目标检测——YOLOV5 Loss 正样本采样
前言
YoloV5中loss由正样本和负样本两部分loss组成,负样本对应着图像的背景,如果负样本远多于正样本,则负样本会淹没正样本的损失,从而降低网络收敛的效率与检测精度。这就是目标检测中常见的正负样本不均衡问题,解决方案之一是增加正样本数。
Yolo anchor_based 系列使用的loss公式如下:

公式中:
S S S: S × S S×S S×S 个网格;
B B B:每个网格产生 B B B 个候选框anchor box;
1 i , j o b j 1_{i,j}^{obj} 1i,jobj: 如果在 i , j i,j i,j 处的box有目标(正样本),其值为1,否则为0;
1 i , j n o o b j 1_{i,j}^{noobj} 1i,jnoobj: 如果在 i , j i,j i,j 处的box没有目标(负样本),其值为1,否则为0;
l i , j b o x l^{box}_{i,j} li,jbox: 在 i , j i,j i,j 处的box损失函数;
l i , j c l s l^{cls}_{i,j} li,jcls:在 i , j i,j i,j 处的cls 损失函数;
l i , j o b j l^{obj}_{i,j} li,jobj:在 i , j i,j i,j 处的obj损失函数
正样本采样
Yolov5算法使用如下3种方式增加正样本个数:
(1) 跨anchor预测
假设一个GT框落在了某个预测分支的某个网格内,该网格具有3种不同大小anchor,若GT可以和这3种anchor中的多种anchor匹配,则这些匹配的anchor都可以来预测该GT框,即一个GT框可以使用多种anchor来预测。
具体方法:
不同于IOU匹配,yolov5采用基于宽高比例的匹配策略,GT的宽高与anchors的宽高对应相除得到ratio1,anchors的宽高与GT的宽高对应相除得到ratio2,取ratio1和ratio2的最大值作为最后的宽高比,该宽高比和设定阈值(默认为4)比较,小于设定阈值的anchor则为匹配到的anchor。
计算例子:
anchor_boxes=torch.tensor([[1.25000, 1.62500],[2.00000, 3.75000],[4.12500, 2.87500]])
gt_box=torch.tensor([5,4])
ratio1=gt_box/anchor_boxes
ratio2=anchor_boxes/gt_box
ratio=torch.max(ratio1, ratio2).max(1)[0]
print(ratio)
anchor_t=4
res=ratio<anchor_t
print(res)
输出:
tensor([4.0000, 2.5000, 1.3913])
tensor([False, True, True])
与GT相匹配的的anchor为anchor 2和anchor3。

(2) 跨grid预测
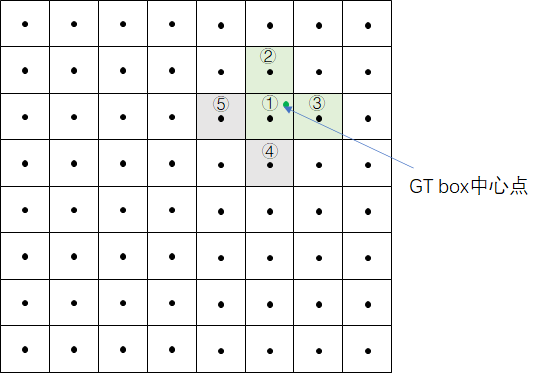
假设一个GT框落在了某个预测分支的某个网格内,则该网格有左、上、右、下4个邻域网格,根据GT框的中心位置,将最近的2个邻域网格也作为预测网格,也即一个GT框可以由3个网格来预测。
计算例子:
GT box中心点处于grid1中,grid1被选中,为了增加增样本,grid1的上下左右grid为候选网格,因为GT中心点更靠近grid2和grid3,grid2和grid3也作为匹配到的网格,根据上步的anchor匹配结果,GT与anchor2、anchor3相匹配,因此GT在当前层匹配到的正样本有6个,分别为:grid1_anchor2,grid1_anchor3,grid2_anchor2,grid2_anchor3,grid3_anchor2,grid3_anchor3。
(3) 跨分支预测
假设一个GT框可以和2个甚至3个预测分支上的anchor匹配,则这2个或3个预测分支都可以预测该GT框,即一个GT框可以由多个预测分支来预测,重复anchor匹配和grid匹配的步骤,可以得到某个GT 匹配到的所有正样本。
debug 代码
上述正样本采样过程在yolov5通过函数build_targets实现,为了方便理解上述代码,对每一步进行debug,具体如下:
def build_targets(self, p, targets):
# Build targets for compute_loss(), input targets(image,class,x,y,w,h)
na, nt = self.na, targets.shape[0] # number of anchors, targets
tcls, tbox, indices, anch = [], [], [], []
gain = torch.ones(7, device=targets.device) # normalized to gridspace gain
## 前置处理
# same as .repeat_interleave(nt)
ai = torch.arange(na, device=targets.device).float().view(na, 1).repeat(1, nt)
targets = torch.cat((targets.repeat(na, 1, 1), ai[:, :, None]), 2) # append anchor indices
g = 0.5 # bias
off = torch.tensor([[0, 0],
[1, 0], [0, 1], [-1, 0], [0, -1], # j,k,l,m
# [1, 1], [1, -1], [-1, 1], [-1, -1], # jk,jm,lk,lm
], device=targets.device).float() * g # offsets
