MapReduce计算流程详解
MapReduce开发总结
(1)输入数据接口: InputFormat
- 默认使用的实现类是: TextInputFormat
- TextInputFormat 的功能逻辑是:一次读一行文本,然后将该行的起始偏移量作为key,行内容作为 value 返回。
- CombineTextInputFormat 可以把多个小文件合并成一个切片处理,提高处理效率。
(2)逻辑处理接口: Mapper
- 用户根据业务需求实现其中三个方法: map() setup() cleanup ()
(3)Partitioner 分区
- 有默认实现 HashPartitioner,逻辑是根据 key 的哈希值和 numReduces 来返回一个分区号; key.hashCode()&Integer.MAXVALUE % numReduces
- 如果业务上有特别的需求,可以自定义分区。
(4)Comparable 排序
- 当我们用自定义的对象作为 key 来输出时,就必须要实现 WritableComparable 接口,重写其中的 compareTo()方法。
- 部分排序:对最终输出的每一个文件进行内部排序。
- 全排序:对所有数据进行排序,通常只有一个 Reduce。
- 二次排序:排序的条件有两个。
(5)Combiner 合并
- Combiner 合并可以提高程序执行效率,减少 IO 传输。但是使用时必须不能影响原有的业务处理结果。
(6)逻辑处理接口: Reducer
- 用户根据业务需求实现其中三个方法: reduce() setup() cleanup ()
(7) 输出数据接口: OutputFormat
- 默认实现类是 TextOutputFormat,功能逻辑是:将每一个 KV 对,向目标文本文件输出一行。
- 用户还可以自定义 OutputFormat。
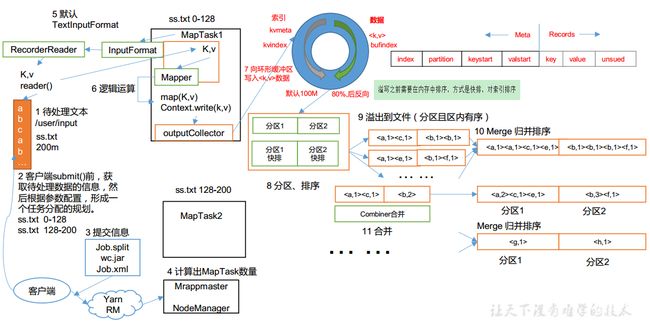
MapReduce流程总结
需要注意:
- Shuffle 过程只是从第 7 步开始到第16 步结束
- MapTask 收集我们的 map()方法输出的 kv 对,进入getpartition方法标记数据分区,放到内存缓冲区(环形缓冲区)中
- 环形缓冲区左边存索引,右边存数据(缓冲区的大小可以通过参数调整,参数: mapreduce.task.io.sort.mb 默认 100M)
- 数据在内存中排序,按照字典序进行快速排序
- 当存储达到80%时开始反向溢写入磁盘,可能会溢出多个文件,多个溢出文件会被合并成大的溢出文件
- 在溢出过程及合并的过程中(具体阶段见上文),都要调用 Partitioner 进行分区和针对 key 进行排序
- MapTask阶段可以提前进行一轮combine操作,降低网络传输的数据大小
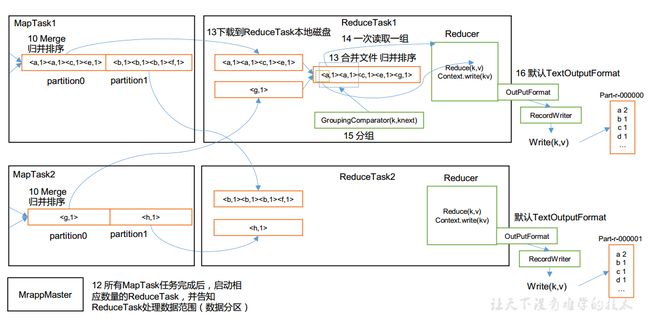
- ReduceTask 根据自己的分区号,去各个 MapTask 机器上取相应的结果分区数据
- ReduceTask 会抓取到同一个分区的来自不同 MapTask 的结果文件, ReduceTask 会将这些文件再进行合并(归并排序)
- 合并成大文件后, Shuffle 的过程也就结束了,后面进入 ReduceTask 的逻辑运算过程(从文件中取出一个一个的键值对 Group,调用用户自定义的 reduce()方法)
InputFormat 数据输入
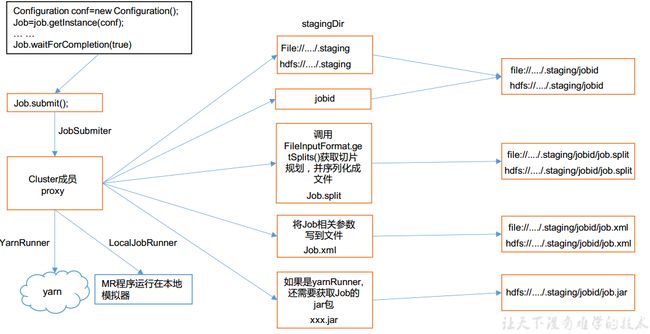
Job创建和提交
总体逻辑如下,job创建集群的代理对象,判断是本地还是集群做出不同的响应,创建staging路径,并根据jobid存储job切片、配置文件和jar包,将staging中文件提交集群运行
主要涉及到如下源码
waitForCompletion()
submit();
// 1 建立连接
connect();
// 1)创建提交 Job 的代理
new Cluster(getConfiguration());
// 断是本地运行环境还是 yarn 集群运行环境
initialize(jobTrackAddr, conf);
// 提交 job
submitter.submitJobInternal(Job.this, cluster)
// 创建给集群提交数据的 Stag 路径
Path jobStagingArea = JobSubmissionFiles.getStagingDir(cluster, conf);
// 获取 jobid ,并创建 Job 路径
