Pytorch — LSTM (nn.LSTM & nn.LSTMCell)
nn.LSTM
在LSTM中,c和h的size是一样的
torch.nn.LSTM()
- 参数
– input_size
– hidden_size
– num_layers
– bias
– batch_first
– dropout
– bidirectional- 输入
– input (seq_len, batch, input_size)
– h_0 (num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size)
– c_0 (num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size)- 输出
– output (seq_len, batch, num_directions * hidden_size)
– h_n (num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size)
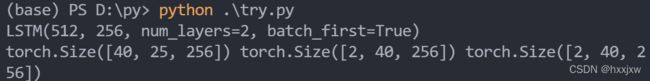
– c_n (num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size)import torch from torch import nn lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=512, hidden_size=256, num_layers=2, batch_first=True) print(lstm) x = torch.randn(40,25,512) output,(h_n,c_n) = lstm(x) print(output.shape,h_n.shape,c_n.shape)lstm中走几个时间步time_step = seq_len
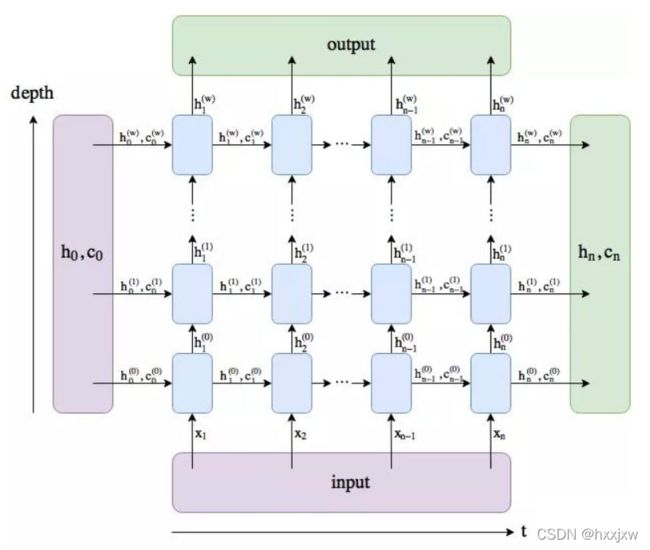
num_layers
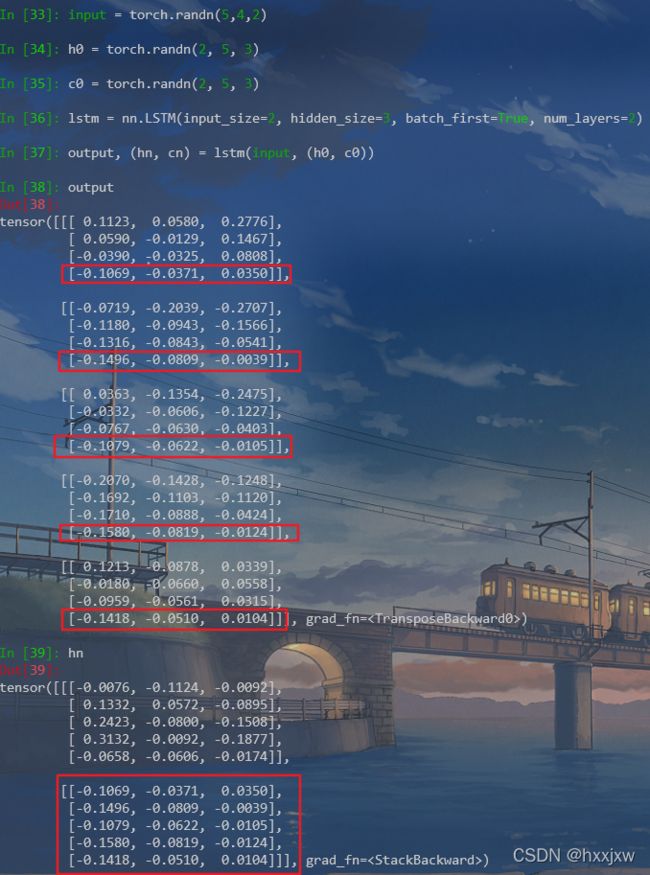
num_layers表示堆叠几层LSTM,如果是2就相当于堆叠2层。默认是1
即如果是2层的话就是这样
注意,num_layers的个数对输出的output的size没有影响,但是会影响输出的h_n和c_n,像上面例子中,如果num_layers=1那h_n是[1,40,256], 如果num_layers=2那h_n是[2,40,256]......., c_n也是
batch_first
batch_first指的是,Pytorch的LSTM层默认输入和输出都是batch在第二维,而我们的习惯都是batch在第一维,所以用这个来告诉模型我们的batch维是在第一维的
但是输出的h_n和c_n的size中batch并不会提前到第一维,注意。
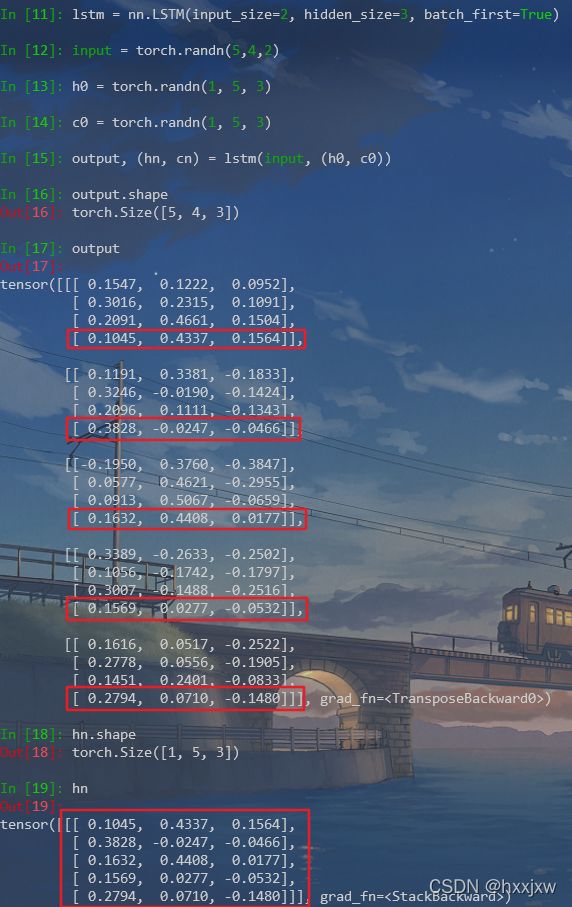
output, h_n和c_n的关系
- h_n:最后一个时间步的输出,即 h_n = output[:, -1, :](一般可以直接输入到后续的全连接层)
- c_n:最后一个时间步 LSTM cell 的状态(一般用不到)
import torch import torch.nn as nn lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=2, hidden_size=3, batch_first=True) input = torch.randn(5,4,2) h0 = torch.randn(1, 5, 3) c0 = torch.randn(1, 5, 3) output, (hn, cn) = lstm(input, (h0, c0))如果是两层
可以看到,如果是多层,那么output还是只会保留最后一层,而h_n则会多层都保留下来
如果是双向
可以看到,双向的output就是把两个方向的给concat到一起了,就是方向是反的
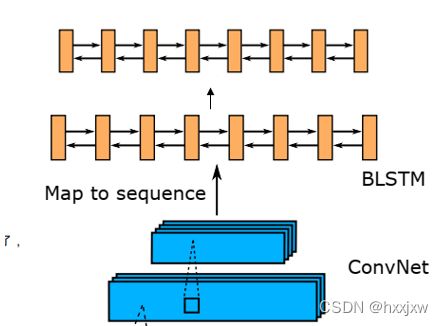
