本文实例为大家分享了java实现五子棋大战的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
这是我接近一年前的项目了,以前没有养成写博客的习惯,打算陆续把以前做过的项目补上来。
一、介绍
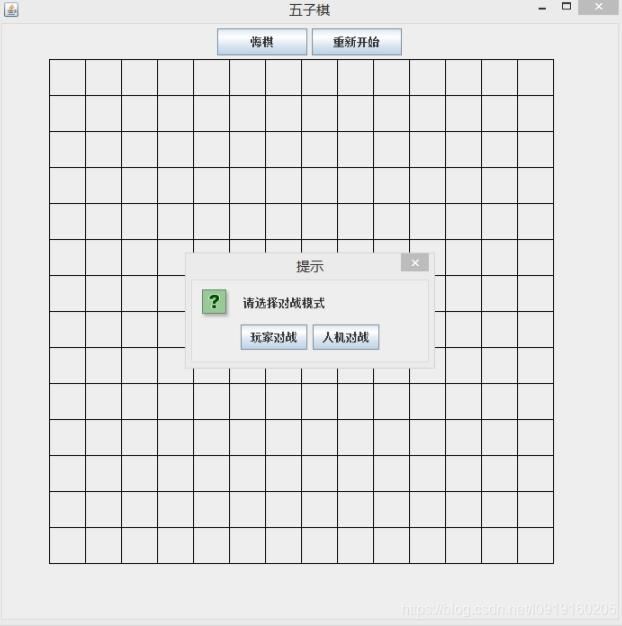
主要实现的功能有棋子颜色选择,悔棋,重新开始,玩家对战和人机对战,效果图如图所是:
模式选择:
棋子选择:
人机对战:
玩家对战:
二、具体实现
五子棋的开发首先需要在界面上绘制一个表格,因为七班是不变的,棋子大小是不变的,所以我们首先可以自定义一个接口来设置项目中的常量,这样改变这些参数时也比较方便,CS.java代码如下:
public interface CS {
public static final int x0=60;//棋盘开始位置
public static final int y0=70;
public static final int line=15;//棋盘有多少条线
public static final int size=40;//棋子大小
}
和上一篇博客中的画图板类似,首先需要一个界面,这里可以定义一个Chess类继承Jframe,然后再重写paint(Graphics g)方法,来绘制棋盘,Chess.java代码如下:
Chess.java:
public class Chess extends JFrame implements CS{
int i=2;
private qizi qizilarry2[][]=new qizi[line][line];//用qizi类型的二维数组来存储棋子
private JButton b = new JButton("悔棋");
private JButton b2=new JButton("重新开始");
private JLabel jLabel=new JLabel("请选择对战模式");
private JLabel jLabel2=new JLabel("请选择棋子颜色");
private int value;//提示框选项的值
private int value2;
Dimension dimension=new Dimension(100, 30);
String color[]= {"白棋","黑棋"};
String moshi[]= {"玩家对战","人机对战"};
public void chessUI() {
b.setPreferredSize(dimension);
b2.setPreferredSize(dimension);
this.setSize(700, 700);
this.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
this.setTitle("五子棋");
this.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(3);
this.setVisible(true);
this.add(b);
this.add(b2);
value=JOptionPane.showOptionDialog(this, jLabel, "提示", JOptionPane.OK_CANCEL_OPTION, JOptionPane.QUESTION_MESSAGE,
null, moshi, null);
value2=JOptionPane.showOptionDialog(this, jLabel2, "提示", JOptionPane.OK_CANCEL_OPTION, JOptionPane.QUESTION_MESSAGE,
null, color, null);
//关闭提示框则退出程序
if(value==JOptionPane.CLOSED_OPTION||value2==JOptionPane.CLOSED_OPTION) {
System.exit(1);
}
Graphics g=this.getGraphics();
mouslistener mouslistener =new mouslistener(g,qizilarry2,this,value,value2);
this.addMouseListener(mouslistener);//窗口添加监听
b.addActionListener(mouslistener);//按钮添加监听
b2.addActionListener(mouslistener);
}
public void paint(Graphics g) {//重绘棋盘和棋子
super.paint(g);
drawChess(g);
drawQZ();
}
//画一个棋盘
public void drawChess(Graphics g) {
g.setColor(Color.black);
for(int i=0;i
用qizi类型的二维数组来存储棋子,在重绘时重绘整个棋盘和二维数组上的棋子,如果二维数组为null则不用重绘。
接下来该创建监听类了,在鼠标点击棋盘时,要使得棋子在棋盘的正中央,代码如下:
//x轴坐标
for(ix=0;x1>0;ix++) {
x1-=size;
}
x1+=size;
x1-=size/2;
ix--;
if(x1<=0) {
x=x0+ix*size;
}else
x=x0+(++ix)*size;
//y轴坐标
for(iy=0;y1>0;iy++) {
y1-=size;
}
y1+=size;
y1-=size/2;
iy--;
if(y1<=0) {
y=y0+iy*size;
}else
y=y0+(++iy)*size;
判赢的方法非常简单,只要计算棋子在它八个方向的相邻的且颜色相同的棋子个数即可,这里只展现向左查找棋子的代码(后续会附上整个监听类的代码):
public int zuo(int x,int y,Color c) {//向左找
int a=x;
for(int i=1;i<5;i++) {
a--;
if(a<0||qizilarry[a][y]==null) {
break;
}else if(qizilarry[a][y].getColor()==c)
count1++;
else
break;
}
return count1;
}
当模式为玩家和玩家模式时,需要每下一个棋子颜色改变,实现的代码如下:
if(a) {
color =c;
a=false;
}else {
color=c2;
a=true;
}
g.setColor(color);