for i in range(self.nl):
## target映射到当前层的尺度
anchors = self.anchors[i]
gain[2:6] = torch.tensor(p[i].shape)[[3, 2, 3, 2]] # xyxy gain
# Match targets to anchors
t = targets * gain
if nt:
# Matches
r = t[:, :, 4:6] / anchors[:, None] # wh ratio
j = torch.max(r, 1 / r).max(2)[0] < self.hyp['anchor_t'] # compare
t = t[j] # filter
# Offsets
gxy = t[:, 2:4] # grid xy
gxi = gain[[2, 3]] - gxy # inverse
j, k = ((gxy % 1 < g) & (gxy > 1)).T
l, m = ((gxi % 1 < g) & (gxi > 1)).T
j = torch.stack((torch.ones_like(j), j, k, l, m))
t = t.repeat((5, 1, 1))[j]
offsets = (torch.zeros_like(gxy)[None] + off[:, None])[j]
else:
t = targets[0]
offsets = 0
# Define
b, c = t[:, :2].long().T # image, class
gxy = t[:, 2:4] # grid xy
gwh = t[:, 4:6] # grid wh
gij = (gxy - offsets).long()
gi, gj = gij.T # grid xy indices
# Append
a = t[:, 6].long() # anchor indices
indices.append((b, a, gj.clamp_(0, gain[3] - 1), gi.clamp_(0, gain[2] - 1))) # image, anchor, grid indices
tbox.append(torch.cat((gxy - gij, gwh), 1)) # box
anch.append(anchors[a]) # anchors
tcls.append(c) # class
return tcls, tbox, indices, anch
输入:targets: shape (7,6),其中7是一个batch的bbox数量,6代表 (image_id, class, x, y, w, h):
tensor([[[0.00000, 2.00000, 0.23471, 0.63425, 0.30464, 0.16110],
[0.00000, 3.00000, 0.08736, 0.64150, 0.11682, 0.21073],
[0.00000, 3.00000, 0.86652, 0.63158, 0.10384, 0.19088],
[0.00000, 2.00000, 0.69091, 0.65983, 0.21684, 0.24738],
[0.00000, 2.00000, 0.95464, 0.64647, 0.09072, 0.13514],
[0.00000, 2.00000, 0.69473, 0.98720, 0.17866, 0.02560],
[0.00000, 3.00000, 0.87034, 0.98758, 0.13743, 0.02484]]], device='cuda:0')
前置处理
ai = torch.arange(na, device=targets.device).float().view(na, 1).repeat(1, nt)
targets = torch.cat((targets.repeat(na, 1, 1), ai[:, :, None]), 2)
g = 0.5 # bias
off = torch.tensor([[0, 0],[1, 0], [0, 1], [-1, 0], [0, -1]],
device=targets.device).float() * g
将target复制3份,shape变成(3,7,7),7代表 (image_id, class, x, y, w, h, anchor_id),复制的目的是为了进行anchor匹配,对应3个anchor:
# targets
tensor([[[0.00000, 2.00000, 0.23471, 0.63425, 0.30464, 0.16110, 0.00000],
[0.00000, 3.00000, 0.08736, 0.64150, 0.11682, 0.21073, 0.00000],
[0.00000, 3.00000, 0.86652, 0.63158, 0.10384, 0.19088, 0.00000],
[0.00000, 2.00000, 0.69091, 0.65983, 0.21684, 0.24738, 0.00000],
[0.00000, 2.00000, 0.95464, 0.64647, 0.09072, 0.13514, 0.00000],
[0.00000, 2.00000, 0.69473, 0.98720, 0.17866, 0.02560, 0.00000],
[0.00000, 3.00000, 0.87034, 0.98758, 0.13743, 0.02484, 0.00000]],
[[0.00000, 2.00000, 0.23471, 0.63425, 0.30464, 0.16110, 1.00000],
[0.00000, 3.00000, 0.08736, 0.64150, 0.11682, 0.21073, 1.00000],