JobID jobId = submitClient.getNewJobID();
// 拷贝 jar 包到集群
copyAndConfigureFiles(job, submitJobDir);
rUploader.uploadFiles(job, jobSubmitDir);
// 计算切片,生成切片规划文件
writeSplits(job, submitJobDir);
maps = writeNewSplits(job, jobSubmitDir);
input.getSplits(job);
// 向 Stag 路径写 XML 配置文件
writeConf(conf, submitJobFile);
conf.writeXml(out);
// 提交 Job,返回提交状态
status = submitClient.submitJob(jobId, submitJobDir.toString(),job.getCredentials());
MapTask 并行度
MapTask负责 Map 阶段的整个数据处理流程
对比数据块Block和数据切片的区别:
- Block是HDFS在物理机上对数据的分块
- 切片是MR程序对输入数据进行裸机上的划分(并不会影响物理存储),每个切片对应一个MapTask
以下是FileInputFormat源码流程(默认是TextInputFormat),位于getSplits方法中
- 程序先找到你数据存储的目录。
- 开始遍历处理(规划切片)目录下的每一个文件
- 遍历第一个文件ss.txt
- 获取文件大小fs.sizeOf(ss.txt)
- 计算切片大小
computeSplitSize(Math.max(minSize,Math.min(maxSize,blocksize)))=blocksize=128M - 默认情况下,切片大小=blocksize
- 开始切,形成第1个切片,每次切片时,都要判断切完剩下的部分是否大于块的1.1倍,不大于1.1倍就划分一块切片
- 将切片信息写到一个切片规划文件中
- 整个切片的核心过程在getSplit()方法中完成
- InputSplit只记录了切片的元数据信息,比如起始位置、长度以及所在的节点列表等。
- 提交切片规划文件到YARN上,YARN上的MrAppMaster就可以根据切片规划文件计算开启MapTask个数
//code节选
public List<InputSplit> getSplits(JobContext job) throws IOException {
StopWatch sw = new StopWatch().start();
long minSize = Math.max(getFormatMinSplitSize(), getMinSplitSize(job));
long maxSize = getMaxSplitSize(job);
//遍历文件
for (FileStatus file: files) {
...
if (isSplitable(job, path)) {
//文件块大小和分片大小
long blockSize = file.getBlockSize();
long splitSize = computeSplitSize(blockSize, minSize, maxSize);
//默认分片大小等于blocksize
//protected long computeSplitSize(long blockSize, long minSize,
// long maxSize) {
//return Math.max(minSize, Math.min(maxSize, blockSize));
//}
//SPLIT_SLOP = 1.1
while (((double) bytesRemaining)/splitSize > SPLIT_SLOP) {
int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length-bytesRemaining);
splits.add(makeSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, splitSize,
blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts(),
blkLocations[blkIndex].getCachedHosts()));
bytesRemaining -= splitSize;
}
//处理不可分片文件
} else { // not splitable
...
