yolov5 调用 usb 摄像头
文章是在yolov5 v5.0版本的detect.py所修改编写
其他v1.0-v4.0没有试过,你们可以试试。
具体用法已经写在代码里面了。
import time
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch
from models.experimental import attempt_load
from utils.datasets import letterbox
from utils.general import check_img_size, non_max_suppression,scale_coords, xyxy2xywh,set_logging,check_requirements
from utils.plots import colors, plot_one_box
from utils.torch_utils import select_device,time_synchronized
@torch.no_grad()
def detect(
#--------------------这里更改配置--------------------
#---------------------------------------------------
weights='runs/train/exp25/weights/best.pt', #训练好的模型路径 (必改)
imgsz=512, #训练模型设置的尺寸 (必改)
cap = 0, #摄像头
conf_thres=0.25, #置信度
iou_thres=0.45, #NMS IOU 阈值
max_det=1000, #最大侦测的目标数
device='', #设备
crop=True, #显示预测框
classes=None, #种类
agnostic_nms=False, #class-agnostic NMS
augment=False, #是否扩充推理
half=False, #使用FP16半精度推理
hide_labels=False, #是否隐藏标签
hide_conf=False, #是否隐藏置信度
line_thickness=3 #预测框的线宽
):
# #--------------------这里更改配置--------------------
#-----------------------------------------------------
#打开摄像头
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(cap)
#-----初始化-----
set_logging()
#设置设备
device = select_device(device)
#CUDA仅支持半精度
half &= device.type != 'cpu'
#-----加载模型-----
#加载FP32模型
model = attempt_load(weights, map_location=device)
#模型步幅
stride = int(model.stride.max())
#检查图像大小
imgsz = check_img_size(imgsz, s=stride)
#获取类名
names = model.module.names if hasattr(model, 'module') else model.names
#toFP16
if half:
model.half()
#------运行推理------
if device.type != 'cpu':
model(torch.zeros(1, 3, imgsz, imgsz).to(device).type_as(next(model.parameters()))) # 跑一次
#-----进入循环:ESC退出-----
while(True):
#设置labels--记录标签/概率/位置
labels = []
#计时
t0 = time.time()
ref,img0=cap.read()
#填充调整大小
img = letterbox(img0, imgsz, stride=stride)[0]
# 转换
img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) #BGR to RGB, to 3x416x416
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(device)
#uint8 to fp16/32
img = img.half() if half else img.float()
#0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
img /= 255.0
if img.ndimension() == 3:
img = img.unsqueeze(0)
# 推断
t1 = time_synchronized()
pred = model(img, augment=augment)[0]
# 添加 NMS
pred = non_max_suppression(pred, conf_thres, iou_thres, classes, agnostic_nms, max_det=max_det)
t2 = time_synchronized()
#目标进程
for i, det in enumerate(pred): # 每幅图像的检测率
s, im0 = '', img0.copy()
#输出字符串
s += '%gx%g ' % img.shape[2:]
#归一化增益
gn = torch.tensor(im0.shape)[[1, 0, 1, 0]]
if len(det):
# 将框从img_大小重新缩放为im0大小
det[:, :4] = scale_coords(img.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im0.shape).round()
# 输出结果
for c in det[:, -1].unique():
#每类检测数
n = (det[:, -1] == c).sum()
#添加到字符串
s += f"{n} {names[int(c)]}{'s' * (n > 1)}, "
# 结果输出
for *xyxy, conf, cls in reversed(det):
#归一化xywh
xywh = (xyxy2xywh(torch.tensor(xyxy).view(1, 4)) / gn).view(-1).tolist()
#标签格式
line = (cls, *xywh, conf)
#整数类
c = int(cls)
#建立标签
label = None if hide_labels else (names[c] if hide_conf else f'{names[c]} {conf:.2f}')
#绘画预测框
if crop:
plot_one_box(xyxy, im0, label=label, color=colors(c, True), line_thickness=line_thickness)
#记录标签/概率/位置
labels.append([names[c],conf,xyxy])
#--------------------这里写/修改代码--------------------
#-------------------------------------------------
'''
labels里面有该图片的标签/概率/坐标(列表)
labels = [ [列表0] , [列表1] , [列表3] ,......]
其中 列表 = [标签,概率,坐标]
例如获取第一个预测框的概率值:print( float( labels[0][1]) )
'''
# 显示图片
cv2.imshow("666",im0)
#输出计算时间
print(f'消耗时间: ({time.time() - t0:.3f}s)')
key = cv2.waitKey(20)
#这里设置ESC退出
if key == 27:
break
#--------------------END--------------------
#-------------------------------------------------
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__ == "__main__":
'''
修改配置在 13-28 行
写代码-显示输出/获取预测框位置/获取预测概率值 在121-END行
'''
#检测安装包--建议注释掉
#check_requirements(exclude=('tensorboard', 'thop'))
#运行
detect()
经研究发现,yolov5-master有time_synchronized 和 time_sync 两种名字,所以如果time_synchronized报错,麻烦换成time_sync
YOLOv5调用本地摄像头
YOLOv5源码:https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
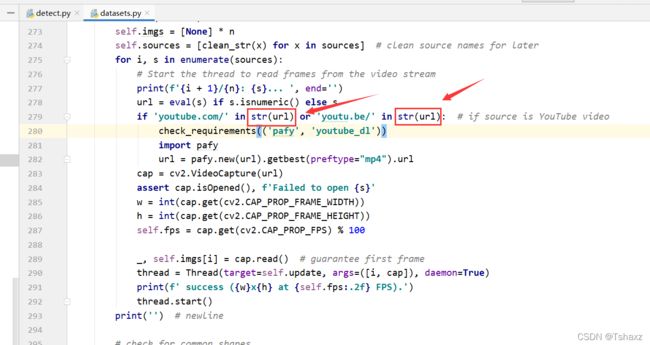
最近用YOLOv5做目标检测,直接调用本地摄像头会报错,需要在dataset中做一点修改。
具体如下:
在279行的这两处改成str类型
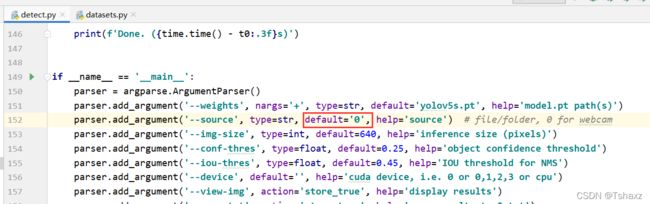
然后在detect里把这里的参数改为0
然后运行detect.py即可调用本地摄像头。
总结
到此这篇关于yolov5调用usb摄像头及本地摄像头的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关yolov5调用摄像头内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!