[0.00000, 3.00000, 0.86652, 0.63158, 0.10384, 0.19088, 1.00000],
[0.00000, 2.00000, 0.69091, 0.65983, 0.21684, 0.24738, 1.00000],
[0.00000, 2.00000, 0.95464, 0.64647, 0.09072, 0.13514, 1.00000],
[0.00000, 2.00000, 0.69473, 0.98720, 0.17866, 0.02560, 1.00000],
[0.00000, 3.00000, 0.87034, 0.98758, 0.13743, 0.02484, 1.00000]],
[[0.00000, 2.00000, 0.23471, 0.63425, 0.30464, 0.16110, 2.00000],
[0.00000, 3.00000, 0.08736, 0.64150, 0.11682, 0.21073, 2.00000],
[0.00000, 3.00000, 0.86652, 0.63158, 0.10384, 0.19088, 2.00000],
[0.00000, 2.00000, 0.69091, 0.65983, 0.21684, 0.24738, 2.00000],
[0.00000, 2.00000, 0.95464, 0.64647, 0.09072, 0.13514, 2.00000],
[0.00000, 2.00000, 0.69473, 0.98720, 0.17866, 0.02560, 2.00000],
[0.00000, 3.00000, 0.87034, 0.98758, 0.13743, 0.02484, 2.00000]]], device='cuda:0')
# off
tensor([[ 0.00000, 0.00000],
[ 0.50000, 0.00000],
[ 0.00000, 0.50000],
[-0.50000, 0.00000],
[ 0.00000, -0.50000]], device='cuda:0')
target坐标映射到当前层的尺度
输入的target坐标值为归一化的值,当前层尺寸为80,target坐标值乘以80则可将target坐标值映射到当前层的尺度:
# anchors
anchors = self.anchors[i]
# gain
gain = torch.ones(7, device=targets.device)
gain[2:6] = torch.tensor(p[i].shape)[[3, 2, 3, 2]]
t = targets * gain
# anchors(anchor在当前层的尺寸)
tensor([[1.25000, 1.62500],
[2.00000, 3.75000],
[4.12500, 2.87500]], device='cuda:0')
# gain (当前层尺寸为80)
tensor([ 1., 1., 80., 80., 80., 80., 1.], device='cuda:0')
# t(target 在当前层的尺寸)
# shape:(3,7,7)
tensor([[[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 18.77713, 50.73999, 24.37135, 12.88811, 0.00000],
[ 0.00000, 3.00000, 6.98848, 51.32027, 9.34541, 16.85838, 0.00000],
[ 0.00000, 3.00000, 69.32172, 50.52621, 8.30702, 15.27027, 0.00000],
[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 55.27307, 52.78621, 17.34703, 19.79027, 0.00000],
[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 76.37107, 51.71729, 7.25761, 10.81135, 0.00000],
[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 55.57848, 78.97575, 14.29298, 2.04826, 0.00000],
[ 0.00000, 3.00000, 69.62713, 79.00629, 10.99460, 1.98718, 0.00000]],
[[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 18.77713, 50.73999, 24.37135, 12.88811, 1.00000],
[ 0.00000, 3.00000, 6.98848, 51.32027, 9.34541, 16.85838, 1.00000],
[ 0.00000, 3.00000, 69.32172, 50.52621, 8.30702, 15.27027, 1.00000],
[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 55.27307, 52.78621, 17.34703, 19.79027, 1.00000],
[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 76.37107, 51.71729, 7.25761, 10.81135, 1.00000],
[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 55.57848, 78.97575, 14.29298, 2.04826, 1.00000],
