- python26
m0_69573627
前端javascripthtml
浙大疏锦行-CSDN博客作业:题目1:计算圆的面积任务:编写一个名为calculate_circle_area的函数,该函数接收圆的半径radius作为参数,并返回圆的面积。圆的面积=π*radius²(可以使用math.pi作为π的值)要求:函数接收一个位置参数radius。计算半径为5、0、-1时候的面积注意点:可以采取try-except使函数变得更加稳健,如果传入的半径为负数,函数应该返回
- 苍穹外卖 -- 完结(学习笔记)
ros275229
苍穹外卖java学习笔记苍穹外卖javaspringintellij-idea数据库
苍穹外卖-day01课程内容-软件开发整体介绍-苍穹外卖项目介绍-开发环境搭建-导入接口文档-Swagger-CSDN博客苍穹外卖-day02-新增员工-员工分页查询-启用禁用员工账号-编辑员工-导入分类模块功能代码-CSDN博客苍穹外卖-day03-公共字段自动填充-新增菜品-菜品分页查询-删除菜品-修改菜品-CSDN博客作业(基本的crud)无Redis入门--用java操作redis--苍穹
- C语言I博客作业02
cm1051425243
c语言开发语言后端
这个作业属于哪个课程https://bbs.csdn.net/forums/csuft_swxy_C?category=0&typeId=17328这个作业要求在哪里https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/603005216这个作业的目标学号1.PTA作业7-1计算分段函数[2](10分)本题目要求计算下列分段函数f(x)的值:f2-11注:可在头文件中包含math.h,并调用sq
- 第二周博客作业
左旋
第一题总结cp、mv命令的用法(要求列出源及目标各种情况的表格)cp命令用法:cp【选项】。。。源文件目标文件-a:此选项通常在复制目录的时候使用,保留链接、文件属性,并复制目录下的所有内容。-d:复制时保留链接。这里所说的链接相当于Windows系统中的快捷方式。-f:覆盖已经存在的目标文件而不给出提示。-i:与-f选项相反,在覆盖目标文件之前给出提示,要求用户确认是否覆盖,回答y时目标文件将被
- OO第三次博客作业
weixin_30530339
目录DesignbyContractJML语言的理论基础JML设计目的书写规范主要表达式JML应用工具链情况部署JMLUnitNG架构设计与两次迭代第一次作业第二次作业第三次作业bug分析心得体会参考资料DesignbyContractJML语言的理论基础JML设计目的契约式设计是一种开发软件的方法,其背后的主要思想是一个类及其客户之间有“契约”。客户必须在调用类定义的方法之前保证某些条件,而作为
- DS博客作业07--查找
weixin_34174322
数据结构与算法大数据
1.本周学习总结1.1.思维导图1.2.对查找运算的认识及学习体会本章学习了查找的相关知识,介绍了线性表查找、数表查找和哈希表查找等相关算法设计查找算法。查找又称为检索,是指在某种数据结构种找出满足给定条件的元素。查找是一种十分有用的操作,例如在学生成绩表种查找某个学生的成绩元素,在图书馆的书目文件中查找某编号的图书元素等。因为查找是对已存入到计算机中的数据进行的运算,所以在研究各种查找方法时,首
- 博客作业
3788ea30a4e8
博客去底部-->跳转指定位置个人博客第二天作业富人碰了吃土,穷人碰了入土的玩意宝马S1000RR百科四缸太费油三缸不成熟双杠不好听单杠没动力大的父母不让买小的自己不想买街车不帅又太闷跑车通过性不好越野不酷踏板太娘风冷的冷却不好水冷的保养太麻烦油冷的又烫腿国际档的不会骑循环档的不安全无级变速又加速不强轮胎宽了阻力大轮胎窄了不好看两轮不会压弯三轮又不敢骑四轮不像摩托车大哥你说买啥???友情链接:百度网
- C语言I博客作业06
啊焱i
深度学习python神经网络
这个作业属于哪个课程这个作业要求在哪里这个作业的目标学号1.PTA作业7-1求交错序列前N项和本题要求编写程序,计算交错序列1-2/3+3/5-4/7+5/9-6/11+…的前N项之和。1.1.1贴图代码展示1.1.2数据处理数据表达:运用了n,sum这些变量的值初始化,类型是整型。数据处理:本题运用了for语句循环结构.1.1.3PTA提交列表及说明7-2求平方根序列前N项和本题要求编写程序,计
- C语言博客作业--函数嵌套调用
weixin_34038652
c/c++
一、实验作业PTA题目:6-7递归法对任意10个数据按降序排序设计思路定义整型变量max=a[0],temp,循环变量i如果n==1a[n-1]=a[0]设置递归出口否则fori=0toi=n-1;如果a[i]>a[n-1]交换a[i]和a[n-1];endfor重复进行,每次n-1,直到递归出口代码截图调试问题1,发现进行到最大值后,其他值都发生了改变--------if语句没有加花括号2,开始
- C语言--指针
驼同学.
