java.lang.ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap#set 方法
private void set(ThreadLocal key, Object value) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// 根据ThreadLocal对象的hash值,定位到table中的位置i
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
// 如果位置i不为空,且这个Entry对象的key正好是即将设置的key,那么就覆盖Entry中的value
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
// 如果当前位置是空的,就初始化一个Entry对象放在位置i上
if (k == null) {
// 里面会调到 expungeStaleEntry
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
// 如果位置i的不为空,而且key不等于entry,那就找下一个空位置,直到为空为止
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
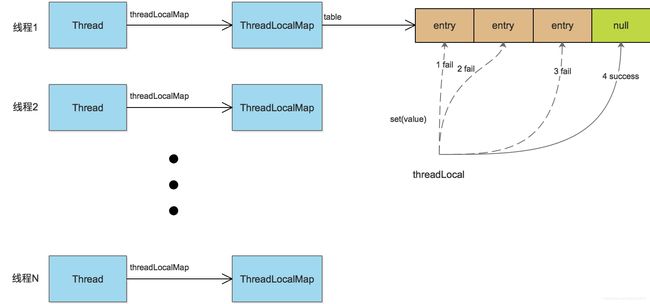
结合代码,set的过程如下图
冲突解决
线性探测的方式解决hash冲突的问题,如果没有找到空闲的slot,就不断往后尝试,直到找到一个空闲的位置,插入entry
get流程
源码摘要:
// java.lang.ThreadLocal#get
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();// 调用initialValue方法
}
// java.lang.ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap#getEntry
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal key) {
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
// 可能是没有,或者hash冲突了
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// get的时候一样是根据ThreadLocal获取到table的i值,然后查找数据拿到后会对比key是否相等
while (e != null) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
// 相等就直接返回,不相等就继续查找,找到相等位置。
if (k == key)
return e;
if (k == null)
// 清理回收无效value、entry
expungeStaleEntry(i);
else
i = nextIndex(i, len);
e = tab[i];
}
return null;
}
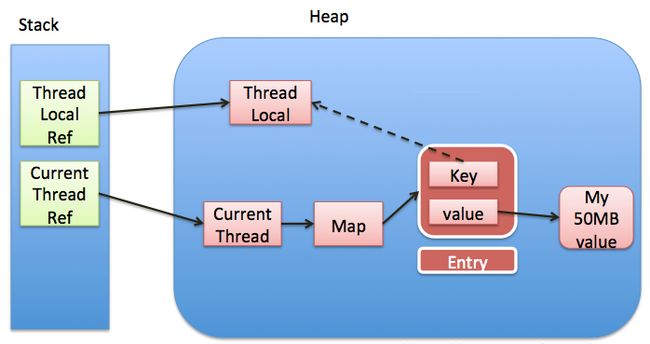
弱引用
static class Entry extends WeakReference> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
为什么使用弱引用?
弱引用的特点:弱引用的对象拥有更短暂的生命周期。垃圾回收器线程扫描的时候,一旦发现了只具有弱引用的对象,不管当前内存空间足够与否,都会回收它的内存。
结合到这里的场景,当ThreadLocal在没有外部强引用的时候,一旦发生gc,key就会被回收。
内存泄露问题
因为有了弱引用,可以确保Entry的key会被内存回收掉。但是Entry的value和Entry对象本身还是没有得到回收。
如果ThreadLocal的线程一直保持运行,那么这个Entry对象中的value就有可能一直得不到回收,发生内存泄露。
解决办法:在finally里面调用remove方法
扩展
InheritableThreadLocal
InheritableThreadLocal 是 JDK 本身自带的一种线程传递解决方案,以完成父线程到子线程的值传递。在创建子线程的时候,就把父线程的ThreadLocal的内容复制过去。
// java.lang.Thread#init(java.lang.ThreadGroup, java.lang.Runnable, java.lang.String, long, java.security.AccessControlContext, boolean)
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,
long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc,
boolean inheritThreadLocals) {
// ...
if (inheritThreadLocals && parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null)
// 复制父线程的InheritableThreadLocal内容
this.inheritableThreadLocals = ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals);
// ...