}
...
return splits;
}
FileInputFormat 切片机制
源码中计算切片大小的公式
Math.max(minSize, Math.min(maxSize, blockSize));
mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.minsize=1 默认值为1
mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize= Long.MAXValue 默认值Long.MAXValue
默认情况下,切片大小=blocksize
maxsize(切片最大值):参数如果调得比blockSize小,则会让切片变小,而且就等于配置的这个参数的值。
minsize(切片最小值):参数调的比blockSize大,则可以让切片变得比blockSize还大。
获取切片信息API
// 获取切片的文件名称
String name = inputSplit.getPath().getName();
// 根据文件类型获取切片信息
FileSplit inputSplit = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit();
FileInputFormat 常见的接口实现类包括: TextInputFormat、 KeyValueTextInputFormat、NLineInputFormat、CombineTextInputFormat 和自定义 InputFormat 等
TextInputFormat
TextInputFormat 是默认的 FileInputFormat 实现类。按行读取每条记录。 键是存储该行在整个文件中的起始字节偏移量, LongWritable 类型。值是这行的内容,不包括任何行终止符(换行符和回车符), Text 类型。
CombineTextInputFormat
CombineTextInputFormat 用于小文件过多的场景, 它可以将多个小文件从逻辑上规划到一个切片中, 这样, 多个小文件就可以交给一个 MapTask 处理
分为两个阶段:虚拟存储阶段和切片阶段
可以设置虚拟存储大小,CombineTextInputFormat.setMaxInputSplitSize(job, 4194304);// 4m
虚拟存储阶段
- 将输入目录下所有文件大小, 依次和设置的 setMaxInputSplitSize 值比较, 如果不大于设置的最大值, 逻辑上划分一个块。
- 如果输入文件大于设置的最大值且大于两倍,那么以默认最大值(例如4m)切割一块
- 当剩余数据大小超过设置的最大值且不大于最大值 2 倍,此时将文件均分成 2 个虚拟存储块(防止出现太小切片) 。
切片阶段
- 判断虚拟存储的文件大小是否大于 setMaxInputSplitSize 值,大于等于则单独形成一个切片。
- 如果不大于则跟下一个虚拟存储文件进行合并,共同形成一个切片
举例:
有 4 个小文件大小分别为 1.7M、 5.1M、 3.4M 以及 6.8M 这四个小文件,默认MaxInputSplitSize为4m,则虚拟存储之后形成 6 个文件块,大小分别为:1.7M,(2.55M、 2.55M) , 3.4M 以及(3.4M、 3.4M)
最终会形成 3 个切片,大小分别为:(1.7+2.55) M, (2.55+3.4) M, (3.4+3.4) M
驱动类设置
// 如果不设置 InputFormat,它默认用的是 TextInputFormat.class
job.setInputFormatClass(CombineTextInputFormat.class);
//虚拟存储切片最大值设置 4m
CombineTextInputFormat.setMaxInputSplitSize(job, 4194304);
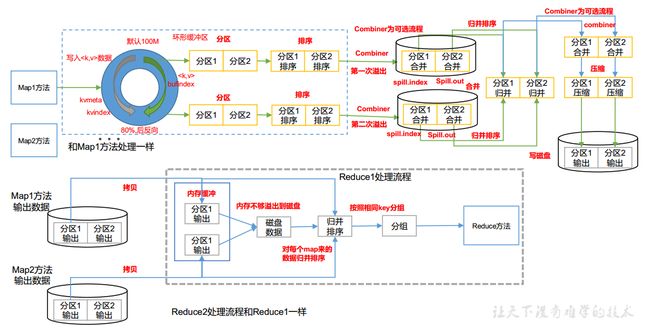
Shuffle 机制
Map 方法之后, Reduce 方法之前的数据处理过程称之为 Shuffle
Partition分区
默认Partitioner分区是计算hashcode的方式
public class HashPartitioner<K, V> extends Partitioner<K, V> {
public int getPartition(K key, V value, int numReduceTasks) {
return (key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks;
}
}
自定义partition分区
创建自定义分区类继承Partition,重写getPartition()方法
getPartition方法接收的是map的输出
public class CustomPartition extends Partitioner<Text, FlowBean> {
@Override
public int getPartition(Text text, FlowBean flowBean, int numPartitions) {
String phone = text.toString();
String prePhone = phone.substring(0, 3);
int partition;
if ("136".equals(prePhone)) {
partition = 0;
} else if ("137".equals(prePhone)) {
partition = 1;
} else if ("138".equals(prePhone)) {
partition = 2;
} else if ("139".equals(prePhone)) {
partition = 3;
} else {
partition = 4;
}
return partition;
}
}
驱动类
//指定自定义分区器
job.setPartitionerClass(ProvincePartitioner.class);
//同时指定相应数量的 ReduceTask
job.setNumReduceTasks(5);
分区大小和reducetask关系
- 如果ReduceTask的数量> getPartition的结果数,则会多产生几个空的输出文件part-r-000xx;
- 如果
- 如果ReduceTask的数量=1,则不管MapTask端输出多少个分区文件,最终结果都交给这一个ReduceTask,最终也就只会产生一个结果文件 part-r-00000;
- 分区号必须从零开始,逐一累加。
WritableComparable 排序
MapTask和 ReduceTask均会对数据按照 key进行排序。 该操作属于Hadoop的默认行为。 任何应用程序中的数据均会被排序,而不管逻辑上是否需要。
默认排序是按照字典顺序排序,且实现该排序的方法是快速排序
对于MapTask,它会将处理的结果暂时放到环形缓冲区中,当环形缓冲区使用率达到一定阈值后,再对缓冲区中的数据进行一次快速排序,并将这些有序数据溢写到磁盘上,而当数据处理完毕后,它会对磁盘上所有文件进行归并排序