C/C++c语言
这个作业属于哪个班级C语言–网络2011/2012这个作业的地址C语言博客作业05–指针这个作业的目标学习指针相关内容姓名骆锟宏文章目录0.展示PTA总分1.本章学习总结(3分)1.1指针定义、指针相关运算、指针做函数参数。1.1.1指针的定义:1.1.2指针相关运算:1.1.3指针做函数参数:1.1.4对指针变量的操作:1.2字符指针1.2.1指针如何指向字符串1.2.2字符串相关函数及函数码原
- python编写自定义函数判断n1-n2范围内的素数_C语言博客作业--函数
weixin_39815879
一、PTA实验作业题目1:使用函数输出水仙花数1.本题PTA提交列表2.设计思路intnarcissistic(intnumber)函数1.定义整型变量inti,j,m;intn,digit=0,N1,N2;intnum,re_number=0;2.让N1,N2赋上number的值N1=number;N2=number;3.for循环{n=N1%10;digit++;N1=N1/10;}用来统计n
- C语言博客作业--嵌套循环
weixin_30877755
c/c++
一、PTA实验作业题目1:换硬币1.本题PTA提交列表2.设计思路第一步:定义5个整形变量,money,count,fen5,fen2,fen1,money为待换金额,count表示换法数量,fen5表示5分的数量,fen2表示2分的数量,fen1表示1分的数量。第二步:初始化count为0。第三步:输入x。第四步:fen5=money/5,当fen5大于0时,循环第五步到第十一步。第五步:fen
- C语言程序设计博客作业07
Anoxia523
c语言开发语言
这个作业要求在哪里C语言程序设计博客作业07我在这个课程的目标是学会结构变量的用法这个作业在那个具体方面帮助我实现目标PTA作业练习和课堂练习参考文献百度、csdn1.PTA实验作业1.1结构体数组实现工资数据的存放与输出用结构体存放下表中的数据,然后输出每人的姓名和实发工资(基本工资+浮动工资-支出)1.1.1数据处理数据表达:结构变量people,定义字符串数组name[10],单精度浮点型变
- C语言博客作业--结构体
dcue86841
c/c++
一、PTA实验作业题目1:6-3结构体数组中查找指定编号人员1.本题PTA提交列表(要提交列表,不是结果)2.设计思路(伪代码或流程图)传入结构体数组str和要查找的人员numstructstudent*pos;forpos=stdtostd+7if(strcmp(pos->num,num)==0)退出循环endfor返回*pos3.代码截图(注意,截图,截图,截图。不要粘贴博客上。不用用···语
- 作业要求 2018091-2 博客作业
albertho2001
此作业的要求参见[https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/nenu/2018fall/homework/2101]1.建博客(1分)我的博客地址是:https://www.cnblogs.com/luditong/2.博客作业(10分)(1)回想一下你曾经对计算机专业的畅想看到这个问题的时候,回答起来也算苦涩,不过也算幸运。小时候的我很喜欢拆玩具,每次父亲给我买了新玩具,我拿
- 第1周小组博客作业——Mantis使用总结
dilao8450
测试php数据库
1.工具概述Mantis是一个基于PHP技术的轻量级的开源缺陷跟踪系统,以Web操作的形式提供项目管理及缺陷跟踪服务。在功能上、实用性上足以满足中小型项目的管理及跟踪。更重要的是其开源,不需要负担任何费用。具有多特性包括:易于安装,易于操作,基于Web,支持任何可运行PHP的平台。需要自行安装MySQL、EasyPHP软件及兼容性测试。2.对应的流程2.1角色介绍系统管理员:主要创建用户,创建项目
- C语言博客作业--函数嵌套调用
weixin_33940102