}
// java.lang.ThreadLocal#createInheritedMap
static ThreadLocalMap createInheritedMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {
return new ThreadLocalMap(parentMap);
}
private ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {
Entry[] parentTable = parentMap.table;
int len = parentTable.length;
setThreshold(len);
table = new Entry[len];
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
Entry e = parentTable[j];
if (e != null) {
ThreadLocal不过,子线程ThreadLocalMap里的Entry.value指向的对象和父线程是同一个。
特殊场景下的缺陷
在线程池的场景下,线程由线程池创建好,并且线程是池化起来反复使用的;这时父子线程关系的ThreadLocal值传递已经没有意义。比如:
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 线程池提前创建好
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 提前创建了一个子线程 [pool-1-thread-1]
executorService.submit(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
Thread.sleep(1000);
InheritableThreadLocal threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal();
threadLocal.set("start");
System.out.println(threadLocal.get());
// 后续,[pool-1-thread-1]线程的ThreadLocal值永远是null
executorService.submit(() -> {
System.out.println(threadLocal.get() + " -> " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
executorService.submit(() -> {
System.out.println(threadLocal.get() + " -> " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
executorService.submit(() -> {
System.out.println(threadLocal.get() + " -> " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.println(threadLocal.get());
executorService.shutdown();
}
// 输出结果
pool-1-thread-1
start
start -> pool-1-thread-2
start -> pool-1-thread-2
null -> pool-1-thread-1
start
尤其是现在都是基于框架开发,线程池一般在项目启动的时候,就创建好了。业务代码提交执行任务的时候,如果复用之前的线程,那么值就没传到子线程中去!
像这种情况,我们至少要求 把任务提交给线程池时 的ThreadLocal值传递到执行线程中。TransmittableThreadLocal的出现就是为了解决这个问题。
TransmittableThreadLocal
TransmittableThreadLocal是Alibaba开源的一个类,它继承了InheritableThreadLocal。能实现在线程池和主线程之间传递,需要配合TtlRunnable 和 TtlCallable使用。
使用示例
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 线程池提前创建好
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 提前创建了一个子线程 [pool-1-thread-1]
executorService.submit(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
Thread.sleep(1000);
TransmittableThreadLocal threadLocal = new TransmittableThreadLocal();
threadLocal.set("start");
System.out.println(threadLocal.get());
// 每次提交时都需要通过修饰操作(即TtlRunnable.get(task))以抓取这次提交时的TransmittableThreadLocal上下文的值
executorService.submit(TtlRunnable.get(() -> {
System.out.println(threadLocal.get() + " -> " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}));
executorService.submit(TtlRunnable.get(() -> {
System.out.println(threadLocal.get() + " -> " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}));
executorService.submit(TtlRunnable.get(() -> {
System.out.println(threadLocal.get() + " -> " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}));
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.println(threadLocal.get());
executorService.shutdown();
}
// 输出结果
pool-1-thread-1
start
start -> pool-1-thread-1
start -> pool-1-thread-2
start -> pool-1-thread-1
start
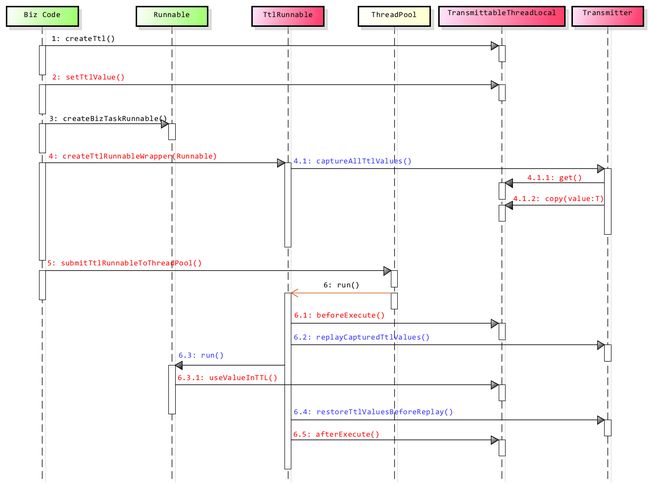
整个过程的完整时序图
修饰线程池
使用TTL的时候,每次提交任务时,都需要用TtlRunnable 或者 TtlCallable对任务修饰一下。这个修饰逻辑可以再线程池中完成。
通过工具类com.alibaba.ttl.threadpool.TtlExecutors完成,有下面的方法:
getTtlExecutor:修饰接口ExecutorgetTtlExecutorService:修饰接口ExecutorServicegetTtlScheduledExecutorService:修饰接口ScheduledExecutorService
示例代码:
ExecutorService executorService = ...