[ 0.00000, 3.00000, 69.62713, 79.00629, 10.99460, 1.98718, 1.00000]],
[[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 18.77713, 50.73999, 24.37135, 12.88811, 2.00000],
[ 0.00000, 3.00000, 6.98848, 51.32027, 9.34541, 16.85838, 2.00000],
[ 0.00000, 3.00000, 69.32172, 50.52621, 8.30702, 15.27027, 2.00000],
[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 55.27307, 52.78621, 17.34703, 19.79027, 2.00000],
[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 76.37107, 51.71729, 7.25761, 10.81135, 2.00000],
[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 55.57848, 78.97575, 14.29298, 2.04826, 2.00000],
[ 0.00000, 3.00000, 69.62713, 79.00629, 10.99460, 1.98718, 2.00000]]], device='cuda:0')
匹配 anchor
step1:对每一个GT框,分别计算它与9种anchor的宽与宽的比值、高与高的比值;
step2:在宽比值、高比值这2个比值中,取最极端的一个比值,作为GT框和anchor的比值,具体实现的伪代码为:max(anchor / GT, GT / anchor );
step3:得到GT框和anchor的比值后,若这个比值小于设定的比值阈值,那么这个anchor就负责预测GT框,这个anchor的预测框就被称为正样本,所有其它的预测框都是负样本。
得到当前层需要检测的GT以及其对应的anchor_id。
# step1
r = t[:, :, 4:6] / anchors[:, None]
# step2
j = torch.max(r, 1 / r).max(2)[0] < self.hyp['anchor_t']
# step3
t = t[j]
输出:
# r
# shape:(3,7,2)
tensor([[[19.49708, 7.93114],
[ 7.47632, 10.37439],
[ 6.64562, 9.39709],
[13.87762, 12.17863],
[ 5.80609, 6.65314],
[11.43438, 1.26047],
[ 8.79568, 1.22288]],
[[12.18568, 3.43683],
[ 4.67270, 4.49557],
[ 4.15351, 4.07207],
[ 8.67351, 5.27741],
[ 3.62881, 2.88303],
[ 7.14649, 0.54620],
[ 5.49730, 0.52992]],
[[ 5.90821, 4.48282],
[ 2.26555, 5.86378],
[ 2.01382, 5.31140],
[ 4.20534, 6.88357],
[ 1.75942, 3.76047],
[ 3.46496, 0.71244],
[ 2.66536, 0.69119]]], device='cuda:0')
# j
tensor([[False, False, False, False, False, False, False],
[False, False, False, False, True, False, False],
[False, False, False, False, True, True, True]], device='cuda:0')
# t(在当前层只检测这4个target)
tensor([[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 76.37107, 51.71729, 7.25761, 10.81135, 1.00000],
[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 76.37107, 51.71729, 7.25761, 10.81135, 2.00000],
[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 55.57848, 78.97575, 14.29298, 2.04826, 2.00000],
[ 0.00000, 3.00000, 69.62713, 79.00629, 10.99460, 1.98718, 2.00000]], device='cuda:0')
匹配 grid
为了扩展正样本数量,将上下左右的gird作为候选grid,更靠近GT 所在的grid的则为匹配到的grid。
gxy = t[:, 2:4]
gxi = gain[[2, 3]] - gxy
j, k = ((gxy % 1 < g) & (gxy > 1)).T # (左,下),gxy > 1排除超出边界的部分
l, m = ((gxi % 1 < g) & (gxi > 1)).T # (右,上),gxi > 1排除超出边界的部分
j = torch.stack((torch.ones_like(j), j, k, l, m))
t = t.repeat((5, 1, 1))[j]
offsets = (torch.zeros_like(gxy)[None] + off[:, None])[j]
