R语言ggplot2|玩转Manhattan图-你有被要求这么画吗?
Manhattan图算是GWAS分析的标配图了,可参考Bio|manhattan图 进行绘制。
由于Manhattan点太多,后期AI/PS修改的话难度有点大,如果可以“个性化”绘制的话那是极好的!
一 载入R包,数据
1)载入数据处理的tidyverse包,使用qqman中gwasResults示例数据集
#载入R包
#install.packages("qqman")
library(qqman)
library(tidyverse)
#查看原始数据
head(gwasResults)
SNP CHR BP P
1 rs1 1 1 0.9148060
2 rs2 1 2 0.9370754
3 rs3 1 3 0.2861395
4 rs4 1 4 0.8304476
5 rs5 1 5 0.6417455
6 rs6 1 6 0.5190959我们知道Manhattan图实际就是点图,横坐标是chr,纵坐标是-log(Pvalue) ,原始P值越小,-log转化后的值越大,在图中就越高。
原始数据中重要的“元素”都有了 ,我们自己的数据也是只需要这四列就可以了。注意绘制前需要转化一下:
2)处理原始数据---计算SNP的累计位置
# 1)计算chr长度
chr_len <- gwasResults %>%
group_by(CHR) %>%
summarise(chr_len=max(BP))
# 2) 计算每条chr的初始位置
chr_pos <- chr_len %>%
mutate(total = cumsum(chr_len) - chr_len) %>%
select(-chr_len)
#3)计算累计SNP的位置
Snp_pos <- chr_pos %>%
left_join(gwasResults, ., by="CHR") %>%
arrange(CHR, BP) %>%
mutate( BPcum = BP + total)
#查看转化后的数据
head(Snp_pos,2)
SNP CHR BP P total BPcum
1 rs1 1 1 0.9148060 0 1
2 rs2 1 2 0.9370754 0 2
数据准备完成,开始绘图。
二 ggplot2绘制Manhattan图
1 纵坐标为P值转-log10()
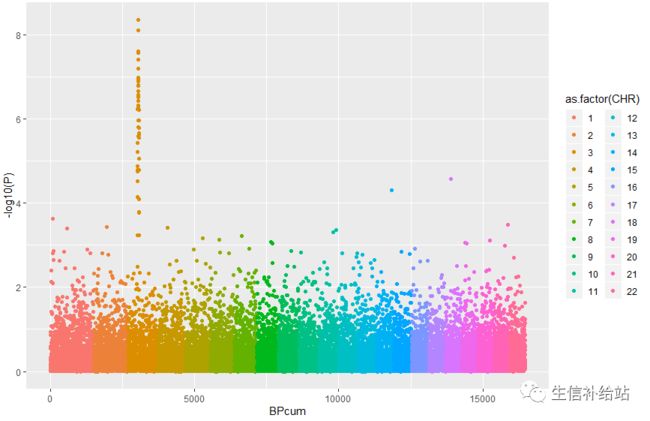
ggplot(Snp_pos, aes(x=BPcum, y=-log10(P))) +
geom_point( aes(color=as.factor(CHR)))基本图形出来了,但是有点怪;不急,一点点改进:
横坐标标签设置在每个chr中间位置;
背景色去掉,线去掉等
去掉点和X轴之间的 “gap” (很多地方可用)
添加阈值线
2 绘制加强版Manhattan图
1) 准备X轴标签位置--在每条chr的中间
X_axis <- Snp_pos %>% group_by(CHR) %>% summarize(center=( max(BPcum) +min(BPcum) ) / 2 )2)绘制“改良版”Manhattan图
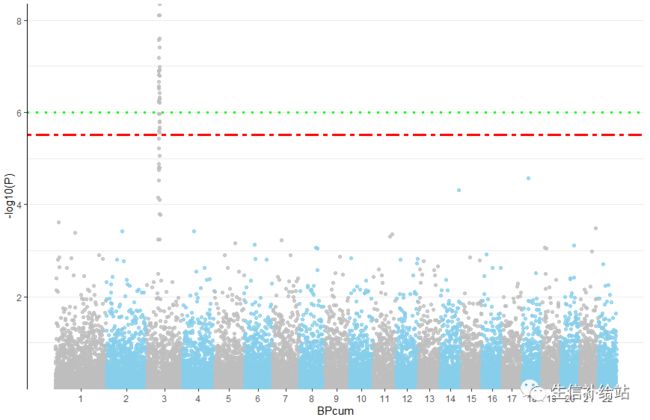
p <- ggplot(Snp_pos, aes(x=BPcum, y=-log10(P))) +
#设置点的大小,透明度
geom_point( aes(color=as.factor(CHR)), alpha=0.8, size=1.3) +
#设置颜色
scale_color_manual(values = rep(c("grey", "skyblue"), 22 )) +