// 额外的处理,生成修饰了的对象executorService
executorService = TtlExecutors.getTtlExecutorService(executorService);
TransmittableThreadLocal context = new TransmittableThreadLocal<>();
// =====================================================
// 在父线程中设置
context.set("value-set-in-parent");
Runnable task = new RunnableTask();
Callable call = new CallableTask();
executorService.submit(task);
executorService.submit(call);
// =====================================================
// Task或是Call中可以读取,值是"value-set-in-parent"
String value = context.get();
FastThreadLocal
前面分析了ThreadLocal的get和set,当遇到hash冲突的时候,会以nextIndex计算下一个位置的方式来解决hash冲突。
使用线性探测的方式解决hash冲突的问题,如果没有找到空闲的slot,就不断往后尝试,直到找到一个空闲的位置,插入entry,这种方式在经常遇到hash冲突时,影响效率。
鉴于此,netty提供了FastThreadLocal。与之配套的还有FastThreadLocalThread和FastThreadLocalRunnable。
创建FastThreadLocal对象的时候,直接把位置index(使用AtomicInteger实现)确定下来。每个FastThreadLocal都能获取到一个不重复的下标
public FastThreadLocal() {
index = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex();
}
public static int nextVariableIndex() {
int index = nextIndex.getAndIncrement();
if (index < 0) {
nextIndex.decrementAndGet();
throw new IllegalStateException("too many thread-local indexed variables");
}
return index;
}
不过,FastThreadLocal需要配合FastThreadLocalThread使用,才能发挥它的效率。
public final void set(V value) {
if (value != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get();
setKnownNotUnset(threadLocalMap, value);
} else {
remove();
}
}
public final V get() {
InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = InternalThreadLocalMap.get();
Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(index);// 直接定位
if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
return (V) v;
}
return initialize(threadLocalMap);
}
public Object indexedVariable(int index) {
Object[] lookup = indexedVariables;
return index < lookup.length? lookup[index] : UNSET;
}
// InternalThreadLocalMap.get()
public static InternalThreadLocalMap get() {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
// 判断当前Thread类型
if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {
return fastGet((FastThreadLocalThread) thread);
} else {
return slowGet();
}
}
private static InternalThreadLocalMap fastGet(FastThreadLocalThread thread) {
// FastThreadLocalThread继承Thread,额外有InternalThreadLocalMap类型属性
InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = thread.threadLocalMap();
if (threadLocalMap == null) {
thread.setThreadLocalMap(threadLocalMap = new InternalThreadLocalMap());
}
return threadLocalMap;
}
private static InternalThreadLocalMap slowGet() {
// 普通Thread无InternalThreadLocalMap,但有ThreadLocal属性,在它里面存InternalThreadLocalMap等于间接有了InternalThreadLocalMap
ThreadLocal slowThreadLocalMap = UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap.slowThreadLocalMap;
InternalThreadLocalMap ret = slowThreadLocalMap.get();
if (ret == null) {
ret = new InternalThreadLocalMap();
slowThreadLocalMap.set(ret);
}
return ret;
}
也就是说,如果是普通Thread使用FastThreadLocal,则需要先拿到ThreadLocal对象,然后再get到里面存的InternalThreadLocalMap。这一get过程完全是ThreadLocal的get,也需要执行hash碰撞&getEntryAfterMiss等逻辑。(有的地方称之为退化)