输出:
# gxy
tensor([[76.37107, 51.71729],
[76.37107, 51.71729],
[55.57848, 78.97575],
[69.62713, 79.00629]], device='cuda:0')
# gxi
tensor([[ 3.62893, 28.28271],
[ 3.62893, 28.28271],
[24.42152, 1.02425],
[10.37287, 0.99371]], device='cuda:0')
# j, k
j: tensor([ True, True, False, False], device='cuda:0')
k: tensor([False, False, False, True], device='cuda:0')
# l, m
l: tensor([False, False, True, True], device='cuda:0')
m: tensor([ True, True, True, False], device='cuda:0')
# j
tensor([[ True, True, True, True],
[ True, True, False, False],
[False, False, False, True],
[False, False, True, True],
[ True, True, True, False]], device='cuda:0')
# t
tensor([[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 76.37107, 51.71729, 7.25761, 10.81135, 1.00000],
[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 76.37107, 51.71729, 7.25761, 10.81135, 2.00000],
[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 55.57848, 78.97575, 14.29298, 2.04826, 2.00000],
[ 0.00000, 3.00000, 69.62713, 79.00629, 10.99460, 1.98718, 2.00000],
[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 76.37107, 51.71729, 7.25761, 10.81135, 1.00000],
[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 76.37107, 51.71729, 7.25761, 10.81135, 2.00000],
[ 0.00000, 3.00000, 69.62713, 79.00629, 10.99460, 1.98718, 2.00000],
[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 55.57848, 78.97575, 14.29298, 2.04826, 2.00000],
[ 0.00000, 3.00000, 69.62713, 79.00629, 10.99460, 1.98718, 2.00000],
[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 76.37107, 51.71729, 7.25761, 10.81135, 1.00000],
[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 76.37107, 51.71729, 7.25761, 10.81135, 2.00000],
[ 0.00000, 2.00000, 55.57848, 78.97575, 14.29298, 2.04826, 2.00000]], device='cuda:0')
# offsets
tensor([[ 0.00000, 0.00000],
[ 0.00000, 0.00000],
[ 0.00000, 0.00000],
[ 0.00000, 0.00000],
[ 0.50000, 0.00000],
[ 0.50000, 0.00000],
[ 0.00000, 0.50000],
[-0.50000, 0.00000],
[-0.50000, 0.00000],
[ 0.00000, -0.50000],
[ 0.00000, -0.50000],
[ 0.00000, -0.50000]], device='cuda:0')
grid坐标
计算匹配到的grid左上坐标点:
b, c = t[:, :2].long().T # image, class
gxy = t[:, 2:4] # grid xy
gwh = t[:, 4:6] # grid wh
gij = (gxy - offsets).long()
gi, gj = gij.T # grid
输出:
# b
tensor([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], device='cuda:0')
# c
tensor([2, 2, 2, 3, 2, 2, 3, 2, 3, 2, 2, 2], device='cuda:0')
# gxy
tensor([[76.37107, 51.71729],
[76.37107, 51.71729],
[55.57848, 78.97575],
[69.62713, 79.00629],
[76.37107, 51.71729],
[76.37107, 51.71729],