#设定X轴
scale_x_continuous( label = X_axis$CHR, breaks= X_axis$center ) +
#去除绘图区和X轴之间的gap
scale_y_continuous(expand = c(0, 0) ) +
#添加阈值线
geom_hline(yintercept = c(6, -log10(0.05/nrow(Snp_pos))), color = c('green', 'red'),size = 1.2, linetype = c("dotted", "twodash")) +
#设置主题
theme_bw() +
theme(
legend.position="none",
panel.border = element_blank(),
axis.line.y = element_line(),
panel.grid.major.x = element_blank(),
panel.grid.minor.x = element_blank()
)这时候是不是就可以了,????。
当然了既然是ggplot2绘制的Manhattan图(点图),那么关于点,线,坐标,主题的设置当然都可以设置了,看这里
ggplot2|详解八大基本绘图要素
ggplot2|theme主题设置,详解绘图优化-“精雕细琢”
3 玩转Manhattan图
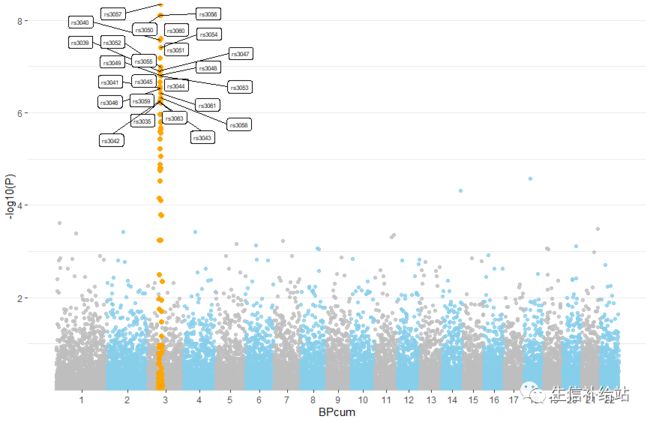
1) 利用数据集自带的snpsOfInterest标示显著的位点,展示重要的基因信息
library(ggrepel)
#准备数据
data <- Snp_pos %>%
# 添加高亮和注释信息:snpsOfInterest中的rs编号和P值大于6的点
mutate( is_highlight=ifelse(SNP %in% snpsOfInterest, "yes", "no")) %>%
mutate( is_annotate=ifelse(-log10(P)>6, "yes", "no"))
#绘图
p1 <- ggplot(data, aes(x=BPcum, y=-log10(P))) +
geom_point( aes(color=as.factor(CHR)), alpha=0.8, size=1.3) +
scale_color_manual(values = rep(c("grey", "skyblue"), 22 )) +
scale_x_continuous( label = X_axis$CHR, breaks= X_axis$center ) +
scale_y_continuous(expand = c(0, 0) ) +
# 添加高亮点
geom_point(data=subset(data, is_highlight=="yes"), color="orange", size=2) +
# 添加高亮label,且防止重叠
geom_label_repel( data=subset(data, is_annotate=="yes"), aes(label=SNP), size=2)+
theme_bw() +
theme(
legend.position="none",
panel.border = element_blank(),
panel.grid.major.x = element_blank(),
panel.grid.minor.x = element_blank()
)如果我们自己的gwas结果数据是Gene的话,label更改即可标示基因。
2) 自定义重要的基因,标示
如果有某些“目的基因”,想查看这些基因的P值呢?
新加gene和gene_annotate列即可!