对于ReduceTask,它从每个MapTask上远程拷贝相应的数据文件,如果文件大小超过一定阈值,则溢写磁盘上,否则存储在内存中。如果磁盘上文件数目达到一定阈值,则进行一次归并排序以生成一个更大文件;如果内存中文件大小或者数目超过一定阈值,则进行一次合并后将数据溢写到磁盘上。当所有数据拷贝完毕后,ReduceTask统一对内存和磁盘上的所有数据进行一次归并排序
bean 对象做为 key 传输,需要实现 WritableComparable 接口重写 compareTo 方法, 就可以实现排序
@Override
public int compareTo(FlowBean bean) {
int result;
// 按照总流量大小,倒序排列
if (this.sumFlow > bean.getSumFlow()) {
result = -1;
}else if (this.sumFlow < bean.getSumFlow()) {
result = 1;
}else {
result = 0;
}
return result;
}
Combiner 合并
Combiner是MR程序中Mapper和Reducer之外的一种组件。
Combiner组件的父类就是Reducer(意味着甚至可以直接复用reducer类)。
Combiner和Reducer的区别在于运行的位置,Combiner是在每一个MapTask所在的节点运行;
Combiner的意义就是对每一个MapTask的输出进行局部汇总,以减小网络传输量。
Combiner能够应用的前提是不能影响最终的业务逻辑,而且,Combiner的输出kv应该跟Reducer的输入kv类型要对应起来。
public class WordCountCombiner extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
private IntWritable outV = new IntWritable();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable value : values) {
sum += value.get();
}
outV.set(sum);
context.write(key,outV);
}
}
可见combiner的code和reducer一样,区别是一个在maptask节点提前合并,另一个对map的输出进行总体的合并
驱动类
job.setCombinerClass(WordCountCombiner.class);
//或者直接指定reducer
job.setCombinerClass(WordCountReducer.class);
运行前后变化
注意:如果在驱动类设置job.setNumReduceTasks(0)那么将不会执行combine,因为reduce也不存在了
OutputFormat 数据输出
总体思路
原始数据如下,将www.one.com输出到one.log,其他的输出到other.log
www.escook.com
www.lanous.com
www.one.com
www.lanous.com
www.two.com
www.google.com
www.baidu.com
www.csdn.com
www.escook.com
www.lanous.com
www.one.com
www.lanous.com
www.two.com
...
创建LogOutputFormat
public class LogOutputFormat extends FileOutputFormat<Text, NullWritable> {
@Override
public RecordWriter<Text, NullWritable> getRecordWriter(TaskAttemptContext job) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
LogRecordWriter logRecordWriter = new LogRecordWriter(job);
return logRecordWriter;
}
}
生成LogRecordwriter,并创建输出流
public class LogRecordWriter extends RecordWriter<Text, NullWritable> {
private FSDataOutputStream onefs;
private FSDataOutputStream otherfs;
public LogRecordWriter(TaskAttemptContext job) {
try {
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(job.getConfiguration());
onefs = fs.create(new Path("D:/localstage/outputformat/one.log"));
otherfs = fs.create(new Path("D:/localstage/outputformat/other.log"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void write(Text key, NullWritable value) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String log = key.toString();
if(log.contains("one")){
onefs.writeBytes(log+"\n");
}else {
otherfs.writeBytes(log+"\n");
}
}
@Override
public void close(TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
IOUtils.closeStream(onefs);
IOUtils.closeStream(otherfs);
}
}
在LogDriver中注册
//设置自定义的 outputformat
job.setOutputFormatClass(LogOutputFormat.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("D:/localstage/outputformat/input/"));
// 虽然定义了outputformat,但是outputformat继承自fileoutputformat
//而 fileoutputformat 要输出一个_SUCCESS 文件,所以在这还得指定一个输出目录
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("D:/localstage/outputformat/output/"));