c/c++数据结构与算法
一、实验作业1.1PTA题目6-4十进制转换二进制设计思路voiddectobin(intn)定义整型变量i;当i不比二小时,i=n/2执行该函数递归输出n%2的值代码截图调试问题一开始的思路有点模糊,然后感觉该题与课堂派的期中考递归题的思路有点相似,借鉴思考后正确1.2学生成绩管理系统1.2.1画函数模块图,简要介绍函数功能1.2.2截图展示你的工程文件1.2.3函数代码部分截图头文件插入学生信
- C语言博客作业03--函数
weixin_30865427
c/c++
1.本章学习总结(2分)1.1思维导图1.2本章学习体会及代码量学习体会1.2.1学习体会本周学习感受:经过这一周对于函数的学习,我对于模块化的程序设计有了深刻的理解,并学会了利用函数把复杂的问题分解为多个小问题来解决。这样的代码具有良好的可读性,同时也便于我们日后对于代码的修改。个人认为函数的最大优点是可以多次调用,这样极大地缩短了代码的长度。如同之前学过的循环结构,有时候我们的代码需要反复执行
- C语言I博客作业10
TL6789
c语言排序算法开发语言
这个作业属于哪个课程https://bbs.csdn.net/forums/csuft_swxy_C?typeId=17328这个作业要求在哪里https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/603798003?username=tl6789这个作业的目标对C语言的练习学号202191131.PTA作业1.1(题目名称):7-1求一批整数中出现最多的个位数字(20分)给定一批整数,分析每个
- C语言程序设计博客作业03
通信三班姚元敏202201120341
c语言算法矩阵
这个作业要求在哪里http://t.csdn.cn/ULQVf我在这个课程的目标是可以熟练掌握一些常见的字符串处理的函数,正确使用并读懂数组这个作业在那个具体方面帮助我实现目标理解数组变量在内存中的存放形式,数组元素的引用,二维数组的理解,字符串与字符数组的区别参考文献《C语言程序设计教程(第3版)》、百度1.PTA实验作业1.1找出矩阵中最小值所在的位置将1个mxn的矩阵存入1个mxn的二维数组
- C语言程序设计博客作业04
通信三班姚元敏202201120341
c语言算法
这个作业要求在哪里http://t.csdn.cn/OS9BZ我在这个课程的目标是理解并正确运用函数的定义和调用形式这个作业在那个具体方面帮助我实现目标各种类型函数的基本运行规则,变量的作用域和生存期参考文献《C语言程序设计教程》、百度1.PTA实验作业1.1输出Fibonacci数列的前n项已知Fibonacci数列的规律是1,1,2,3,5,8,…,即数列的前两项是1,其后的每一项都是其前两项
- 2022北航敏捷软件工程 第四次博客作业
Kuma-XX
软件工程
2022北航敏捷软件工程第四次博客作业项目内容这个作业属于哪个课程2022年北航敏捷软件工程这个作业的要求在哪里个人作业-提问回顾与个人总结我在这个课程的目标是了解软件工程的方法论、在实践中学习软件工程的各个层次、获得以敏捷流程进行软件开发和产品构建的相关经验、尝试以软件工程的方式来实现脑中想法。这个作业在哪个具体方面帮助我实现目标了解软件工程的方法论:结合第一次博客的问题,结合所学软件工程理论重
- c语言I博客作业02
An165
c语言python算法
这个作业属于哪个课程这个作业要求在哪里这个作业的目标学号1.1.1完成PTA作业,并给出编程题完成截图,截图上有自己的学号及姓名标识7-1计算摄氏温度本题要求编写程序,计算华氏温度100°F对应的摄氏温度。计算公式:C=5×(F−32)/9,式中:C表示摄氏温度,F表示华氏温度,输出数据要求为整型。输入格式:本题目没有输入。输出格式:按照下列格式输出fahr=100,celsius=计算所得摄氏温
- 第一次博客作业
akq5168
c/c++python移动开发
