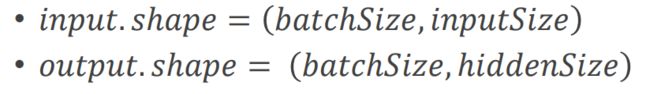pytorch循环神经网络(七)
循环神经网络
- 循环神经网络架构
- torch.nn.RNNCell
- 数据维度
- RNNCell的input,output
- 使用RNNCell训练模型
- torch.nn.RNN
- 使用RNN训练模型
- RNNCell进行文本预测
- RNN进行文本预测
- 关于loss维度
视频链接
一篇博客
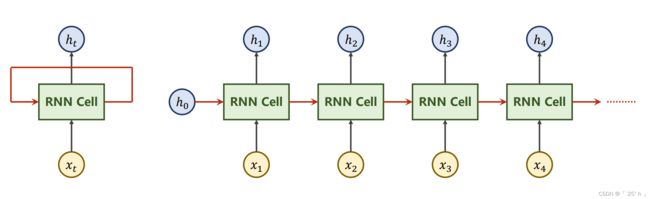
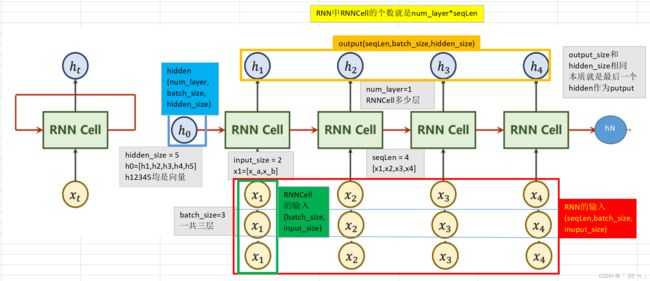
循环神经网络架构
-
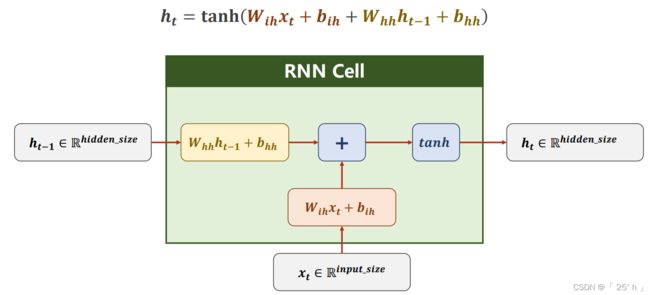
W i h 的 s h a p e 就 是 i n p u t _ s i z e ∗ h i d d e n _ s i z e , W h h 就 是 h i d d e n _ s i z e ∗ h i d d e n _ s i z e W_{ih}的shape就是input\_size*hidden\_size,W_{hh}就是hidden\_size*hidden\_size Wih的shape就是input_size∗hidden_size,Whh就是hidden_size∗hidden_size
-
W i h x t + b i h + W h h h t − 1 + b h h W_{i h} x_{t}+b_{i h}+W_{h h} h_{t-1}+b_{h h} Wihxt+bih+Whhht−1+bhh最后结果就是 h i d d e n _ s i z e ∗ 1 hidden\_size*1 hidden_size∗1大小的
-
这仅仅是一个样本情况,若是单次网络输入样本量为batch_size,那么参数维度要增加一维,增加的维度长度为batch_size
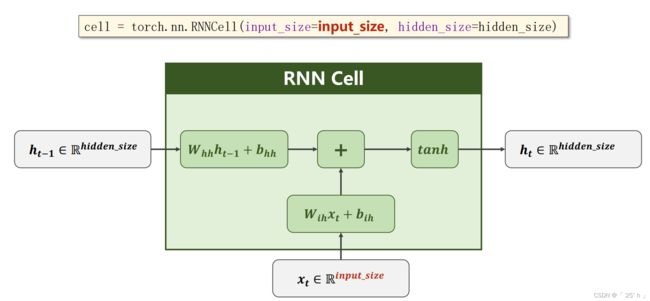
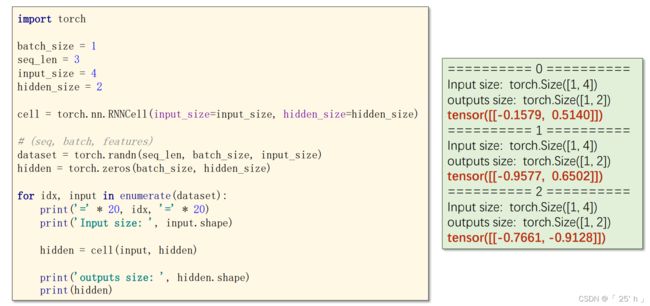
torch.nn.RNNCell
数据维度
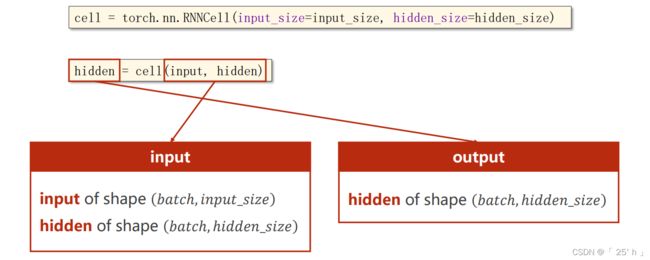
RNNCell的input,output
使用RNNCell训练模型
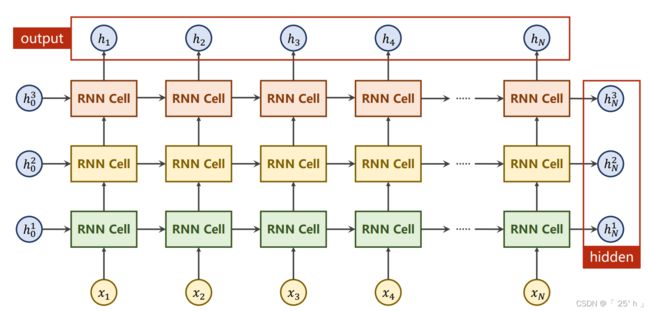
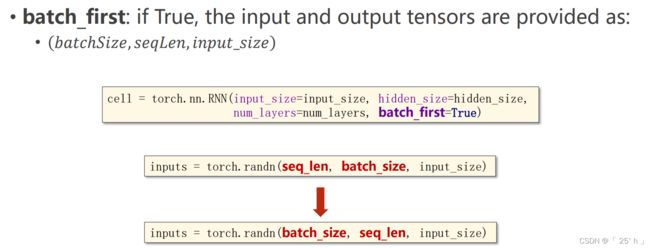
torch.nn.RNN
使用RNN训练模型
RNNCell进行文本预测
import torch
batch_size = 1
input_size = 4
hidden_size = 4
idx2char = ['e', 'h', 'l', 'o']
x_data = [1, 0, 2, 2, 3]
y_data = [2, 3, 2, 0, 1]
# (seq_len, input_size, hidden_size)
one_hot_lookup = [[1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1]]
x_one_hot = [one_hot_lookup[x] for x in x_data]
inputs = torch.tensor(x_one_hot).view(-1, batch_size, input_size)
inputs = inputs.float()
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, batch_size):
super(Net, self).__init__()
# 初始化属性size
self.input_size = input_size
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.batch_size = batch_size
# 初始化RNNCell
self.rnncell = torch.nn.RNNCell(input_size=input_size, hidden_size=hidden_size)
def forward(self, input, hidden):
hidden = self.rnncell(input, hidden)
return hidden
def init_hidden(self):
return torch.zeros(self.batch_size, self.hidden_size)
net = Net(input_size, hidden_size, batch_size)
# construct Criterion and Optimizer
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
Optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.1)
for epoch in range(15):
loss = 0
net.zero_grad()
hidden = net.init_hidden() # 初始化 h_0