[69.62713, 79.00629],
[55.57848, 78.97575],
[69.62713, 79.00629],
[76.37107, 51.71729],
[76.37107, 51.71729],
[55.57848, 78.97575]], device='cuda:0')
# gwh
tensor([[ 7.25761, 10.81135],
[ 7.25761, 10.81135],
[14.29298, 2.04826],
[10.99460, 1.98718],
[ 7.25761, 10.81135],
[ 7.25761, 10.81135],
[10.99460, 1.98718],
[14.29298, 2.04826],
[10.99460, 1.98718],
[ 7.25761, 10.81135],
[ 7.25761, 10.81135],
[14.29298, 2.04826]], device='cuda:0')
# gij
tensor([[76, 51],
[76, 51],
[55, 78],
[69, 79],
[75, 51],
[75, 51],
[69, 78],
[56, 78],
[70, 79],
[76, 52],
[76, 52],
[55, 79]], device='cuda:0')
# gi
tensor([76, 76, 55, 69, 75, 75, 69, 56, 70, 76, 76, 55], device='cuda:0')
# gj
tensor([51, 51, 78, 79, 51, 51, 78, 78, 79, 52, 52, 79], device='cuda:0')
结果放到列表中
a = t[:, 6].long() # anchor indices
indices.append((b, a, gj.clamp_(0, gain[3] - 1), gi.clamp_(0, gain[2] - 1))) # image, anchor, grid indices
tbox.append(torch.cat((gxy - gij, gwh), 1)) # box
anch.append(anchors[a]) # anchors
tcls.append(c) # class
输出:
tensor([1, 2, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2], device='cuda:0')
[(tensor([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], device='cuda:0'), # image_id
tensor([1, 2, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 2, 2], device='cuda:0'), # anchor_id
tensor([51, 51, 78, 79, 51, 51, 78, 78, 79, 52, 52, 79], device='cuda:0'), # grid_indices
tensor([76, 76, 55, 69, 75, 75, 69, 56, 70, 76, 76, 55], device='cuda:0'))]
# tbox
[tensor([[ 3.71071e-01, 7.17293e-01, 7.25761e+00, 1.08114e+01],
[ 3.71071e-01, 7.17293e-01, 7.25761e+00, 1.08114e+01],
[ 5.78480e-01, 9.75746e-01, 1.42930e+01, 2.04826e+00],
[ 6.27129e-01, 6.28662e-03, 1.09946e+01, 1.98718e+00],
[ 1.37107e+00, 7.17293e-01, 7.25761e+00, 1.08114e+01],
[ 1.37107e+00, 7.17293e-01, 7.25761e+00, 1.08114e+01],
[ 6.27129e-01, 1.00629e+00, 1.09946e+01, 1.98718e+00],
[-4.21520e-01, 9.75746e-01, 1.42930e+01, 2.04826e+00],
[-3.72871e-01, 6.28662e-03, 1.09946e+01, 1.98718e+00],
[ 3.71071e-01, -2.82707e-01, 7.25761e+00, 1.08114e+01],
[ 3.71071e-01, -2.82707e-01, 7.25761e+00, 1.08114e+01],
[ 5.78480e-01, -2.42538e-02, 1.42930e+01, 2.04826e+00]], device='cuda:0')]
# anch
[tensor([[2.00000, 3.75000],
[4.12500, 2.87500],
[4.12500, 2.87500],
[4.12500, 2.87500],
[2.00000, 3.75000],
[4.12500, 2.87500],
[4.12500, 2.87500],
[4.12500, 2.87500],
[4.12500, 2.87500],
[2.00000, 3.75000],
[4.12500, 2.87500],
[4.12500, 2.87500]], device='cuda:0')]
# tcls
[tensor([2, 2, 2, 3, 2, 2, 3, 2, 3, 2, 2, 2], device='cuda:0')]
参考
YOLOV5: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5