g.fillOval(x-size/2, y-size/2, size, size);
prex=ix;
prey=iy;
qizi qizi=new qizi(g, color,ix,iy);
qizilarry[ix][iy]=qizi;
inte++;
玩家VS玩家和玩家VS电脑的判赢方法基本类似,这里只展现了玩家与玩家的判赢方法,即每下一个新的棋子,就计算这个棋子八个方向上相同且相邻棋子的个数,当同一直线两个方向的棋子个数之和为5时,则获取棋子颜色,判定为获胜,具体代码实现如下:
//判断输赢
if(zuo(ix,iy,color)+you(ix,iy,color)>=4||shang(ix,iy,color)+xia(ix,iy,color)>=4
||zuoshang(ix, iy,color)+youxia(ix, iy,color)>=4||zuoxia(ix, iy,color)+youshang(ix, iy,color)>=4) {
JLabel jLabel =new JLabel("白棋获胜!");
JLabel jlabel2 =new JLabel("黑棋获胜!");
if(color==Color.white)
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(jFrame, jLabel, "游戏结束", JOptionPane.PLAIN_MESSAGE);
else
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(jFrame, jlabel2, "游戏结束", JOptionPane.PLAIN_MESSAGE);
}else {
count1=0;//如果没有赢重新置0重新计算
count2=0;
countS=0;
countX=0;
countZS=0;
countZX=0;
countYS=0;
countYX=0;
}
这样玩家与玩家模式的大体功能就基本实现了,接下类就要实现五子棋的AI功能了
五子棋AI
这里我们主要针权值法讨论下,大致思路如下:
1.我们绘制好一个棋盘后,大小为 15*15;
2.下棋之前,对于棋盘中的每个空位,我们每都替电脑人“掂一掂”下在哪里合算;(估权过程)
3.对每个空位按照规则都计算完权重,我们找出权重最大的位置,此位置就是npc落子位置。
空子位置我们用 “0” 表示,白子用“2”表示,黑子用“1”表示;
我们主要分为以下几种情况:
定义 棋子相连情况 权值
活一连 010、020 40
活二连 0110、0220 400
活三连 01110、02220 3000
活四连 011110、022220 10000
眠一连 012、021 20
眠二连 0112、0221 200
眠三连 01112、02221 500
眠四连 011112、022221 3000
用hash表存储所有可能的情况并赋予一定的权值,每下一个棋子便更新棋盘上所有空位置的权值,电脑再寻找棋盘上权值最大的点下棋,computerChess()函数代码如下:
public void computerChess() {
hashMap.put("10000", 15);//眠1连
hashMap.put("20000", 10);//眠1连
hashMap.put("20100",17);//眠1连,15
hashMap.put("10200",12);//眠1连,10
hashMap.put("21000",15);//眠1连,15
hashMap.put("12000",10);//眠1连,10
hashMap.put("20010",19);//眠1连,15
hashMap.put("10020",14);//眠1连,10
hashMap.put("20100",17);//眠1连,15
hashMap.put("10200",12);//眠1连,10
//
// hashMap.put("00010",21);//活1连,15
// hashMap.put("00020",16);//活1连,10
// hashMap.put("00100",19);//活1连,15
// hashMap.put("00200",14);//活1连,10
// hashMap.put("01000",17);//活1连,15
// hashMap.put("02000",12);//活1连,10
//
//被堵住
hashMap.put("10100",65);//眠2连,40
hashMap.put("20200",60);//眠2连,30
hashMap.put("01100",65);//眠2连,40
hashMap.put("02200",60);//眠2连,30
hashMap.put("11000",65);//眠2连,40
hashMap.put("22000",60);//眠2连,30
hashMap.put("21010",65);//眠2连,40
hashMap.put("12020",60);//眠2连,30
hashMap.put("20110",65);//眠2连,40
hashMap.put("10220",60);//眠2连,30
hashMap.put("21100",65);//眠2连,40
hashMap.put("12200",60);//眠2连,30
// hashMap.put("01010",75);//活2连,40
// hashMap.put("02020",70);//活2连,30
// hashMap.put("00110",75);//活2连,40
// hashMap.put("00220",70);//活2连,30
// hashMap.put("01100",75);//活2连,40
// hashMap.put("02200",70);//活2连,30
// hashMap.put("11000",75);//活2连,40
// hashMap.put("00022",70);//活2连,30
//
// //被堵住
hashMap.put("11100",150);//眠3连,100
hashMap.put("22200",140);//眠3连,80
hashMap.put("21110",150);//眠3连,100
hashMap.put("12220",140);//眠3连,80
//
// hashMap.put("10110",1000);//活3连,130
// hashMap.put("20220",800);//活3连,110