#准备数据,使用基础函数
data <- Snp_pos
#根据目的基因的位置,新加gene和gene_annotate列
data$gene[data$CHR == 3 & data$BP == 366] <- "geneA"
data$gene_annotate[data$CHR == 3 & data$BP == 366] <- "yes"
data$gene[data$SNP == "rs4064"] <- "geneB"
data$gene_annotate[data$SNP == "rs4064"] <- "yes"
# 绘图
p2 <- ggplot(data, aes(x=BPcum, y=-log10(P))) +
geom_point( aes(color=as.factor(CHR)), alpha=0.8, size=1.3) +
scale_color_manual(values = rep(c("grey", "skyblue"), 22 )) +
scale_x_continuous( label = X_axis$CHR, breaks= X_axis$center ) +
scale_y_continuous(expand = c(0, 0) ) +
geom_label_repel( data=subset(data, gene_annotate=="yes"), aes(label=gene),size=4, col = "red") +
theme_bw() +
theme(
legend.position="none",
panel.border = element_blank(),
panel.grid.major.x = element_blank(),
panel.grid.minor.x = element_blank()
)
3)区域放大展示
重点展示某一区域的P值情况
library(ggforce)
data <- Snp_pos %>%
# 添加高亮和注释信息:snpsOfInterest中的rs编号和P值大于6的点
mutate( is_highlight=ifelse(SNP %in% snpsOfInterest, "yes", "no")) %>%
mutate( is_annotate=ifelse(-log10(P)>6, "yes", "no"))
p3 <- ggplot(data, aes(x=BPcum, y=-log10(P))) +
geom_point( aes(color=as.factor(CHR)), alpha=0.8, size=1.3) +
scale_color_manual(values = rep(c("grey", "skyblue"), 22 )) +
scale_x_continuous( label = X_axis$CHR, breaks= X_axis$center ) +
scale_y_continuous(expand = c(0, 0) ) +
geom_point(data=subset(data, is_highlight=="yes"), color="orange", size=2)+facet_zoom(x = BPcum >= 3000 & BPcum <=3500)+
theme_bw() +
theme(
legend.position="none",
panel.border = element_blank(),
panel.grid.major.x = element_blank(),
panel.grid.minor.x = element_blank()
)可参考ggforce|绘制区域轮廓-区域放大-寻找你的“onepiece”
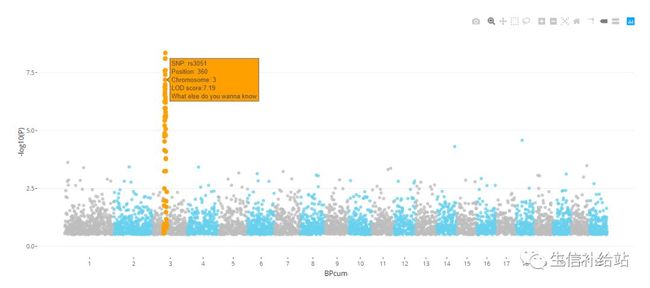
4)plotly 交互展示
library(plotly)
data <- Snp_pos %>%
mutate( is_highlight=ifelse(SNP %in% snpsOfInterest, "yes", "no")) %>% filter(-log10(P)>0.5) #过滤一些点,交互式压力小
# 准备SNP展示的text信息
data$text <- paste("SNP: ", data$SNP, "\nPosition: ", data$BP, "\nChromosome: ",data$CHR, "\nLOD score:", -log10(data$P) %>% round(2), "\nWhat else do you wanna know", sep="")
p4 <- ggplot(data, aes(x=BPcum, y=-log10(P), text=text)) +
geom_point( aes(color=as.factor(CHR)), alpha=0.8, size=1.3) +
scale_color_manual(values = rep(c("grey", "skyblue"), 22 )) +
scale_x_continuous( label = X_axis$CHR, breaks= X_axis$center ) +
scale_y_continuous(expand = c(0, 0) ) +
ylim(0,9) +
geom_point(data=subset(data, is_highlight=="yes"), color="orange", size=2) +
theme_bw() +
theme(
legend.position="none",
panel.border = element_blank(),
panel.grid.major.x = element_blank(),
panel.grid.minor.x = element_blank()
)
ggplotly(p4, tooltip="text")好吧,其实这个用处不太大,,,![]()
以上就是ggplot2绘制一些常见的Manhattan图,好处当然就是兼容ggplot2的参数,也就可以根据需要自行设置。
猜你喜欢
K-近邻算法通俗理解与实践
11种概率分布,你了解几个?
贝叶斯定理的通俗理解
R语言资源整理——史上最全
R语言读取xlsx文件
![]()