1 前言
为什么我们在使用SpringBoot框架开发Java Web应用需要引入大量的starter?例如,我们引入Redis就在Maven中导入spring-boot-starter-data-redis。大家都知道SpringBoot的核心功能是自动装配,简化配置,我们通过starter实现SpringBoot自动装配的功能。那么我们如何去构建自己的starter呢?
SpringBoot现在几乎占据的Java的大半壁江山,它的优势显而易见,它通过自动装配功能为我们简化了Spring繁杂的配置,并且内嵌Tomcat让我们启动Web项目不需要去自己配置Tomcat,这些都能大大提高我们的开发效率和代码质量。至于我们为什么在使用SpringBoot框架构建项目时,导入其它依赖都是什么什么starter?其实,这些starte就为我们实现了SpringBoot自动装配的功能,下面我们将一起将一下自动装配功能如何实现,自己怎样去构建一个SpringBoot的starter应用。
2 @EnableConfigurationProperties实现自动装配
2.1 创建一个starter项目
通过Maven创建一个项目
在pom文件中添加对应的依赖:
org.projectlombok lombok 1.18.22 org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-web 2.5.6
2.2 创建一个需要自动装配的Bean
使用@EnableConfigurationProperties注解
创建一个类这个类最后是可以通过配置文件自动装配的,添加注解@EnableConfigurationProperties时会报错,因为这个是需要将当前对象定义为Spring的一个组件,但是我们不是通过@Component注解注册成为Spring组件的。
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "com.zhj.vo.student")
public class Student {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
2.3 自动装配类实现
@Configuration是需要进行Bean注册的类
@EnableConfigurationProperties({Student.class}) 将该Bean注册进去
/**
* 自动装配类
*/
@Configuration // 需要进行Bean注册的
@EnableConfigurationProperties({Student.class}) //Bean注册
public class AutoConfiguration {
}
2.4 编写测试项目
pom文件导入测试需要的依赖
junit junit 4.12 test org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-test 2.5.6
编写配置文件:
com: zhj: vo: student: id: 1 name: '小明' age: 12
编写测试类:
/**
* 自动注入测试类
*/
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) // junit4 测试环境
@WebAppConfiguration // 启动web运行环境
@SpringBootTest(classes = AutoConfigApplication.class) // 指定启动类
public class AutoConfigTest {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("com.zhj.vo.student-com.zhj.vo.Student") // 前缀-类名 注入
private Student student;
@Test
public void test01() {
System.out.println(student);
}
}
可以看到Bean通过配置文件成功注入Spring容器中,可以获取到Student对象
Student(id=1, name=小明, age=12)
3 @import 实现自动注入
@import注解的主要作用就是将Bean注入Spring容器
3.1 方式一 直接制定Bean的导入
1 修改需要自动装配类
/**
* 自动装配类
*/
@Configuration // 需要进行Bean注册的
@Import({Student.class}) //Bean注册
public class AutoConfiguration {
}
2 修改测试类
/**
* 自动注入测试类
*/
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) // junit4 测试环境
@WebAppConfiguration // 启动web运行环境
@SpringBootTest(classes = AutoConfigApplication.class) // 指定启动类
public class AutoConfigTest {
@Autowired
private Student student;
@Test
public void test01() {
System.out.println(student);
}
}
发现这样也是可以通过配置文件将Bean注入Spring容器中
3.2 方式二 使用ImportSelector注入Bean
如果需要注册的类很多,第一种方式就得将所有需要注入的Bean一一列出来
1 创建DefaultImportSelector实现ImportSelector接口
public class DefaultImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
return new String[] {"com.zhj.vo.Student"};
}
}
2 修改需要自动装配类
/**
* 自动装配类
*/
@Configuration // 需要进行Bean注册的
@Import({DefaultImportSelector.class})
public class AutoConfiguration {
}
3.3 方式三 使用ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar注入Bean
以上方式都是Spring容器负责了Bean的注册,我们可以通过ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar自己去向Spring容器注入Bean
1 创建DefaultImportBeanDefinitionRegister 实现ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口
public class DefaultImportBeanDefinitionRegister implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
RootBeanDefinition rootBeanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(Student.class); // 配置bean
registry.registerBeanDefinition("studentInstance", rootBeanDefinition); // Bean 注册
}
}
2 修改需要自动装配类
/**
* 自动装配类
*/
@Configuration // 需要进行Bean注册的
@Import({DefaultImportBeanDefinitionRegister.class})
public class AutoConfiguration {
}
4 实现跨项目自动配置
上述自动装配的实现都是通过starter项目的配置文件,将bean注入,并在starter项目中进行测试。那么我们如何
4.1 添加依赖
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-configuration-processor 2.5.6
4.2 编译项目
使用Maven编译项目会产生spring-configuration-metadata.json这个文件
{
"groups": [
{
"name": "com.zhj.vo.student",
"type": "com.zhj.vo.Student",
"sourceType": "com.zhj.vo.Student"
}
],
"properties": [
{
"name": "com.zhj.vo.student.age",
"type": "java.lang.Integer",
"sourceType": "com.zhj.vo.Student"
},
{
"name": "com.zhj.vo.student.id",
"type": "java.lang.Long",
"sourceType": "com.zhj.vo.Student"
},
{
"name": "com.zhj.vo.student.name",
"type": "java.lang.String",
"sourceType": "com.zhj.vo.Student"
}
],
"hints": []
}
4.3 修改自动装配类修改
使自动装配类可以自动注入Bean
/**
* 自动装配类
*/
@Configuration // 需要进行Bean注册的
@Import({DefaultImportBeanDefinitionRegister.class})
public class AutoConfiguration {
// 自动注册Bean
@Bean(name = "Students")
public List getNameList() {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("小明");
list.add("小红");
list.add("小李");
return list;
}
}
4.4 spring.factories 文件
固定存放位置src/main/resources/META-INF/spring.factories
这个文件就是支持不同文件自动装配的核心文件。
添加内容,指定自动装配的类
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=com.zhj.config.AutoConfiguration
4.5 其它Web项目引入spring-boot-auto-config-starter
com.zhj spring-boot-auto-config-starter 1.0-SNAPSHOT
4.6 测试
将vo也就是Student写入web项目:
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "com.zhj.vo.student")
public class Student {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
将配置写入web项目:
com: zhj: vo: student: id: 1 name: '小明' age: 12
构建测试接口:
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private Student student;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello "+ student;
}
}
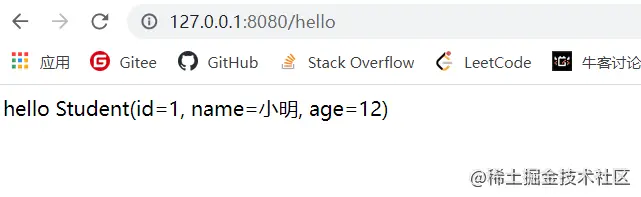
结果:
5 总结
本文就通过自己构建一个SpringBoot的简单的starter项目,让我们去理解SpringBoot的自动装配。SpringBoot为开发者提供了多种Bean装配的方式,我们需要做的就是理解这些自动装配机制,并且能够灵活应用在企业的开发中,可以开发自己开发starter,充分利用SpringBoot的优势,让我们的项目也可以通过简单的配置,就将Bean注入Spring容器中,供我们灵活应用这些Bean。spring.factories这个文件也是重中之重,让我们可以轻松的跨项目向Spring容器注入Bean。
到此这篇关于SpringBoot项目为何引入大量的starter?如何自定义starter?的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot自定义starter内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!