// hashMap.put("11010",1000);//活3连,130
// hashMap.put("22020",800);//活3连,110
// hashMap.put("01110", 1000);//活3连
// hashMap.put("02220", 800);//活3连
hashMap.put("11110",3000);//4连,300
hashMap.put("11112",3000);//4连,300
hashMap.put("22220",3500);//4连,280
hashMap.put("22221",3500);//4连,280
int a;
int b;
for(int y=0;y
完整代码
mouslistener.java:
public class mouslistener extends MouseAdapter implements CS,ActionListener{
private int x;//棋子像素坐标
private int y;
private int ix;//用户棋子坐标
private int iy;
private int cx;//电脑棋子坐标
private int cy;
private int n=1;//下黑棋或白棋
public int inte=0;//棋子数目
private int prex;//上一个棋子的坐标
private int prey;
private int count1=0;
private int count2=0;
private int countS=0;
private int countX=0;
private int countZS=0;
private int countYX=0;
private int countZX=0;
private int countYS=0;
private int value;
private int value2;
String zuo="";
String you="";
String shang="";
String xia="";
String zuoshang="";
String zuoxia="";
String youshang="";
String youxia="";
private boolean a=true;//玩家对战下棋顺序
private boolean b=true;//是否在同一个位置
// private boolean end=true;//是否电脑胜利
private Color c;//用户棋子颜色
private Color c2;//电脑棋子颜色
private Color color;//玩家对战颜色交替下棋
public qizi qizilarry[][]=new qizi[line][line];
private int chessValue[][]=new int[line][line];//权值表
private JLabel j=new JLabel("请选择对战模式");
private JLabel j2=new JLabel("请选择棋子颜色");
String moshi[]= {"玩家对战","人机对战"};
String co[]= {"白棋","黑棋"};
JFrame jFrame;//悔棋重绘传参
Graphics g;
HashMap hashMap=new HashMap();
public mouslistener(Graphics g,qizi qizi[][],JFrame jFrame,int value,int value2) {
this.g=g;
qizilarry=qizi;
this.jFrame=jFrame;
this.value=value;
this.value2=value2;
if(value2==1) {
c=Color.black;
c2=Color.white;
}else {
c=Color.white;
c2=Color.black;
}
}
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e) {
x=e.getX();
y=e.getY();
int x1=x-x0;
int y1=y-y0;
//x轴坐标
for(ix=0;x1>0;ix++) {
x1-=size;
}
x1+=size;
x1-=size/2;
ix--;
if(x1<=0) {
x=x0+ix*size;
}else
x=x0+(++ix)*size;
//y轴坐标
for(iy=0;y1>0;iy++) {
y1-=size;
}
y1+=size;
y1-=size/2;
iy--;
if(y1<=0) {
y=y0+iy*size;
}else
y=y0+(++iy)*size;
//判断是否在同一个地方
b=true;
if(qizilarry[ix][iy]!=null) {
JLabel jLabel =new JLabel("不能下在同一个地方!");
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(jFrame, jLabel, "警告", JOptionPane.WARNING_MESSAGE);
b=false;
}
//--------------------
//画圆及重构,一个黑棋一个白棋
//--------------------
if(b) {
if(value==1) {
g.setColor(c);
g.fillOval(x-size/2, y-size/2, size, size);
prex=ix;
prey=iy;
qizi qizi=new qizi(g, c,ix,iy);
qizilarry[ix][iy]=qizi;
inte++;
System.out.println("用户下棋");
computerChess();
int qzmax=0;
for(int b=0;bqzmax) {
qzmax=chessValue[a][b];
cx=a;
cy=b;
}
}
}
g.setColor(c2);
g.fillOval(x0+cx*size-size/2, y0+cy*size-size/2, size, size);
qizi qizi2=new qizi(g, c2,cx,cy);
qizilarry[cx][cy]=qizi2;
inte++;
System.out.println("电脑下棋");
for(int b=0;b=4||shang(ix,iy,c)+xia(ix,iy,c)>=4