Q1:学习《C++语言程序设计》课程之前,你知道什么是编程吗?谈谈上这门课之前你对编程的理解,以及你对自己编程能力的评估:A1:在课程之前我简单的学过python,并跟着教材上的材料试着做了个小游戏,在那时候我觉得编程是用计算机的写一些软件开发游戏等等;上这门课之前我对编程的理解就是把一个现实问题用计算机的语言和数学的方法表达出来,然后交给计算机运算解决,所以那时候觉得只要把编程语言学好然后再学好
- C语言博客作业04--数组
dbwuawuuq822801895
c/c++
1.本章学习总结1.1思维导图1.2本章学习体会及代码量学习体会1.2.1学习体会在这几周的学中,我的体会如下1.在学习数组的初始化时,学习了可以使用static进行初始化,而不必用到for循环2.在学习二维数组的过程中,第一次知道了二维数组赋值时行数可不做规定,编译器会自动依照输入的数据以及列数而定3.二分法可以更快地在有序数组中查找所需要的值4.flag也可以转化为数组的形式,做到判断数组是否
- C语言博客作业--函数
weixin_30378623
c/c++
---恢复内容开始---一、PTA实验作业题目1:使用函数判断完全平方数1.本题PTA提交列表2.设计思路1.将表达式根号n强制转换成整型2.判断根号n是否等于转换类型后的根号n3.如果等于,返回1,否则返回03.本题调试过程碰到问题及PTA提交列表情况说明遇到的问题:写的代码过于取巧,想用输入一个数判断参数n是否为完全平方数,但是这个方法只能取特殊值才有效,例如检查点2的100就如此,需要输入的
- UML 类图画法规则
Yeeman_Z
学习笔记javauml类图
UML类图画法规则本学期OO课程用java来学习面向对象程序设计与构造,课程博客作业要求自行独立绘制类图、协作图等,所以简单学习一下类图和协作图的绘制,本篇博客主要记录类图绘制的一些关键点,方便日后查阅。类型表示类(class):用如图方块表示,其中最上方一空格区为类名,紧接着为属性(:)、方法()、异常等。接口:用圆圈表示,注明接口名称类间关系继承(extends):空心三角箭头的实线表示,从子
- C语言博客作业--嵌套循环
diaoxiaxin0941
c/c++
一、PTA实验作业题目1:7-4换硬币1.本题PTA提交列表2.设计思路1.定义整数型变量money,count,total分别用来存放要换的零钱,换法个数和硬币数量和,定义整数型变量fen1.fen2.fen5分别代表一分两分五分的数量2.赋初值,count=0,total=03.输入money4.枚举法,讨论所有可能的五分钱的个数情况5.枚举法,讨论所有可能的两分钱的个数情况6.枚举法,讨论所
- C语言第二次博客作业---分支结构
weixin_30587927
c/c++
一、PTA实验作业1.计算分段函数[2]本题目要求计算下列分段函数f(x)的值:注:可在头文件中包含math.h,并调用sqrt函数求平方根,调用pow函数求幂。1.代码doublex,result;scanf("%lf",&x);if(x>=0){result=sqrt(x);}else{result=pow(x+1,2)+2*x+1/x;}printf("f(%.2f)=%.2f",x,res
- 软工第二次博客作业-软件案例分析
Carves123
软件工程
软件案例分析-CSDN技能树项目内容这个作业属于哪个课程2023年北航敏捷软件工程这个作业的要求在哪里作业要求我在这个课程的目标是学习软件工程知识,提升团队合作能力,积累网页开发经验。这个作业在哪个具体方面帮助我实现目标帮助学习从开发者和用户角度分析软件的质量。第一部分调研,评测软件评测基本功能在CSDN主页,通过“CSDN-学习-技能树”进入技能树主界面,默认技能树是python。点击左上角技能
- 多线程编程之卫生间
周凡杨
java并发卫生间线程厕所