print('Predicted string: ', end='')
# 取出每一个input,和结果,这个过程就是在用RNNCell模拟RNN
for input, label in zip(inputs, y_data):
# 对于每一个RNNCell,填入input和hidden
hidden = net(input, hidden) # 本质上来说隐藏层输出的值在后面作为loss,就是将隐藏层作为概率了,
# 计算loss,必要取出.item(),因为整个inputs都是loss的一部分
loss += criterion(hidden, torch.tensor([label]).long())
# 取出当次预测的字符
_, idx = hidden.max(dim=1)
print(idx2char[idx.item()], end='')
# 梯度值清零
Optimizer.zero_grad()
# 反馈
loss.backward()
# 优化
Optimizer.step()
print(", Epoch: [%d/15] loss = %.4f" % (epoch + 1, loss.item()))
RNN进行文本预测
import torch
batch_size = 1
input_size = 4
hidden_size = 8
num_layers = 2
embedding_size = 10
idx2char = ['e', 'h', 'l', 'o']
x_data = [1, 0, 2, 2, 3]
y_data = [2, 3, 2, 0, 1]
seq_len = len(x_data)
num_class = len(idx2char)
inputs = torch.tensor(x_data)
labels = torch.tensor(y_data)
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
# 嵌入法进行数据处理
self.emb = torch.nn.Embedding(num_embeddings=input_size,
embedding_dim=embedding_size)
self.rnn = torch.nn.RNN(input_size=embedding_size,
hidden_size=hidden_size,
num_layers=num_layers,
batch_first=True)
# 全连接转成输出
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(in_features=hidden_size,
out_features=num_class)
def forward(self, x):
hidden = torch.zeros(num_layers, batch_size, hidden_size) # h0
# 嵌入法处理
x = self.emb(x)
x = x.view(batch_size, seq_len, embedding_size)
# 调用RNN模型训练
x, _ = self.rnn(x, hidden) # _ is hn
# 全连接转成类别
x = self.fc(x)
return x.view(-1, num_class)
net = Net()
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
Optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.05)
Epoch = 15
for epoch in range(Epoch):
Optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = net(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
Optimizer.step()
_, idx = outputs.max(dim=1)
idx = idx.data.numpy()
print("Predicted string:", ''.join(idx2char[x] for x in idx), end='')
print(", Epoch: [%d/%d] loss: %.3f" % (epoch + 1, Epoch, loss.item()))
关于loss维度
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
a = torch.tensor(np.random.random((30, 5)))
b = torch.tensor(np.random.randint(0, 4, (30))).long()
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
print("a的维度:", a.size()) # torch.Size([30, 5])
print("b的维度:", b.size()) # torch.Size([30])
print(loss(a, b)) # tensor(1.6319, dtype=torch.float64)