||zuoshang(ix, iy,c)+youxia(ix, iy,c)>=4||zuoxia(ix, iy,c)+youshang(ix, iy,c)>=4) {
JLabel jLabel =new JLabel("玩家获胜!");
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(jFrame, jLabel, "游戏结束", JOptionPane.PLAIN_MESSAGE);
}else {
count1=0;
count2=0;
countS=0;
countX=0;
countZS=0;
countZX=0;
countYS=0;
countYX=0;
if((zuo(cx,cy,c2)+you(cx,cy,c2)>=4||shang(cx,cy,c2)+xia(cx,cy,c2)>=4
||zuoshang(cx, cy,c2)+youxia(cx, cy,c2)>=4||zuoxia(cx, cy,c2)+youshang(cx, cy,c2)>=4) ){
JLabel jLabel =new JLabel("电脑获胜!");
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(jFrame, jLabel, "游戏结束", JOptionPane.PLAIN_MESSAGE);
}else {
count1=0;
count2=0;
countS=0;
countX=0;
countZS=0;
countZX=0;
countYS=0;
countYX=0;
}
}
}else {
if(a) {
color =c;
a=false;
}else {
color=c2;
a=true;
}
g.setColor(color);
g.fillOval(x-size/2, y-size/2, size, size);
prex=ix;
prey=iy;
qizi qizi=new qizi(g, color,ix,iy);
qizilarry[ix][iy]=qizi;
inte++;
//判断输赢
if(zuo(ix,iy,color)+you(ix,iy,color)>=4||shang(ix,iy,color)+xia(ix,iy,color)>=4
||zuoshang(ix, iy,color)+youxia(ix, iy,color)>=4||zuoxia(ix, iy,color)+youshang(ix, iy,color)>=4) {
JLabel jLabel =new JLabel("白棋获胜!");
JLabel jlabel2 =new JLabel("黑棋获胜!");
if(color==Color.white)
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(jFrame, jLabel, "游戏结束", JOptionPane.PLAIN_MESSAGE);
else
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(jFrame, jlabel2, "游戏结束", JOptionPane.PLAIN_MESSAGE);
}else {
count1=0;//如果没有赢重新置0重新计算
count2=0;
countS=0;
countX=0;
countZS=0;
countZX=0;
countYS=0;
countYX=0;
}
}
}
}
public int zuo(int x,int y,Color c) {//向左找
int a=x;
for(int i=1;i<5;i++) {
a--;
if(a<0||qizilarry[a][y]==null) {
break;
}else if(qizilarry[a][y].getColor()==c)
count1++;
else
break;
}
return count1;
}
public int you(int x,int y,Color c){//向右找
int a =x;
for(int i=1;i<5;i++) {
a++;
if(a==15||qizilarry[a][y]==null) {
break;
}else if(qizilarry[a][y].getColor()==c)
count2++;
else
break;
}
return count2;
}
public int xia(int x,int y,Color c) {//向下找
int a=y;
for(int i=1;i<5;i++) {
a++;
if(a==15||qizilarry[x][a]==null) {
break;
}else if(qizilarry[x][a].getColor()==c)
countX++;
else
break;
}
return countX;
}
public int shang(int x,int y,Color c){//向上找
int a =y;
for(int i=1;i<5;i++) {
a--;
if(a<0||qizilarry[x][a]==null) {
break;
}else if(qizilarry[x][a].getColor()==c)
countS++;
else
break;
}
return countS;
}
public int zuoshang(int x,int y,Color c) {//向左上找
int a=x;
int b=y;
for(int i=1;i<5;i++) {
a--;
b++;
if(a<0||b==15||qizilarry[a][b]==null) {
break;
}else if(qizilarry[a][b].getColor()==c)
countZS++;
else
break;
}
return countZS;
}
public int youxia(int x,int y,Color c) {//向右下找
int a=x;
int b=y;
for(int i=1;i<5;i++) {
a++;
b--;
if(b<0||a==15||qizilarry[a][b]==null) {
break;
}else if(qizilarry[a][b].getColor()==c)
countYX++;
else
break;
}
return countYX;
}
public int zuoxia(int x,int y,Color c) {//向左下找