如大家所知,火车上车厢的卫生间很小,每次只能容纳一个人,一个车厢只有一个卫生间,这个卫生间会被多个人同时使用,在实际使用时,当一个人进入卫生间时则会把卫生间锁上,等出来时打开门,下一个人进去把门锁上,如果有一个人在卫生间内部则别人的人发现门是锁的则只能在外面等待。问题分析:首先问题中有两个实体,一个是人,一个是厕所,所以设计程序时就可以设计两个类。人是多数的,厕所只有一个(暂且模拟的是一个车厢)。
- How to Install GUI to Centos Minimal
sunjing
linuxInstallDesktopGUI
http://www.namhuy.net/475/how-to-install-gui-to-centos-minimal.html
I have centos 6.3 minimal running as web server. I’m looking to install gui to my server to vnc to my server. You can insta
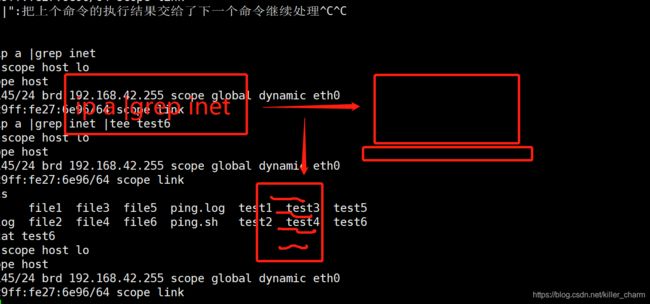
- Shell 函数
daizj
shell函数
Shell 函数
linux shell 可以用户定义函数,然后在shell脚本中可以随便调用。
shell中函数的定义格式如下:
[function] funname [()]{
action;
[return int;]
}
说明:
1、可以带function fun() 定义,也可以直接fun() 定义,不带任何参数。
2、参数返回
- Linux服务器新手操作之一
周凡杨
Linux 简单 操作
1.whoami
当一个用户登录Linux系统之后,也许他想知道自己是发哪个用户登录的。
此时可以使用whoami命令。
[ecuser@HA5-DZ05 ~]$ whoami
e
- 浅谈Socket通信(一)
朱辉辉33
socket
在java中ServerSocket用于服务器端,用来监听端口。通过服务器监听,客户端发送请求,双方建立链接后才能通信。当服务器和客户端建立链接后,两边都会产生一个Socket实例,我们可以通过操作Socket来建立通信。
首先我建立一个ServerSocket对象。当然要导入java.net.ServerSocket包
ServerSock
- 关于框架的简单认识
西蜀石兰
框架
入职两个月多,依然是一个不会写代码的小白,每天的工作就是看代码,写wiki。
前端接触CSS、HTML、JS等语言,一直在用的CS模型,自然免不了数据库的链接及使用,真心涉及框架,项目中用到的BootStrap算一个吧,哦,JQuery只能算半个框架吧,我更觉得它是另外一种语言。
后台一直是纯Java代码,涉及的框架是Quzrtz和log4j。
都说学前端的要知道三大框架,目前node.
- You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your
林鹤霄
You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near 'option,changed_ids ) values('0ac91f167f754c8cbac00e9e3dc372
- MySQL5.6的my.ini配置
aigo
mysql
注意:以下配置的服务器硬件是:8核16G内存
[client]
port=3306
[mysql]
default-character-set=utf8
[mysqld]
port=3306
basedir=D:/mysql-5.6.21-win
- mysql 全文模糊查找 便捷解决方案
alxw4616
mysql
mysql 全文模糊查找 便捷解决方案
2013/6/14 by 半仙
[email protected]
目的: 项目需求实现模糊查找.
原则: 查询不能超过 1秒.
问题: 目标表中有超过1千万条记录. 使用like '%str%' 进行模糊查询无法达到性能需求.
解决方案: 使用mysql全文索引.
