图像分割性能评价指标
图像语义分割及常用评价指标
常用指标
什么是混淆矩阵(Confusion Matrix)
混淆矩阵实际就是一个矩阵,该矩阵的元素是模型的分类结果,即模型正确分类、错误分类的样本的个数。
目前只看了基于二分类的混淆矩阵(以后看到其他多分类混淆矩阵后再来补充叭)。所谓的二分类,即分类器(或称之为网络\学习器)对两个类别进行分类处理,其中第一类为正例(Positive),第二类为反例(Negative)。若模型预测正确则记为真(True),预测错误则记为假(False)。那么混淆矩阵的组成元素便是这四个基本术语的组合:
TP (True Positive):真正例,即模型预测为正例,实际也为正例;
FP (False Positive):假正例,即模型预测为正例,实际为反例;
FN (False Negative):假反例,即模型预测为反例,实际为正例;
TN (True Negative):真反例,即模型预测为反例,实际也为反例。
将这四种指标放在同一表格中,便构成了混淆矩阵:
对分类模型的预测效果而言,当上述表格中TP与TN的数量越大时,分类结果是越准确的,相反,若想得到较高的分类精确性,应当使得FP与FN的个数越少。
实例:宠物店有10只动物,其中6只狗,4只猫(真实值)。现有一个模型将这10只动物进行分类,分类结果为:5只狗,5只猫(预测值),设狗为正例,猫为反例,可以得到分类结果的对应混淆矩阵:
按照我们上面所说,在该混淆矩阵中,TP与TN的样本个数较多,可以认为模型的分类结果比较准确,但实际中我们并不是仅采用这种方式来评价模型,这就是下面要说的几种评价指标
四种二级指标
由于构成混淆矩阵的元素是各种预测结果的样本个数,而实际问题中样本数往往很大,因此若仅凭计算样本个数,很难衡量模型的优劣,因此产生了如下4个指标,称之为二级指标(通过最底层指标加减乘除得到的):

通过上面的四个二级指标,可以将混淆矩阵中数量的结果转化为0-1之间的比率,便于进行标准化的衡量。
实例计算
以上面实例的混淆矩阵为例,我们来计算一下各评价指标:
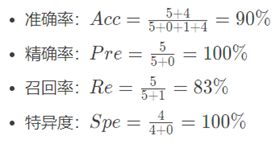
非二分类问题拓展
以下面的混淆矩阵为例

这是一个三分类问题,在这种问题下,我么应该如何计算上述几种评价指标呢?容易求得的是:
准确率:A c c = (10 + 15 + 20)/ 66 = 68.2 %
那么其他三种指标应如何计算?实际上,多分类问题往往都可以转化为二分类问题,对上面的混淆矩阵,我们假设猫为正例,狗和猪为反例,那么就可以得到一个是猫与不是猫的二分类问题,进而也可得到一个新的混淆矩阵:
这样我们就可以继续计算评价指标:

当然上述的指标计算都是基于猫为正例这一假设的,用同样的方法也可以计算出猪和狗的几种评价指标。
一种三级指标
在上述四种二级指标的基础上,还有另外一种评价指标——F1-Score,它的计算公式为:
F1-Score=2PR/(P+R)
其中,P代表Precision,R代表Recall。
F1-Score指标综合了Precision与Recall的产出的结果。F1-Score的取值范围从0到1的,1代表模型的输出最好,0代表模型的输出结果最差。
语义分割模型的五种评价指标
无论模型的分类对象是动物还是图片像素点,混淆矩阵的计算方式与评价指标的计算都是相同的:
PA对应着二级指标中的准确率。
CPA则对应了二级指标中的精确率。
评价指标代码实现
"""
计算分割的性能
refer to https://github.com/jfzhang95/pytorch-deeplab-xception/blob/master/utils/metrics.py
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41936775/article/details/108717925
"""
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
__all__ = ['SegmentationMetric']
from PIL import Image
"""
confusionMetric # 注意:此处横着代表预测值,竖着代表真实值,与之前介绍的相反
P\L P N
P TP FP
N FN TN
"""
class SegmentationMetric(object):
def __init__(self, numClass):
self.numClass = numClass
self.confusionMatrix = np.zeros((self.numClass,)*2)
def pixelAccuracy(self):
# return all class overall pixel accuracy
# PA = acc = (TP + TN) / (TP + TN + FP + TN)
acc = np.diag(self.confusionMatrix).sum() / self.confusionMatrix.sum()
return acc
def classPixelAccuracy(self):
# return each category pixel accuracy(A more accurate way to call it precision)
# acc = (TP) / TP + FP
classAcc = np.diag(self.confusionMatrix) / self.confusionMatrix.sum(axis=1)
return classAcc # 返回的是一个列表值,如:[0.90, 0.80, 0.96],表示类别1 2 3各类别的预测准确率
def meanPixelAccuracy(self):
classAcc = self.classPixelAccuracy()
meanAcc = np.nanmean(classAcc) # np.nanmean 求平均值,nan表示遇到Nan类型,其值取为0
return meanAcc # 返回单个值,如:np.nanmean([0.90, 0.80, 0.96, nan, nan]) = (0.90 + 0.80 + 0.96) / 3 = 0.89
def IntersectionOverUnion(self):
# Intersection = TP Union = TP + FP + FN
# IoU = TP / (TP + FP + FN)
intersection = np.diag(self.confusionMatrix) # 取对角元素的值,返回列表
union = np.sum(self.confusionMatrix, axis=1) + np.sum(self.confusionMatrix, axis=0) - np.diag(self.confusionMatrix) # axis = 1表示混淆矩阵行的值,返回列表; axis = 0表示取混淆矩阵列的值,返回列表
IoU = intersection / union # 返回列表,其值为各个类别的IoU
return IoU
def meanIntersectionOverUnion(self):
# Intersection = TP Union = TP + FP + FN
# IoU = TP / (TP + FP + FN)
intersection = np.diag(self.confusionMatrix) # 取对角元素的值,返回列表
union = np.sum(self.confusionMatrix, axis=1) + np.sum(self.confusionMatrix, axis=0) - np.diag(self.confusionMatrix) # axis = 1表示混淆矩阵行的值,返回列表; axis = 0表示取混淆矩阵列的值,返回列表
IoU = intersection / union # 返回列表,其值为各个类别的IoU
mIoU = np.nanmean(IoU) # 求各类别IoU的平均
return mIoU
def genConfusionMatrix(self, imgPredict, imgLabel): # 同FCN中score.py的fast_hist()函数
# mask = (imgLabel >= 0) & (imgLabel < self.numClass)
# hist = np.bincount(
# self.numClass * imgLabel[mask].astype(int) +
# imgPredict[mask], minlength=self.numClass ** 2).reshape(self.numClass, self.numClass)
# return hist
mask = (imgLabel >= 0) & (imgLabel < self.numClass)
label = self.numClass * imgLabel[mask] + imgPredict[mask]
count = np.bincount(label, minlength=self.numClass**2)
confusionMatrix = count.reshape(self.numClass, self.numClass)
return confusionMatrix
def Frequency_Weighted_Intersection_over_Union(self):
# FWIOU = [(TP+FN)/(TP+FP+TN+FN)] *[TP / (TP + FP + FN)]
freq = np.sum(self.confusion_matrix, axis=1) / np.sum(self.confusion_matrix)
iu = np.diag(self.confusion_matrix) / (
np.sum(self.confusion_matrix, axis=1) + np.sum(self.confusion_matrix, axis=0) -
np.diag(self.confusion_matrix))
FWIoU = (freq[freq > 0] * iu[freq > 0]).sum()
return FWIoU
def addBatch(self, imgPredict, imgLabel):
assert imgPredict.shape == imgLabel.shape
self.confusionMatrix += self.genConfusionMatrix(imgPredict, imgLabel)
def reset(self):
self.confusionMatrix = np.zeros((self.numClass, self.numClass))
if __name__ == '__main__':
label_path='/home/qq/Myproject/segmentation/unet/data/test/truth/'
predict_path='/home/qq/Myproject/segmentation/unet/data/test/pred/'
pa_l = []
cpa_l = []
mpa_l = []
IoU_l = []
mIoU_l = []
files = os.listdir(label_path)
for filename in files:
imgLabel = Image.open(label_path +filename)
# imgPredict = Image.open(predict_path +filename.replace('.png','_res.png'))
imgPredict = Image.open(predict_path +filename)
imgPredict = np.array(imgPredict) # 可直接换成预测图片
imgLabel = np.array(imgLabel,dtype='uint8') # 可直接换成标注图片
# imgLabel = cv2.imread(label_path +filename)
# 将数据转为单通道的图片
imgLabel = cv2.cvtColor(imgLabel, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
imgPredict[imgPredict > 0] = 1
imgLabel[imgLabel >0] = 1
metric = SegmentationMetric(2) # 2表示有1个分类,有几个分类就填几
print(imgPredict.shape , imgLabel.shape)
metric.addBatch(imgPredict, imgLabel)
PA = metric.pixelAccuracy()
CPA = metric.classPixelAccuracy()
MPA = metric.meanPixelAccuracy()
IoU = metric.IntersectionOverUnion()
MIoU = metric.meanIntersectionOverUnion()
FWIoU = metric.Frequency_Weighted_Intersection_over_Union()
print('像素准确率PA: %.2f%%' %(PA*100))
print('类别像素准确率CPA: %.2f%%' %(CPA*100))
print('类别平均像素准确率MPA: %.2f%%' %(MPA*100))
# print('交并比IoU: %.2f%%' %(meanIoU[0,0]*100))
print('交并比IoU: %.2f%%' %(IoU*100))
print('平均交并比MIoU: %.2f%%' %(MIoU*100))
print('权频交并比FWIoU: %.2f%%' %(FWIoU*100))