int a=x;
int b=y;
for(int i=1;i<5;i++) {
a--;
b--;
if(a<0||b<0||qizilarry[a][b]==null) {
break;
}else if(qizilarry[a][b].getColor()==c)
countZX++;
else
break;
}
return countZX;
}
public int youshang(int x,int y,Color c) {//向右上找
int a=x;
int b=y;
for(int i=1;i<5;i++) {
a++;
b++;
if(a==15||b==15||qizilarry[a][b]==null) {
break;
}else if(qizilarry[a][b].getColor()==c)
countYS++;
else
break;
}
return countYS;
}
public void computerChess() {
hashMap.put("10000", 15);//眠1连
hashMap.put("20000", 10);//眠1连
hashMap.put("20100",17);//眠1连,15
hashMap.put("10200",12);//眠1连,10
hashMap.put("21000",15);//眠1连,15
hashMap.put("12000",10);//眠1连,10
hashMap.put("20010",19);//眠1连,15
hashMap.put("10020",14);//眠1连,10
hashMap.put("20100",17);//眠1连,15
hashMap.put("10200",12);//眠1连,10
//
// hashMap.put("00010",21);//活1连,15
// hashMap.put("00020",16);//活1连,10
// hashMap.put("00100",19);//活1连,15
// hashMap.put("00200",14);//活1连,10
// hashMap.put("01000",17);//活1连,15
// hashMap.put("02000",12);//活1连,10
//
//被堵住
hashMap.put("10100",65);//眠2连,40
hashMap.put("20200",60);//眠2连,30
hashMap.put("01100",65);//眠2连,40
hashMap.put("02200",60);//眠2连,30
hashMap.put("11000",65);//眠2连,40
hashMap.put("22000",60);//眠2连,30
hashMap.put("21010",65);//眠2连,40
hashMap.put("12020",60);//眠2连,30
hashMap.put("20110",65);//眠2连,40
hashMap.put("10220",60);//眠2连,30
hashMap.put("21100",65);//眠2连,40
hashMap.put("12200",60);//眠2连,30
// hashMap.put("01010",75);//活2连,40
// hashMap.put("02020",70);//活2连,30
// hashMap.put("00110",75);//活2连,40
// hashMap.put("00220",70);//活2连,30
// hashMap.put("01100",75);//活2连,40
// hashMap.put("02200",70);//活2连,30
// hashMap.put("11000",75);//活2连,40
// hashMap.put("00022",70);//活2连,30
//
// //被堵住
hashMap.put("11100",150);//眠3连,100
hashMap.put("22200",140);//眠3连,80
hashMap.put("21110",150);//眠3连,100
hashMap.put("12220",140);//眠3连,80
//
// hashMap.put("10110",1000);//活3连,130
// hashMap.put("20220",800);//活3连,110
// hashMap.put("11010",1000);//活3连,130
// hashMap.put("22020",800);//活3连,110
// hashMap.put("01110", 1000);//活3连
// hashMap.put("02220", 800);//活3连
hashMap.put("11110",3000);//4连,300
hashMap.put("11112",3000);//4连,300
hashMap.put("22220",3500);//4连,280
hashMap.put("22221",3500);//4连,280
int a;
int b;
for(int y=0;y
qizi.java:
package com.lxr.wzq1230;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import jicheng.boss;
public class qizi implements CS{
Graphics g;
Color color;
int x;
int y;
public qizi(Graphics g,Color color,int x,int y) {
this.g=g;
this.color=color;
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
//获取x坐标
public int getX() {
return x;
}
//获取y坐标
public int getY() {
return y;
}
//获取颜色
public Color getColor() {
return color;
}
public void drawq(){
g.setColor(color);
g.fillOval(x0+x*size-size/2, y0+y*size-size/2, size, size);
}
}
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。