双向LSTM(BiLSTM)
很简单,只要加个bidirectional的参数就行了
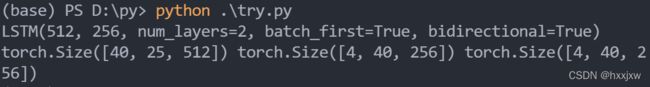
import torch from torch import nn lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=512, hidden_size=256, num_layers=2, batch_first=True, bidirectional=True) print(lstm) x = torch.randn(40,25,512) out,(h_n,c_n) = lstm(x) print(out.shape,h_n.shape,c_n.shape)但是需要注意一点,双向RNN的话,输出的output的size会是2*hidden_size。
h_n和c_n的size不会变,但是他们的第一维会变,第一维是num_layers, 如果双向的话还要乘个2
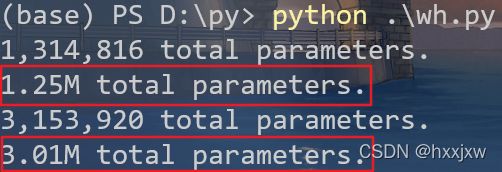
如果用了Bi-LSTM,参数量会变为两倍
from torch import nn def print_params(model): total_params = sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters()) print(f'{total_params:,} total parameters.') print(f'{total_params/(1024*1024):.2f}M total parameters.') lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=512, hidden_size=256, batch_first=True, num_layers=2) lstm_bi = nn.LSTM(input_size=512, hidden_size=256, batch_first=True,bidirectional=True, num_layers=2) for i in [lstm,lstm_bi]: print_params(i)
nn.LSTMCell
第二种方式,灵活性更大的cell,人为来决定每一次喂数据
单层
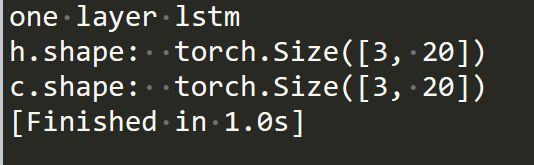
import torch from torch import nn import numpy as np print('one layer lstm') cell=nn.LSTMCell(input_size=100, hidden_size=20) h=torch.zeros(3,20) c=torch.zeros(3,20) x = torch.randn(10,3,100) for xt in x: h,c = cell(xt, [h,c]) print('h.shape: ',h.shape) print('c.shape: ',c.shape)双层
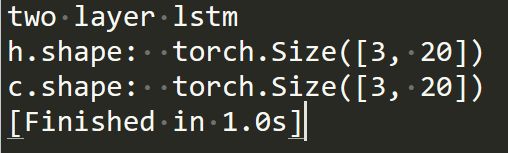
import torch from torch import nn import numpy as np x = torch.randn(10,3,100) print('two layer lstm') cell1=nn.LSTMCell(input_size=100, hidden_size=30) cell2=nn.LSTMCell(input_size=30, hidden_size=20) h1=torch. zeros(3,30) c1=torch. zeros(3,30) h2=torch. zeros(3,20) c2=torch. zeros(3,20) for xt in x: h1,c1=cell1(xt,[h1, c1]) h2,c2=cell2(h1,[h2, c2]) print('h.shape: ',h2.shape) print('c.shape: ',c2.shape)