1.全文索引 : MySQL支持全文索引和搜索功能。MySQL中的全文索
- 自定义数据结构 链表(单项 ,双向,环形)
百合不是茶
单项链表双向链表
链表与动态数组的实现方式差不多, 数组适合快速删除某个元素 链表则可以快速的保存数组并且可以是不连续的
单项链表;数据从第一个指向最后一个
实现代码:
//定义动态链表
clas
- threadLocal实例
bijian1013
javathreadjava多线程threadLocal
实例1:
package com.bijian.thread;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
private static ThreadLocal tl = new ThreadLocal() {
protected synchronized Object initialValue() {
return new Inte
- activemq安全设置—设置admin的用户名和密码
bijian1013
javaactivemq
ActiveMQ使用的是jetty服务器, 打开conf/jetty.xml文件,找到
<bean id="adminSecurityConstraint" class="org.eclipse.jetty.util.security.Constraint">
<p
- 【Java范型一】Java范型详解之范型集合和自定义范型类
bit1129
java
本文详细介绍Java的范型,写一篇关于范型的博客原因有两个,前几天要写个范型方法(返回值根据传入的类型而定),竟然想了半天,最后还是从网上找了个范型方法的写法;再者,前一段时间在看Gson, Gson这个JSON包的精华就在于对范型的优雅简单的处理,看它的源代码就比较迷糊,只其然不知其所以然。所以,还是花点时间系统的整理总结下范型吧。
范型内容
范型集合类
范型类
- 【HBase十二】HFile存储的是一个列族的数据
bit1129
hbase
在HBase中,每个HFile存储的是一个表中一个列族的数据,也就是说,当一个表中有多个列簇时,针对每个列簇插入数据,最后产生的数据是多个HFile,每个对应一个列族,通过如下操作验证
1. 建立一个有两个列族的表
create 'members','colfam1','colfam2'
2. 在members表中的colfam1中插入50*5
- Nginx 官方一个配置实例
ronin47
nginx 配置实例
user www www;
worker_processes 5;
error_log logs/error.log;
pid logs/nginx.pid;
worker_rlimit_nofile 8192;
events {
worker_connections 4096;}
http {
include conf/mim
- java-15.输入一颗二元查找树,将该树转换为它的镜像, 即在转换后的二元查找树中,左子树的结点都大于右子树的结点。 用递归和循环
bylijinnan
java
//use recursion
public static void mirrorHelp1(Node node){
if(node==null)return;
swapChild(node);
mirrorHelp1(node.getLeft());
mirrorHelp1(node.getRight());
}
//use no recursion bu
- 返回null还是empty
bylijinnan
javaapachespring编程
第一个问题,函数是应当返回null还是长度为0的数组(或集合)?
第二个问题,函数输入参数不当时,是异常还是返回null?
先看第一个问题
有两个约定我觉得应当遵守:
1.返回零长度的数组或集合而不是null(详见《Effective Java》)
理由就是,如果返回empty,就可以少了很多not-null判断:
List<Person> list
- [科技与项目]工作流厂商的战略机遇期
comsci
工作流
在新的战略平衡形成之前,这里有一个短暂的战略机遇期,只有大概最短6年,最长14年的时间,这段时间就好像我们森林里面的小动物,在秋天中,必须抓紧一切时间存储坚果一样,否则无法熬过漫长的冬季。。。。
在微软,甲骨文,谷歌,IBM,SONY
- 过度设计-举例
cuityang
过度设计
过度设计,需要更多设计时间和测试成本,如无必要,还是尽量简洁一些好。
未来的事情,比如 访问量,比如数据库的容量,比如是否需要改成分布式 都是无法预料的
再举一个例子,对闰年的判断逻辑:
1、 if($Year%4==0) return True; else return Fasle;
2、if ( ($Year%4==0 &am
- java进阶,《Java性能优化权威指南》试读
darkblue086
java性能优化
记得当年随意读了微软出版社的.NET 2.0应用程序调试,才发现调试器如此强大,应用程序开发调试其实真的简单了很多,不仅仅是因为里面介绍了很多调试器工具的使用,更是因为里面寻找问题并重现问题的思想让我震撼,时隔多年,Java已经如日中天,成为许多大型企业应用的首选,而今天,这本《Java性能优化权威指南》让我再次找到了这种感觉,从不经意的开发过程让我刮目相看,原来性能调优不是简单地看看热点在哪里,
- 网络学习笔记初识OSI七层模型与TCP协议
