面向对象三大特征:封装、继承、多态
1、封装(提高程序的安全性)
class Car:
def __init__(self,brand):
self.brand=brand
def start(self):
print('自行车已被蹬跑')
car=Car('自行车')
car.start()
print(car.brand)
运行结果
自行车已被蹬跑
自行车
一开始它报错说没有定义name,我找老大一会不知道哪错了,原来是第六行
self.name,那个时候写成,了。
看在stu里边有哪些方法?就这样写
在类的外部可以通过_Student(类名)_ _age(不希望被访问的)进行访问
class Student:
def __init__(self,name,age):
self.name=name
self.__age=age #年龄不希望在类的外部使用,所以加了两个_
def show(self):
print(self.name,self.__age)
stu=Student('张三',20)
stu.show()
#在类的外部使用name和age
print(stu.name)
print(dir(stu))
print(stu._Student__age)
张三 20 张三 ['_Student__age', '__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__weakref__', 'name', 'show'] 20
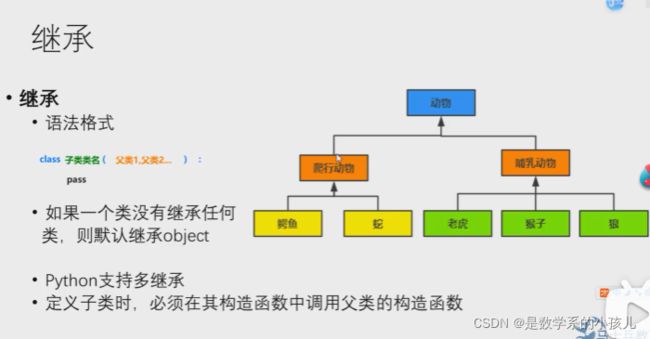
2、继承(提高代码的复用性)
class Person(object):
def __init__(self,name,age):
self.name=name
self.age=age
def info(self):
print(self.name,self.age)
class Student(Person):
def __init__(self,name,age,stu_no):
super().__init__(name,age)
self.stu_no=stu_no
class Teacher(Person):
def __init__(self,name,age,teacherofyear):
super(Teacher, self).__init__(name,age)
self.teacherofyear=teacherofyear
stu=Student('张三',20,'1001')
teacher=Teacher('李四',34,10)
stu.info()
teacher.info()
张三 20
李四 34
3、方法重写
此时只能输出学号,不满足需求
class Person(object):
def __init__(self,name,age):
self.name=name
self.age=age
def info(self):
print(self.name,self.age)
class Student(Person):
def __init__(self,name,age,stu_no):
super().__init__(name,age)
self.stu_no=stu_no
def info(self):
print(self.stu_no)
class Teacher(Person):
def __init__(self,name,age,teacherofyear):
super(Teacher, self).__init__(name,age)
self.teacherofyear=teacherofyear
stu=Student('张三',20,'1001')
teacher=Teacher('李四',34,10)
stu.info()
teacher.info()
1001
李四 34
看下边的重载
class Person(object):
def __init__(self,name,age):
self.name=name
self.age=age
def info(self):
print(self.name,self.age)
class Student(Person):
def __init__(self,name,age,stu_no):
super().__init__(name,age)
self.stu_no=stu_no
def info(self):
super(Student, self).info()
print(self.stu_no)
class Teacher(Person):
def __init__(self,name,age,teacherofyear):
super(Teacher, self).__init__(name,age)
self.teacherofyear=teacherofyear
stu=Student('张三',20,'1001')
teacher=Teacher('李四',34,10)
stu.info()
print('----------------------------')
teacher.info()
运行结果
张三 20
1001
----------------------------
李四 34
把教龄输出
class Person(object):
def __init__(self,name,age):
self.name=name
self.age=age
def info(self):
print(self.name,self.age)
class Student(Person):
def __init__(self,name,age,stu_no):
super().__init__(name,age)
self.stu_no=stu_no
def info(self):
super(Student, self).info()
print(self.stu_no)
class Teacher(Person):
def __init__(self,name,age,teachofyear):
super().__init__(name,age)
self.teachofyear=teachofyear
def info(self):
super().info()
print('教龄',self.teachofyear)
stu=Student('张三',20,'1001')
teacher=Teacher('李四',34,10)
stu.info()
print('----------------------------')
teacher.info()
运行结果
张三 20
1001
----------------------------
李四 34
教龄 10
4、object类
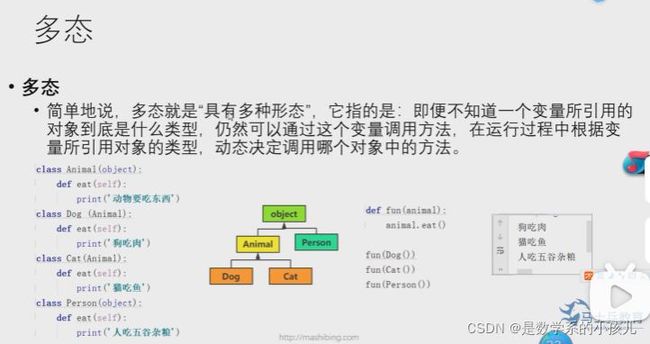
5、多态(提高程序的可拓展性和可维护性)
Java就是静态语言,python就是动态语言
6、特殊方法和特殊属性 特殊方法
两个特殊的方法----创建
1初始化init
2new
特殊属性
两个下划线开始,两个下划线结束就是特殊属性
绑定两个属性
class A:
pass
class B:
pass
class C(A,B):
def __init__(self,name,age):
self.name=name
self.age=age
#创建C类的对象
x=C('Jack',20)#x是C类的一个实例对象
print(x.__dict__)
{'name': 'Jack', 'age': 20}
pycharm使用的小发现
点击加号那里,就会释放,点击减号就会缩成这样,这说明了被缩起来的内容都是隶属于这个类的。
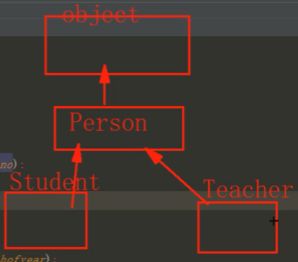
看最左侧出现了箭头,他的意思是重写person类中的方法
英文
总结
本篇文章就到这里了,希望能够给你带来帮助,也希望您能够多多关注脚本之家的更多内容!