dcj3sjt126com
学习笔记
协议:在计算机网络中通信各方面所达成的、共同遵守和执行的一系列约定 计算机网络的体系结构:计算机网络的层次结构和各层协议的集合。 两类服务: 面向连接的服务通信双方在通信之前先建立某种状态,并在通信过程中维持这种状态的变化,同时为服务对象预先分配一定的资源。这种服务叫做面向连接的服务。 面向无连接的服务通信双方在通信前后不建立和维持状态,不为服务对象
- mac中用命令行运行mysql
dcj3sjt126com
mysqllinuxmac
参考这篇博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/macro-cheng/archive/2011/10/25/mysql-001.html 感觉workbench不好用(有点先入为主了)。
1,安装mysql
在mysql的官方网站下载 mysql 5.5.23 http://www.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/,根据我的机器的配置情况选择了64
- MongDB查询(1)——基本查询[五]
eksliang
mongodbmongodb 查询mongodb find
MongDB查询
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2174452 一、find简介
MongoDB中使用find来进行查询。
API:如下
function ( query , fields , limit , skip, batchSize, options ){.....}
参数含义:
query:查询参数
fie
- base64,加密解密 经融加密,对接
y806839048
经融加密对接
String data0 = new String(Base64.encode(bo.getPaymentResult().getBytes(("GBK"))));
String data1 = new String(Base64.decode(data0.toCharArray()),"GBK");
// 注意编码格式,注意用于加密,解密的要是同
- JavaWeb之JSP概述
ihuning
javaweb
什么是JSP?为什么使用JSP?
JSP表示Java Server Page,即嵌有Java代码的HTML页面。使用JSP是因为在HTML中嵌入Java代码比在Java代码中拼接字符串更容易、更方便和更高效。
JSP起源
在很多动态网页中,绝大部分内容都是固定不变的,只有局部内容需要动态产生和改变。
如果使用Servl
- apple watch 指南
啸笑天
apple
1. 文档
WatchKit Programming Guide(中译在线版 By @CocoaChina) 译文 译者 原文 概览 - 开始为 Apple Watch 进行开发 @星夜暮晨 Overview - Developing for Apple Watch 概览 - 配置 Xcode 项目 - Overview - Configuring Yo
- java经典的基础题目
macroli
java编程
1.列举出 10个JAVA语言的优势 a:免费,开源,跨平台(平台独立性),简单易用,功能完善,面向对象,健壮性,多线程,结构中立,企业应用的成熟平台, 无线应用 2.列举出JAVA中10个面向对象编程的术语 a:包,类,接口,对象,属性,方法,构造器,继承,封装,多态,抽象,范型 3.列举出JAVA中6个比较常用的包 Java.lang;java.util;java.io;java.sql;ja
- 你所不知道神奇的js replace正则表达式
qiaolevip
每天进步一点点学习永无止境纵观千象regex
var v = 'C9CFBAA3CAD0';
console.log(v);
var arr = v.split('');
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i ++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) arr[i] = '%' + arr[i];
}
console.log(arr.join(''));
console.log(v.r
- [一起学Hive]之十五-分析Hive表和分区的统计信息(Statistics)
superlxw1234
hivehive分析表hive统计信息hive Statistics
关键字:Hive统计信息、分析Hive表、Hive Statistics
类似于Oracle的分析表,Hive中也提供了分析表和分区的功能,通过自动和手动分析Hive表,将Hive表的一些统计信息存储到元数据中。
表和分区的统计信息主要包括:行数、文件数、原始数据大小、所占存储大小、最后一次操作时间等;
14.1 新表的统计信息
对于一个新创建
- Spring Boot 1.2.5 发布
wiselyman
spring boot
Spring Boot 1.2.5已在7月2日发布,现在可以从spring的maven库和maven中心库下载。
这个版本是一个维护的发布版,主要是一些修复以及将Spring的依赖提升至4.1.7(包含重要的安全修复)。
官方建议所有的Spring Boot用户升级这个版本。
项目首页 | 源